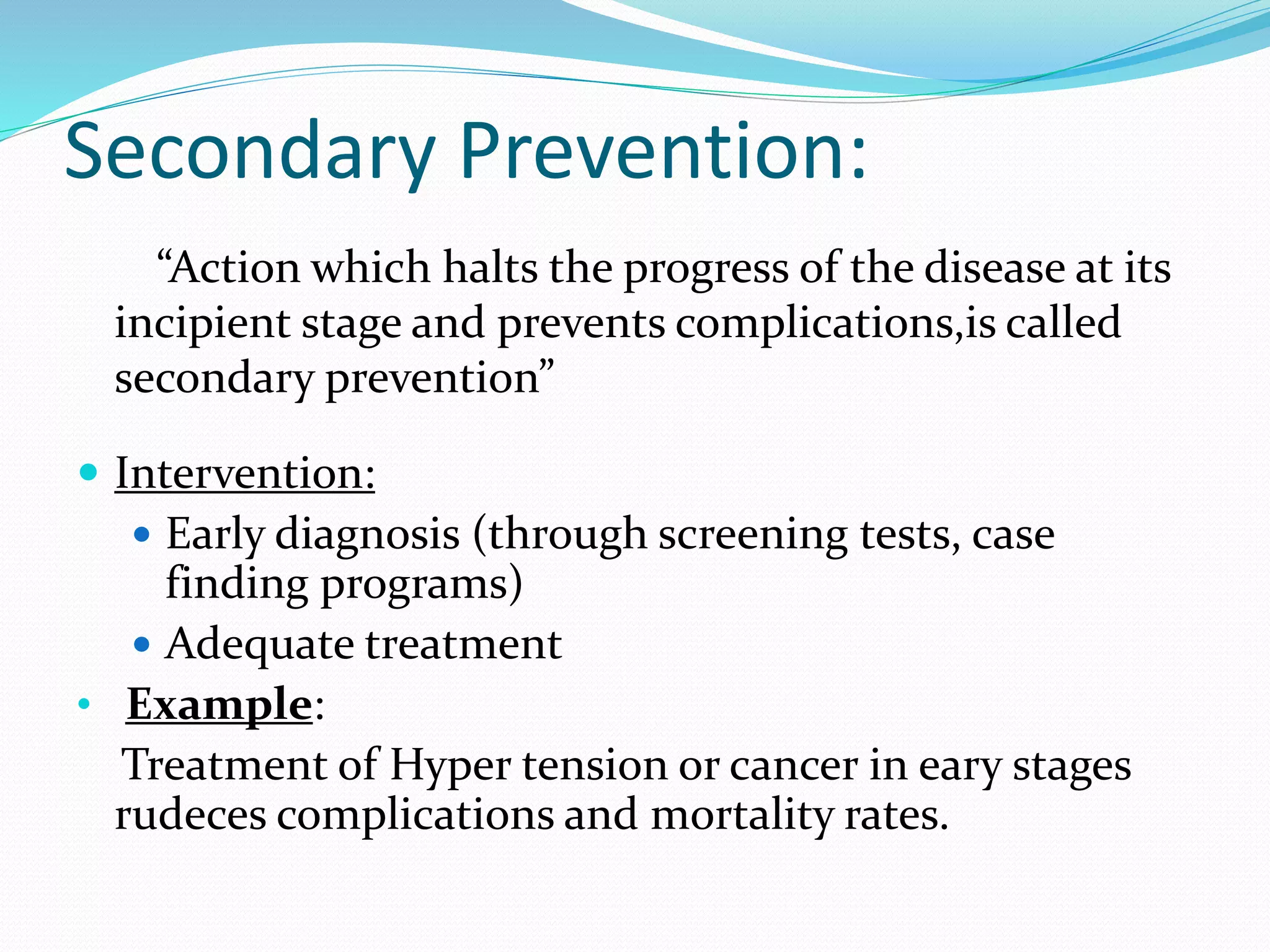
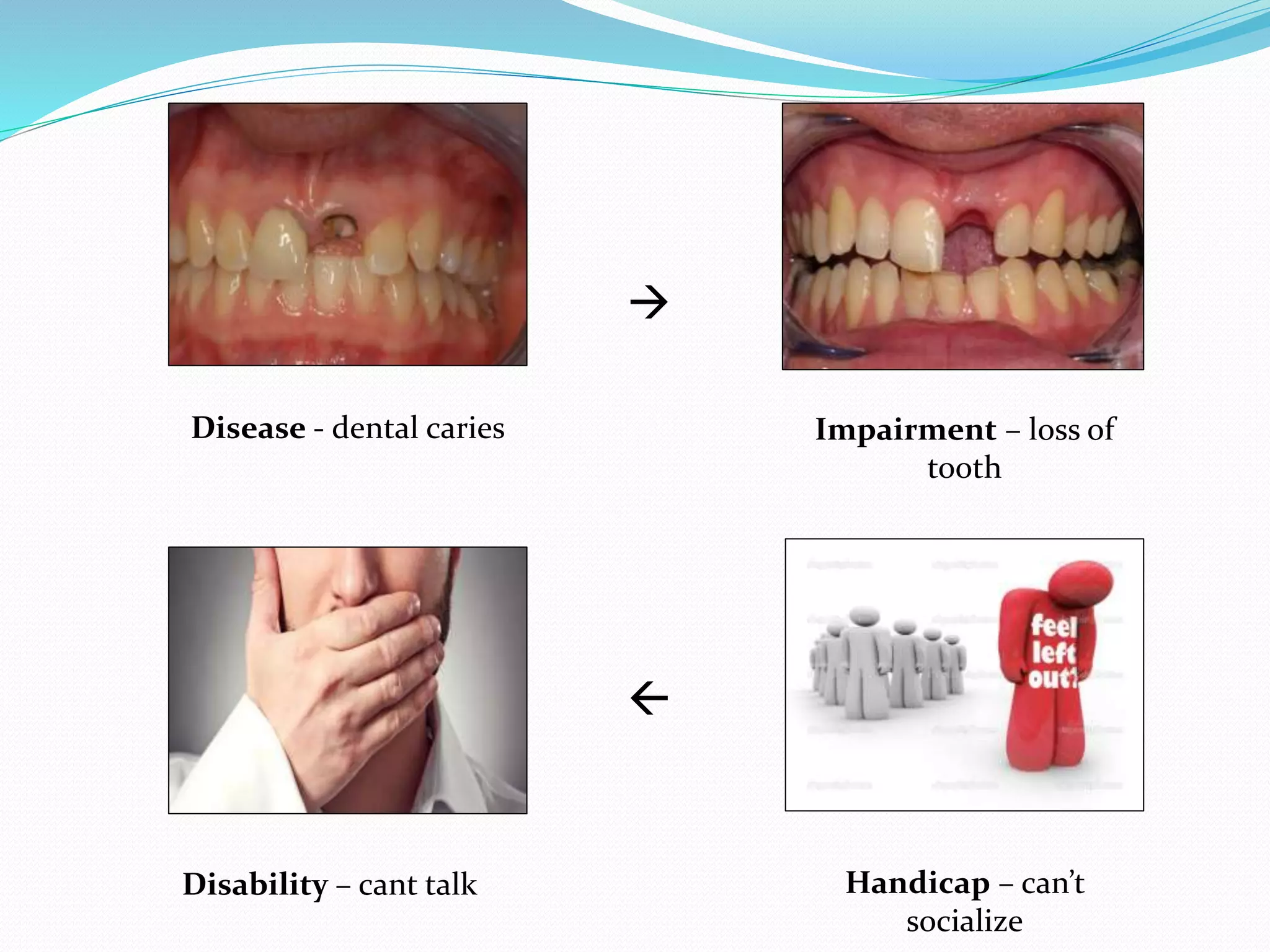
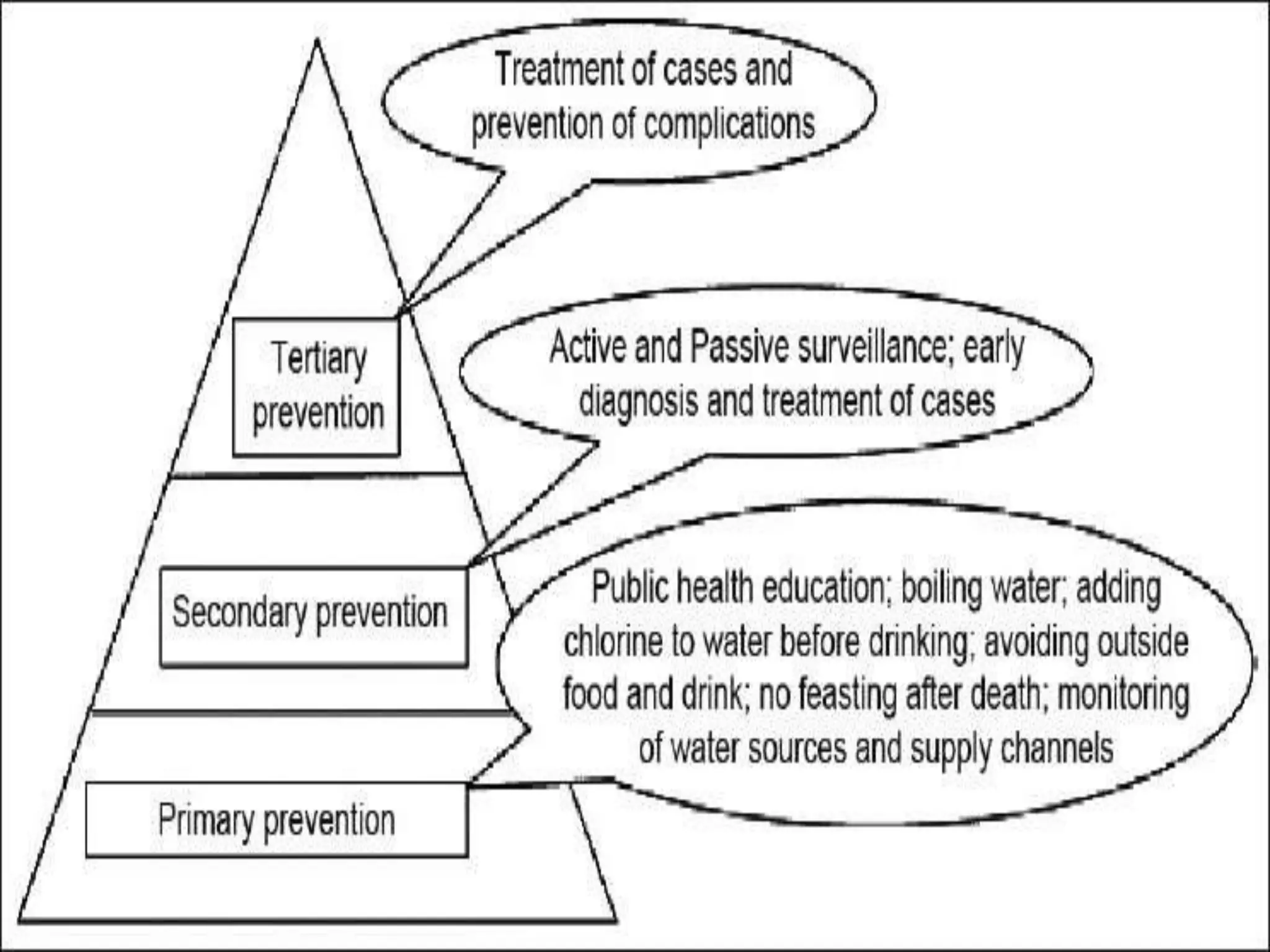
The document discusses the various levels of prevention in public health, including primordial, primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. It emphasizes the importance of early intervention and health promotion to reduce disease incidence and improve health outcomes, particularly focusing on lifestyle changes and education. The conclusion reinforces the idea that prevention is more effective and economical than treating diseases after they occur.