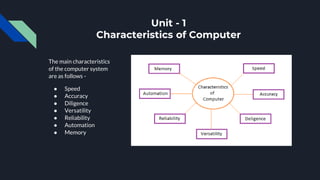
Computers have several key characteristics:
- Speed: Can process millions of instructions per second much faster than humans.
- Accuracy: Perform calculations with 100% accuracy without errors.
- Versatility: Can perform different tasks with the same efficiency.
- Reliability: Provide consistent results for the same input data.
- Automation: Perform tasks automatically without human intervention.
- Memory: Store data and instructions both temporarily and permanently.
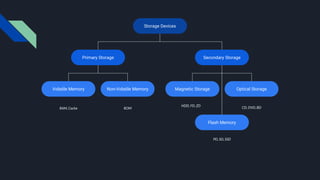
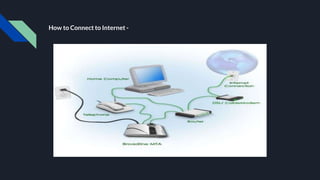
Input devices allow entering data into computers, including keyboards, mice, scanners, microphones. Output devices display or play the processed data, like monitors, printers, speakers, projectors. Common storage devices save data long-term for later use.