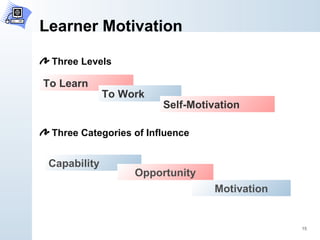
The document discusses various theories of instructional design and learning. It outlines several key psychological foundations of learning, including behavioral learning theory, cognitive information processing theory, schema theory and cognitive load theory, situated learning theory, and Gagne's theory of instruction. It then discusses how the theories align with the author's philosophical beliefs about learning, noting that constructivism best fits their view that learning occurs through relating new information to prior experiences and applying it in daily life.