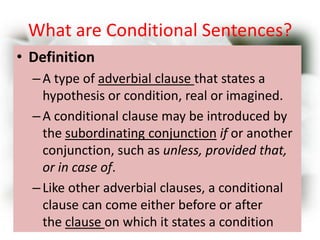
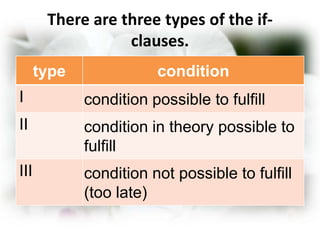
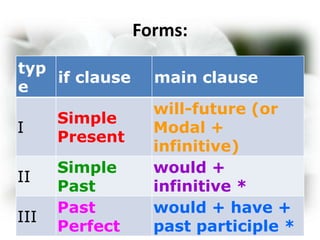
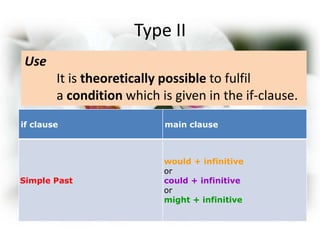
This document discusses conditional sentences in English. It defines conditional sentences as a type of adverbial clause that states a hypothesis or condition, real or imagined, often introduced with "if". There are three main types of conditional sentences: Type I refers to possible conditions using "if + present" and "will/can/may + infinitive". Type II refers to unlikely or hypothetical conditions using "if + past" and "would + infinitive". Type III refers to impossible conditions using "if + past perfect" and "would have + past participle". Several examples are provided for each type.