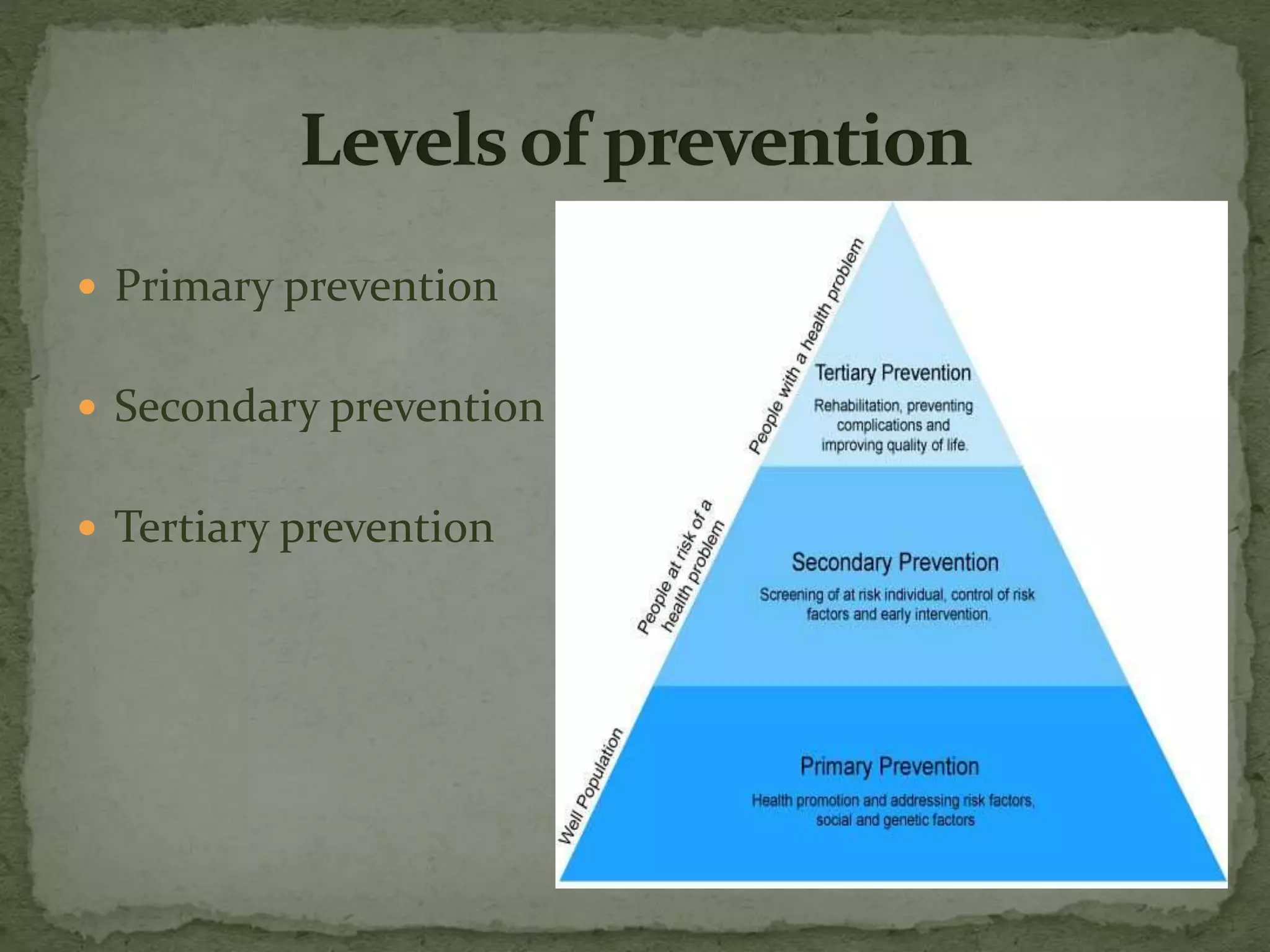
This document discusses dental prevention. It defines prevention and describes its history from the 20th century onward, including the identification of oral diseases and establishment of fluoride's anticaries effects. The principles of prevention are described as primary, secondary, and tertiary. Types of prevention interventions are outlined for dental caries, periodontal disease, oral cancer, and malocclusion. The conclusion emphasizes that combined efforts of dental professionals, patients, and communities can achieve optimal oral health through prevention practices and community health programs.