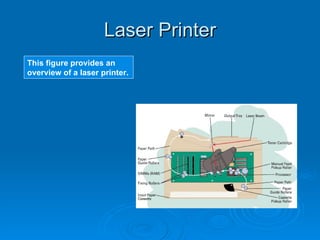
The document discusses computer system input, output, and storage devices. It describes common input devices like keyboards and mice, as well as other input devices such as scanners, cameras, and voice recognition. Output devices discussed include monitors for visual output and printers for hard copies. Storage media include magnetic, optical, and solid-state devices. Input and output devices connect to computers physically or wirelessly to transfer data in and out.