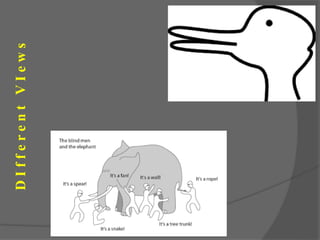
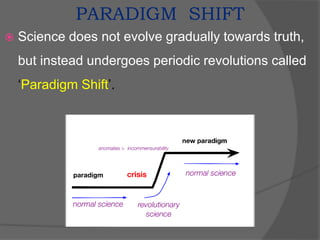
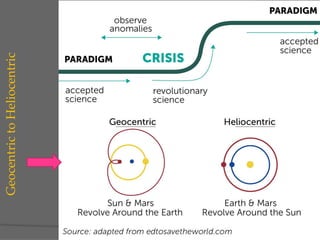
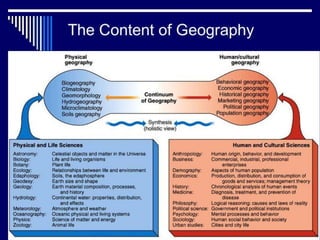
This document discusses geographical thought and paradigms in geography. It defines geography as the study of the relationship between the physical and social environment over space and time. The document notes that scientific paradigms provide models and solutions for a community until a paradigm shift occurs, revolutionizing scientific thought. In geography, there was a shift from a geocentric to heliocentric view of the solar system and from earlier locational views to emphasizing relationships between land and people and regional synthesis.