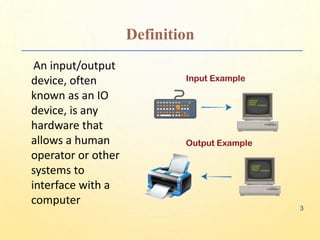
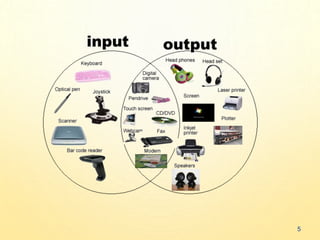
The document outlines input, output, and secondary devices, defining input/output devices as hardware that facilitates communication between humans and computers. It details various input devices like keyboards, mice, joysticks, and scanners, as well as output devices such as monitors and printers. Additionally, it describes secondary storage options, including hard disk drives, CD/DVD drives, and USB drives, emphasizing their roles in data preservation and transfer.