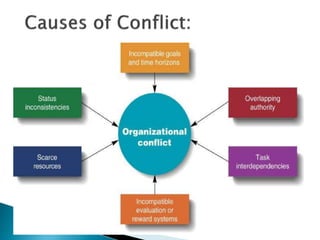
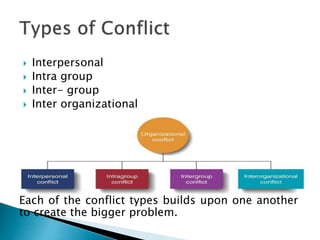
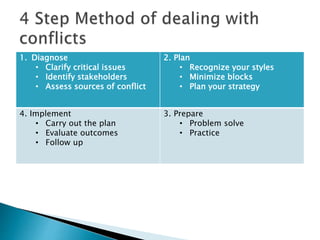
This document discusses the nature and types of conflict, as well as strategies for resolving conflict constructively. It defines conflict as a disagreement resulting from differing ideas, perspectives, or goals. Conflicts can be interpersonal, intra-group, inter-group, or inter-organizational. The document outlines five conflict resolution styles and notes that the most constructive approach is collaboration, which aims for a win-win solution agreeable to all parties. It provides tips for effective conflict diagnosis, planning, preparation, implementation, and positive attitudes in conflict resolution.