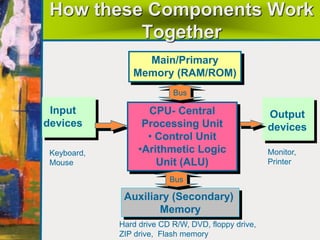
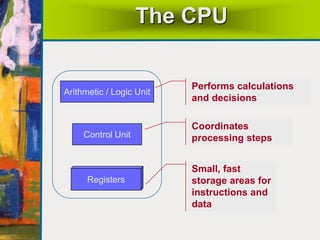
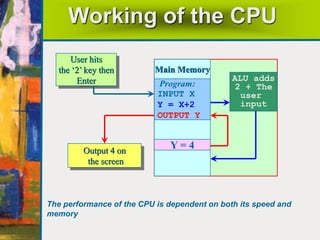
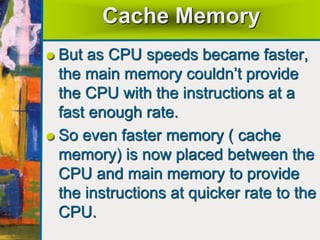
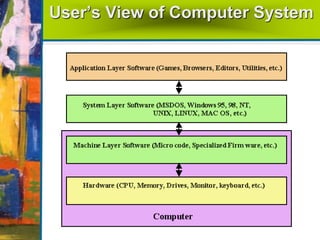
The document summarizes the basic components and functions of a computer system. It discusses how a computer accepts data through input devices, stores and processes the data, and provides results through output devices. The key components are the central processing unit (CPU), memory, hardware, and software. The CPU contains a control unit and arithmetic logic unit to control operations and perform calculations. Hardware refers to the physical and visible parts, while software programs tell the computer what to do. Together, these components work to process data and provide useful information to the user.