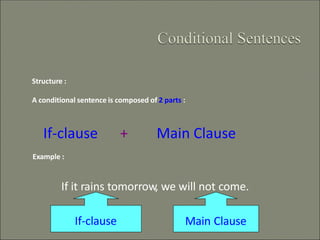
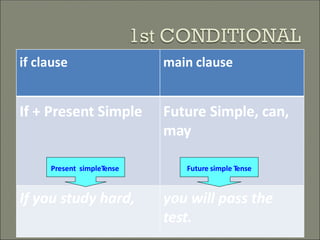
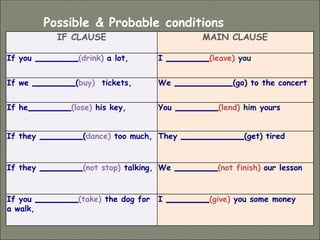
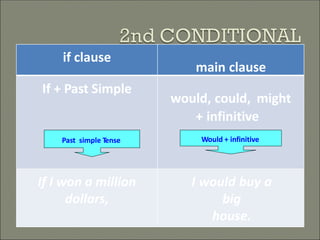
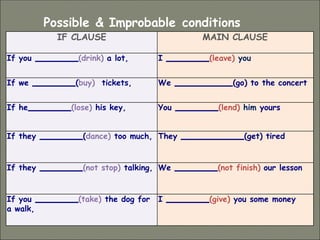
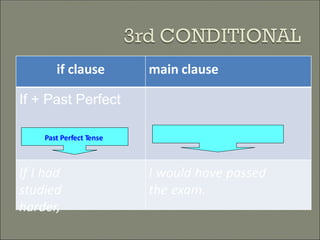
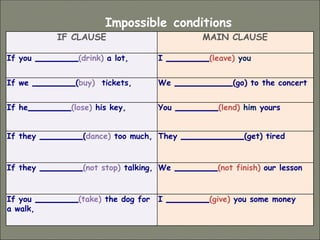
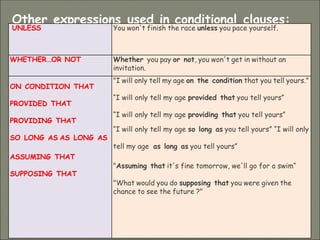
This document discusses conditional sentences, also known as "if" sentences. It explains that conditional sentences have two clauses: the if-clause and the main clause. It also describes the four types of conditional sentences: zero, first, second, and third conditional. Each type uses different verb tenses depending on whether the condition is possible, probable, unlikely, or impossible. Examples are provided to illustrate the different conditional sentence structures and their meanings.