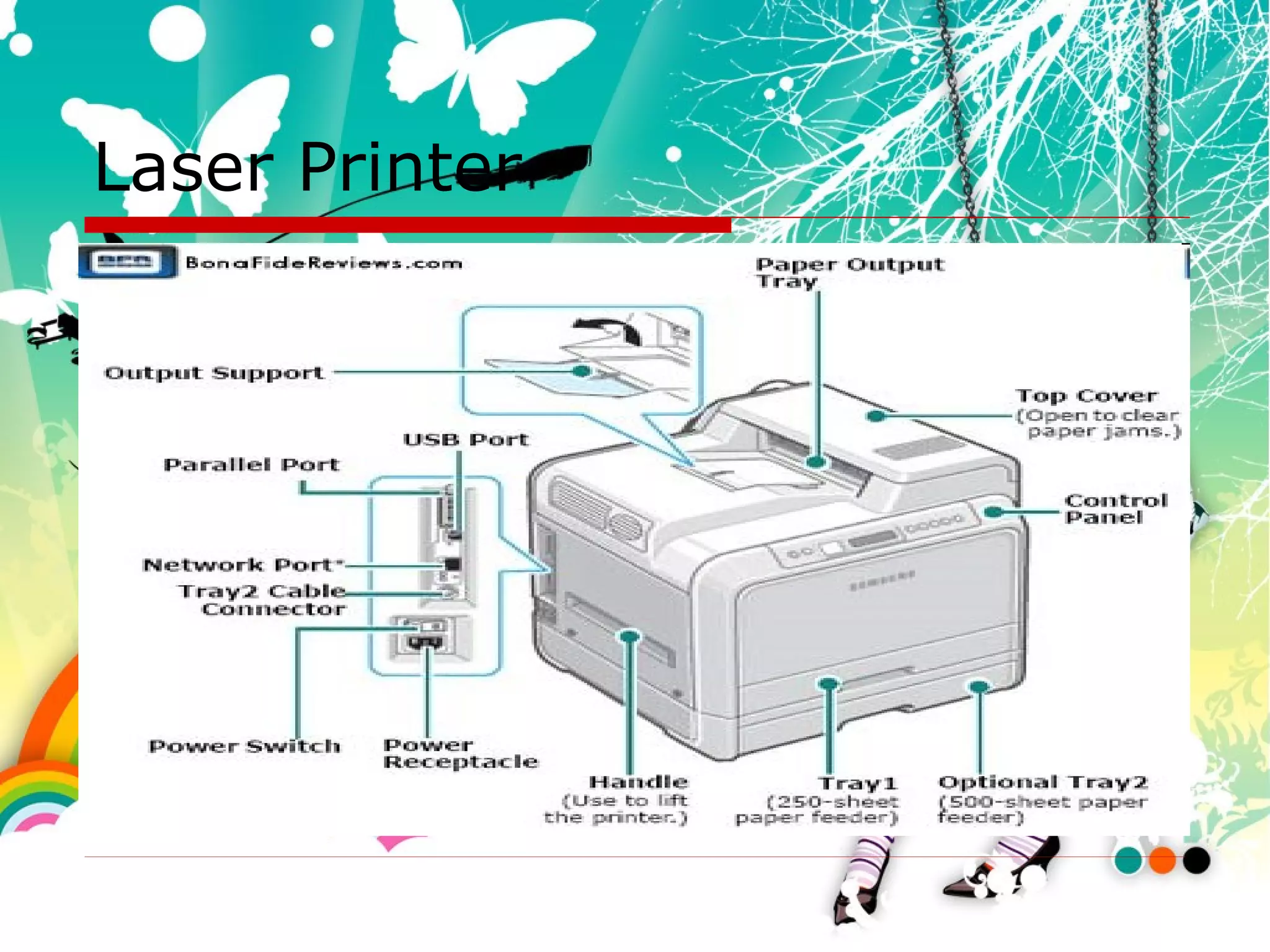
The document discusses computer system hardware input, output, and storage devices. It describes common input devices like keyboards, mice, touchscreens, and microphones. Output devices mentioned include monitors, printers, and speakers. Storage devices covered are magnetic drives, optical discs, solid state drives, and removable media like USB drives. The document also discusses how input/output devices connect to computers and tips for caring for storage media.