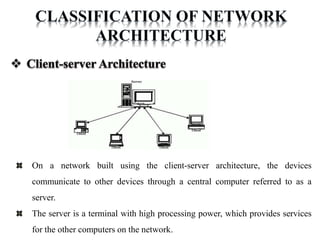
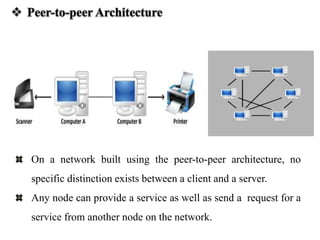
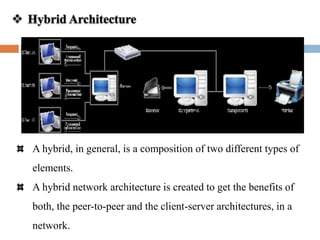
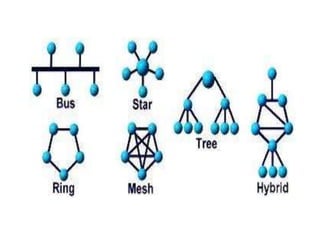
The document discusses different types of computer networks including personal area networks (PANs), local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). It describes how PANs connect devices within 10 meters, LANs connect devices within a building, MANs extend across a city, and WANs span large geographic areas like countries. The document also covers network topologies, architectures including client-server and peer-to-peer, and concludes with references to additional information sources.