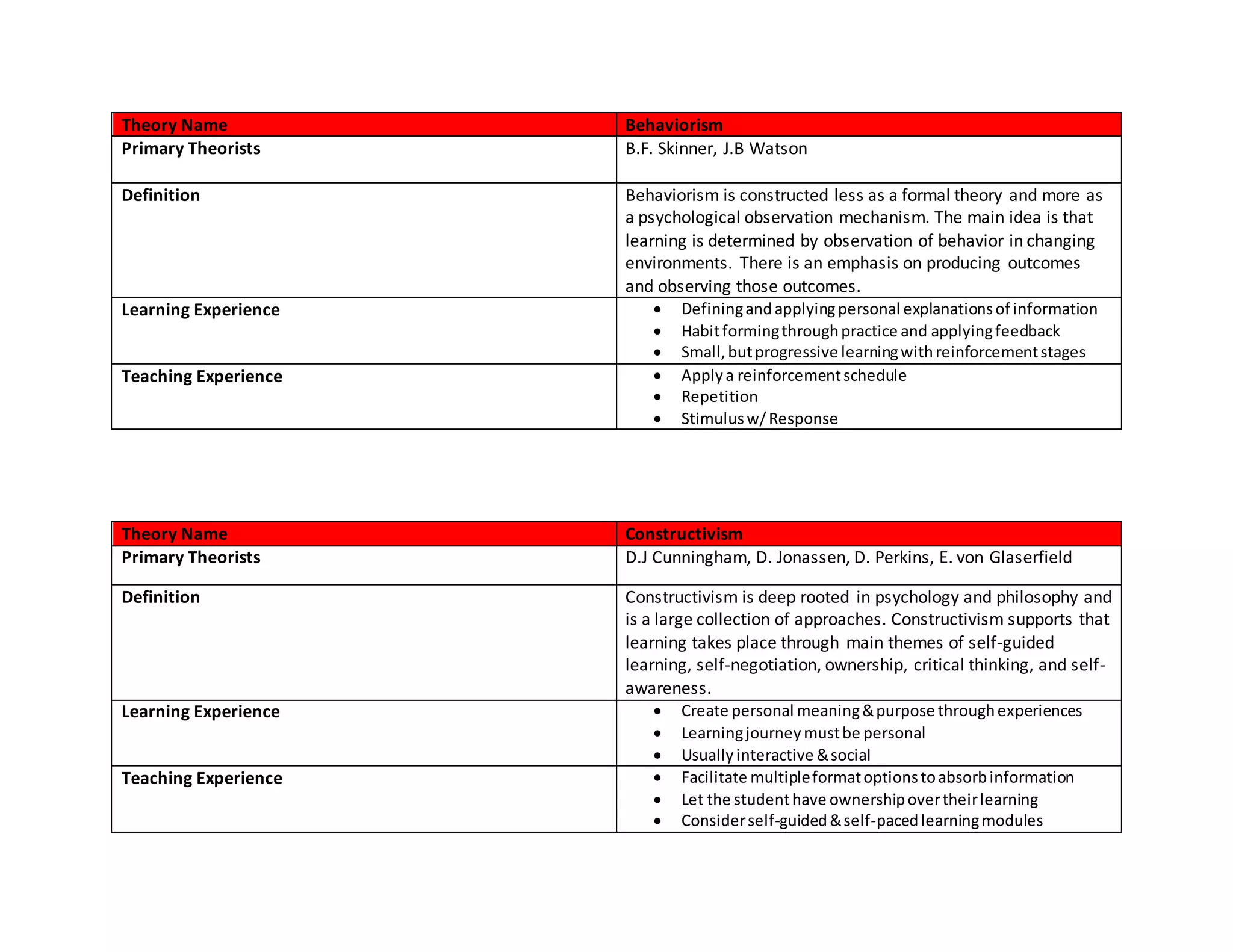
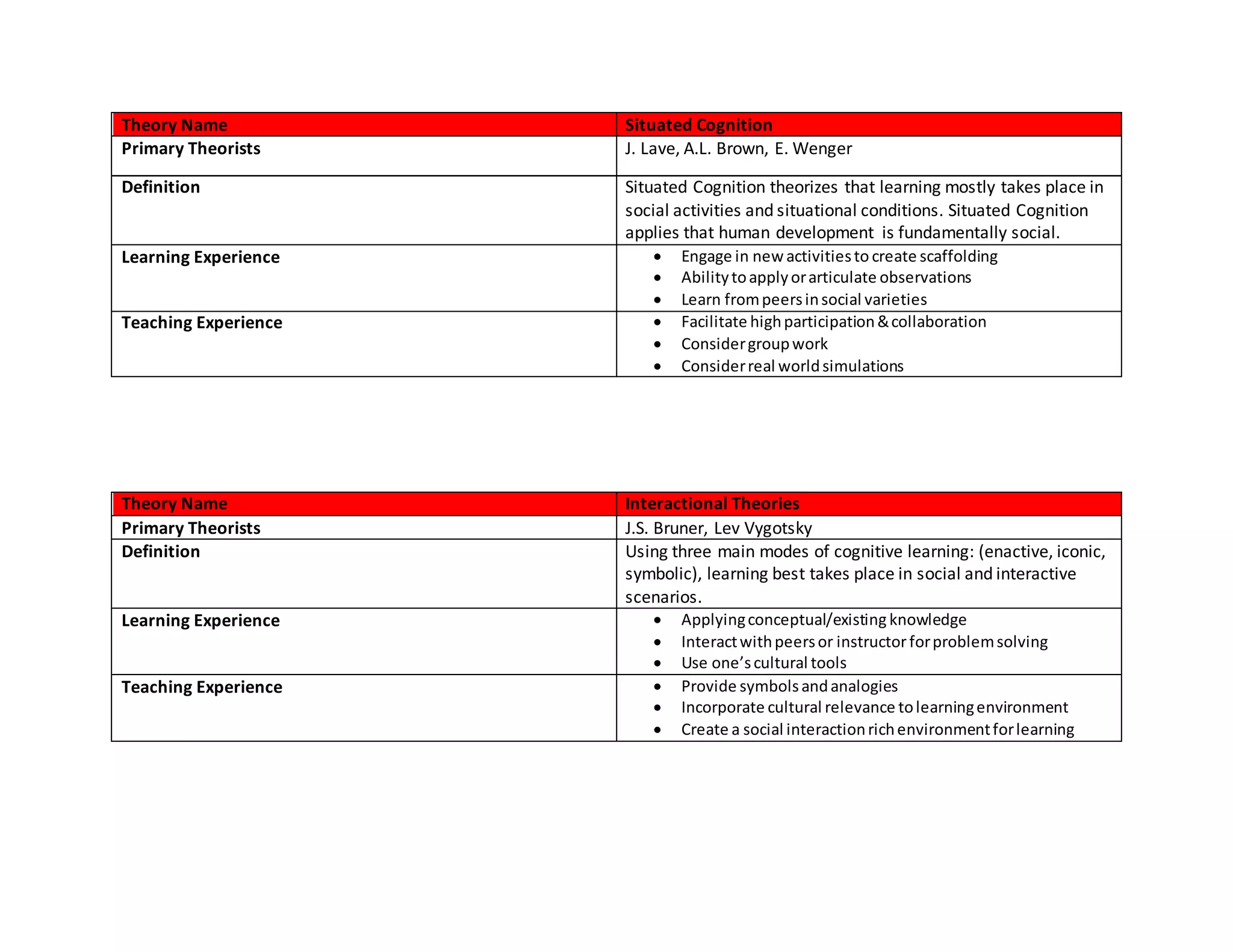
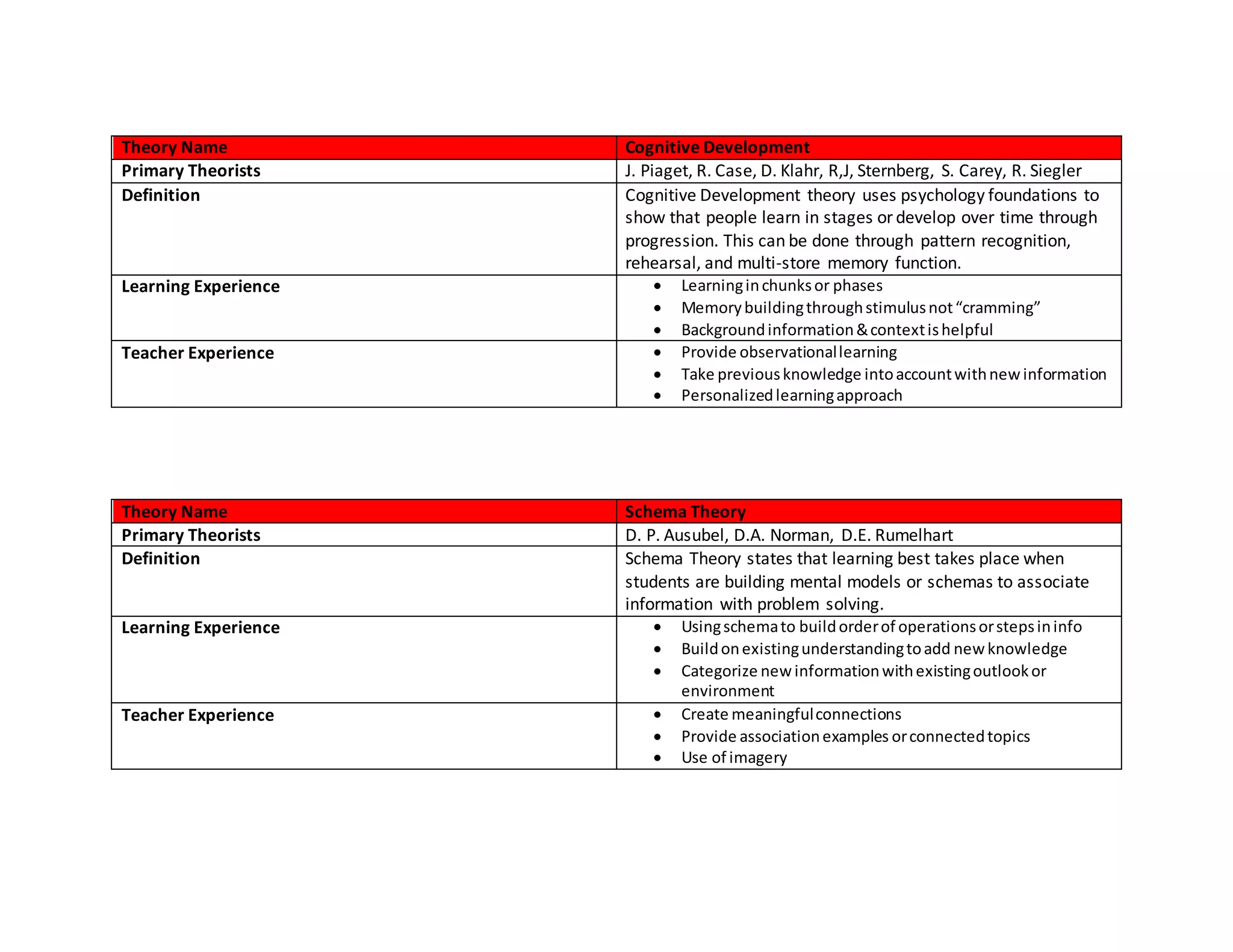
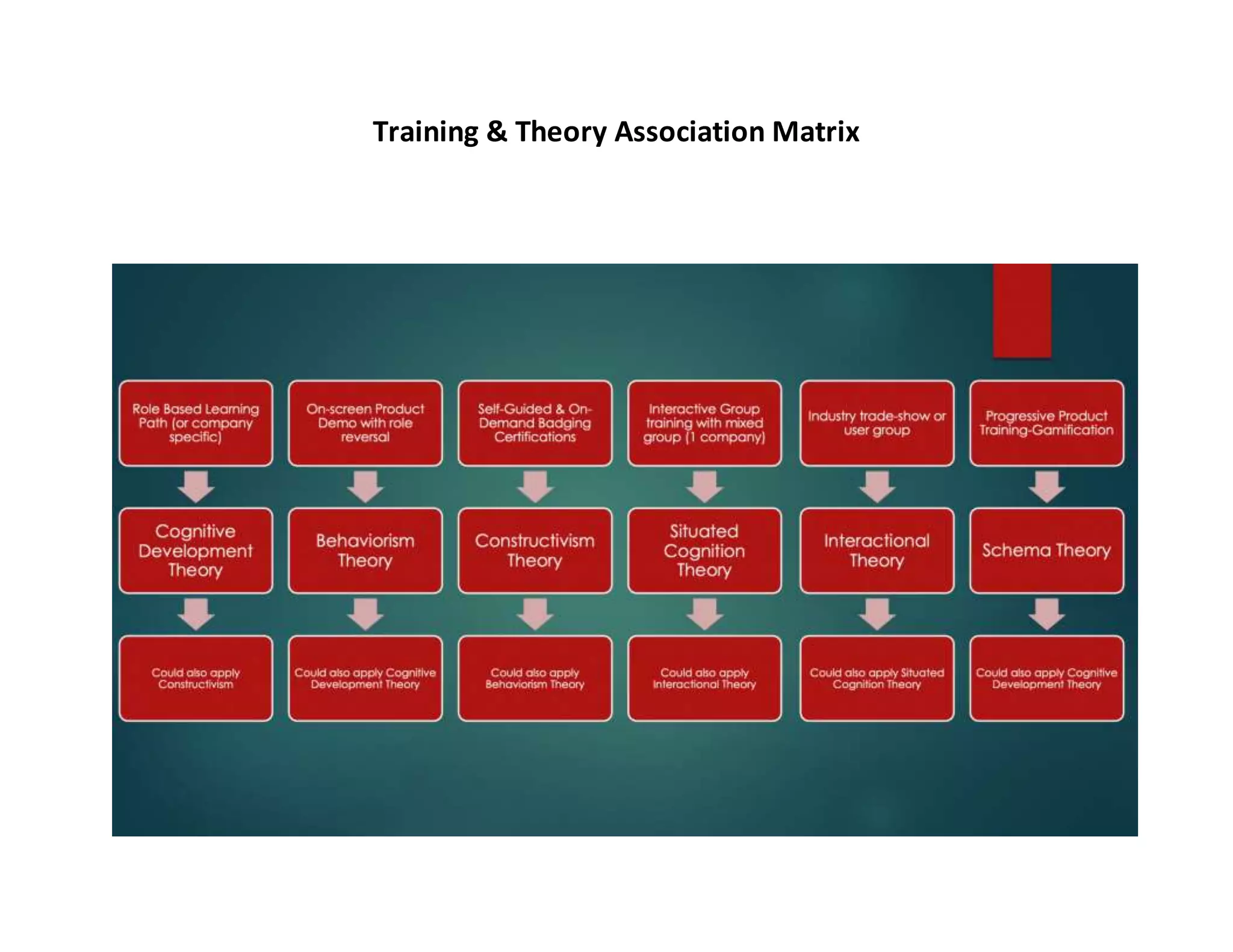
This document provides an overview of six major learning theories that can help Customer Success Managers optimize training and education for their customers. It summarizes Behaviorism, Constructivism, Situated Cognition, Interactional Theories, Cognitive Development theory, and Schema theory. For each theory, it outlines the primary theorists, definition, examples of learning experiences, and teaching experiences that align with that theory. It concludes with a matrix mapping training techniques to the different learning theories.