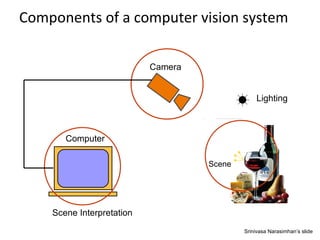
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that uses computer hardware and software to analyze visual images and videos. The goal is to make useful decisions based on sensed images by understanding objects and scenes. Computer vision combines knowledge from fields like computer science, electrical engineering, mathematics, biology and cognitive science. It focuses on extracting useful information from images like detecting and identifying faces, recovering 3D geometry, and tracking motion. Computer vision has applications in manufacturing, city planning, entertainment, forensics and more.