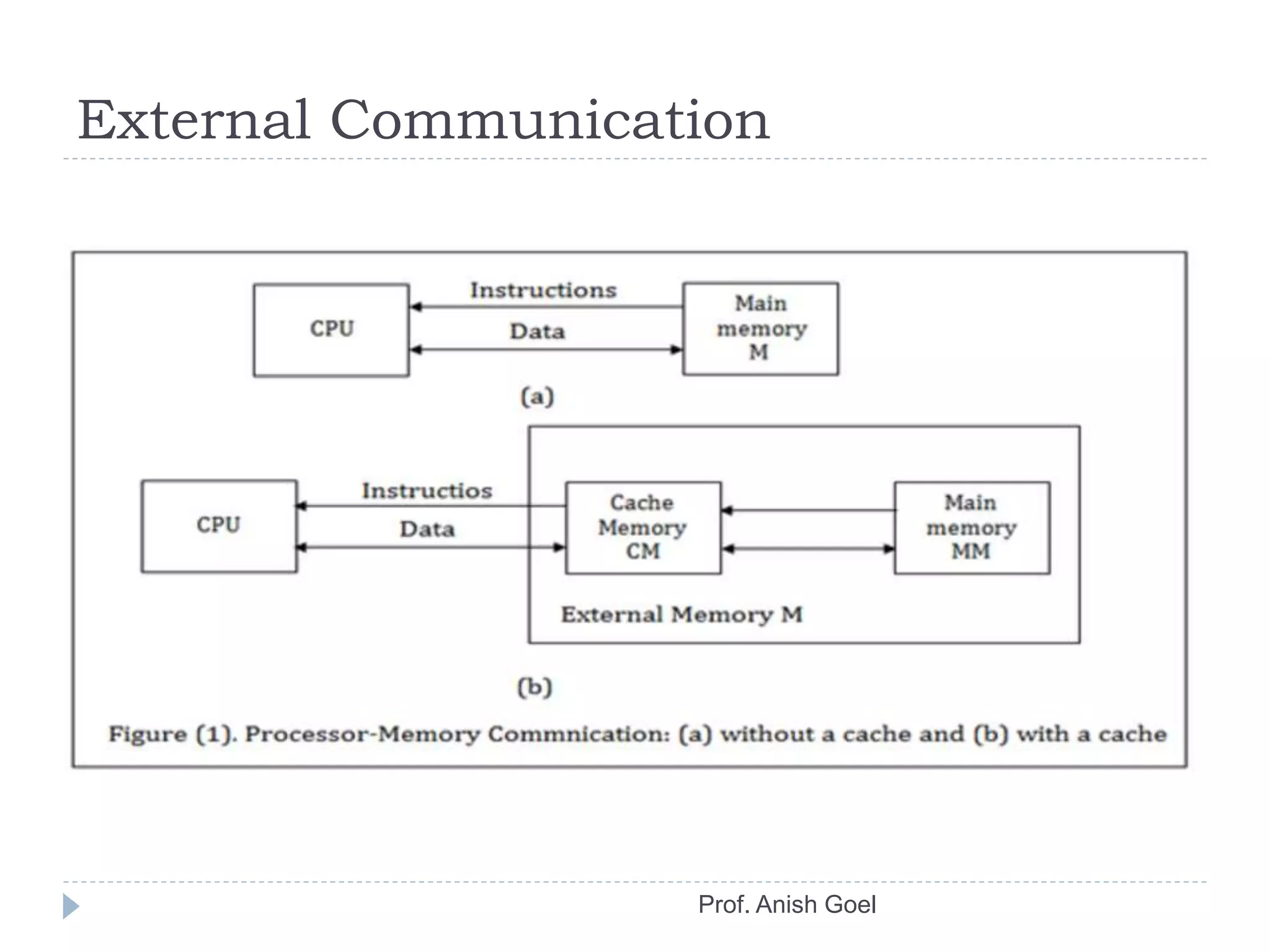
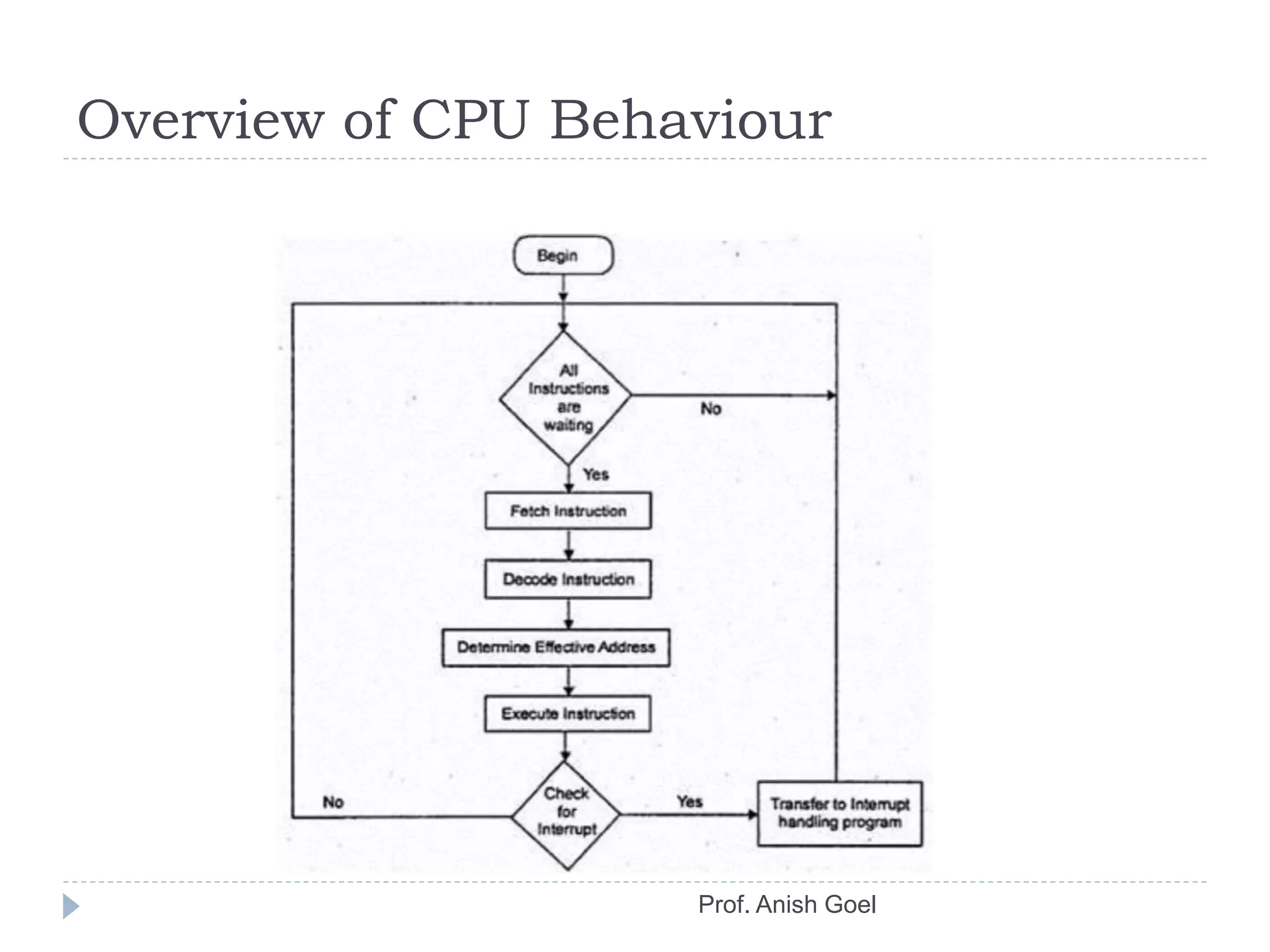
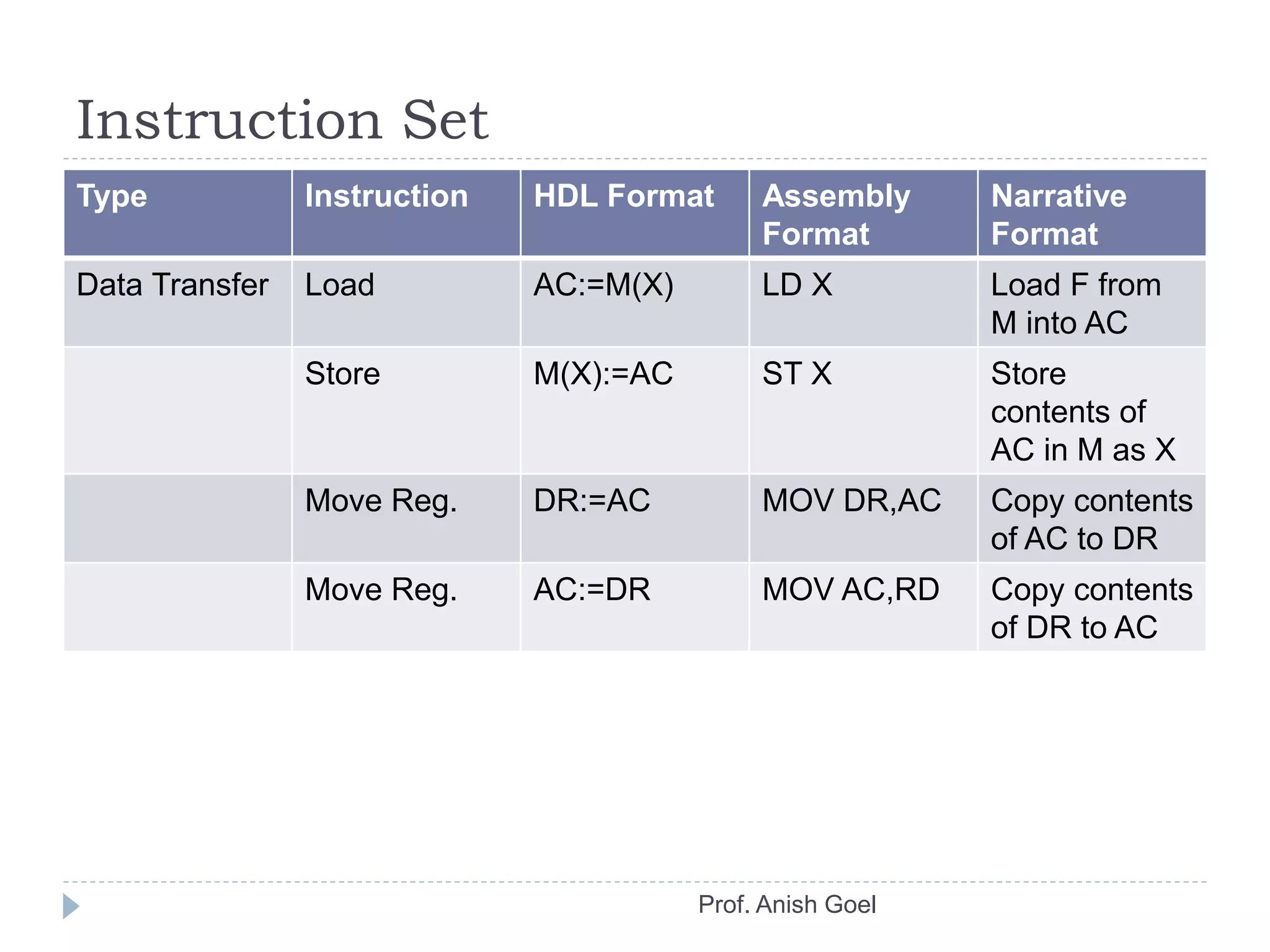
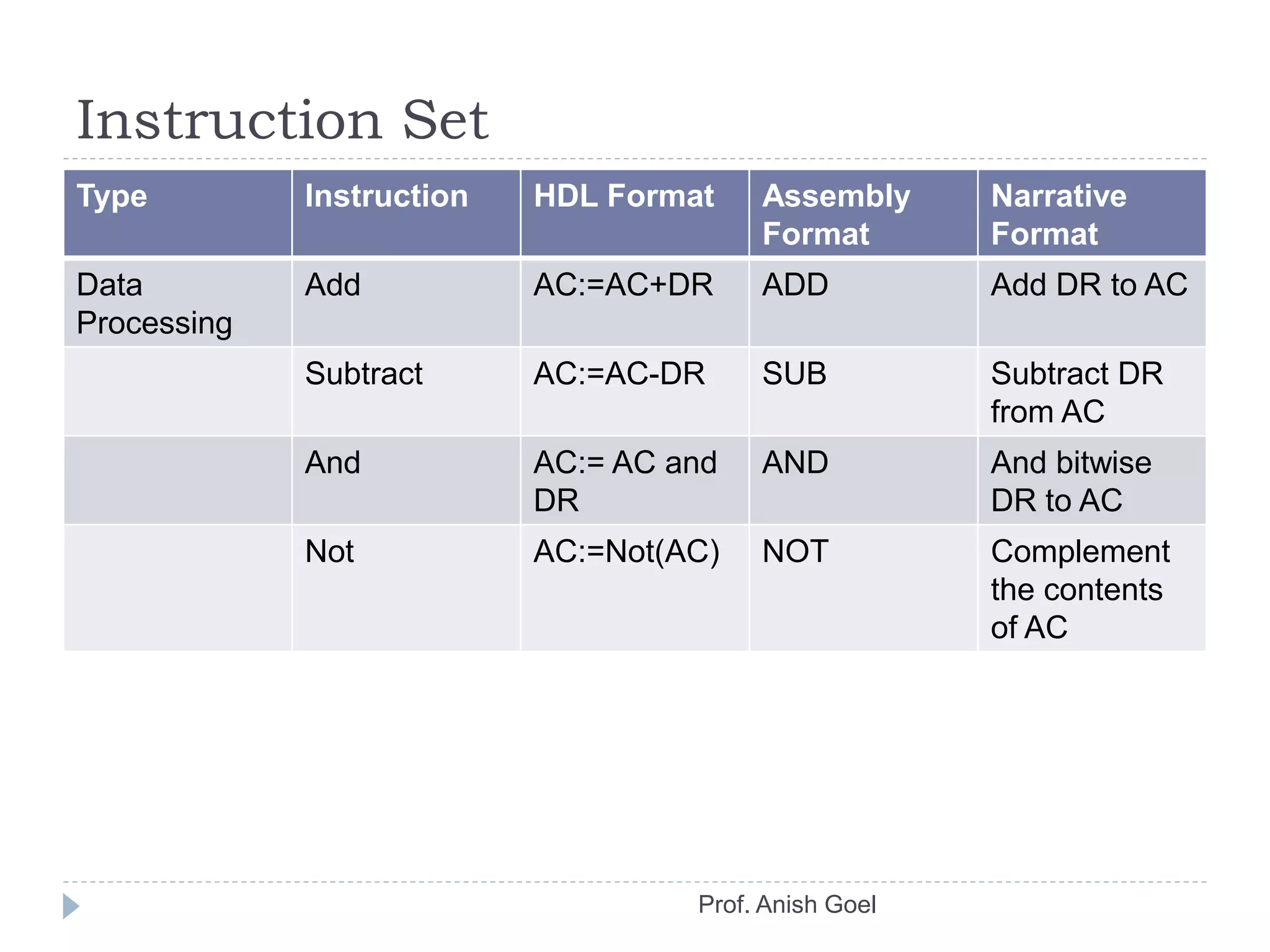
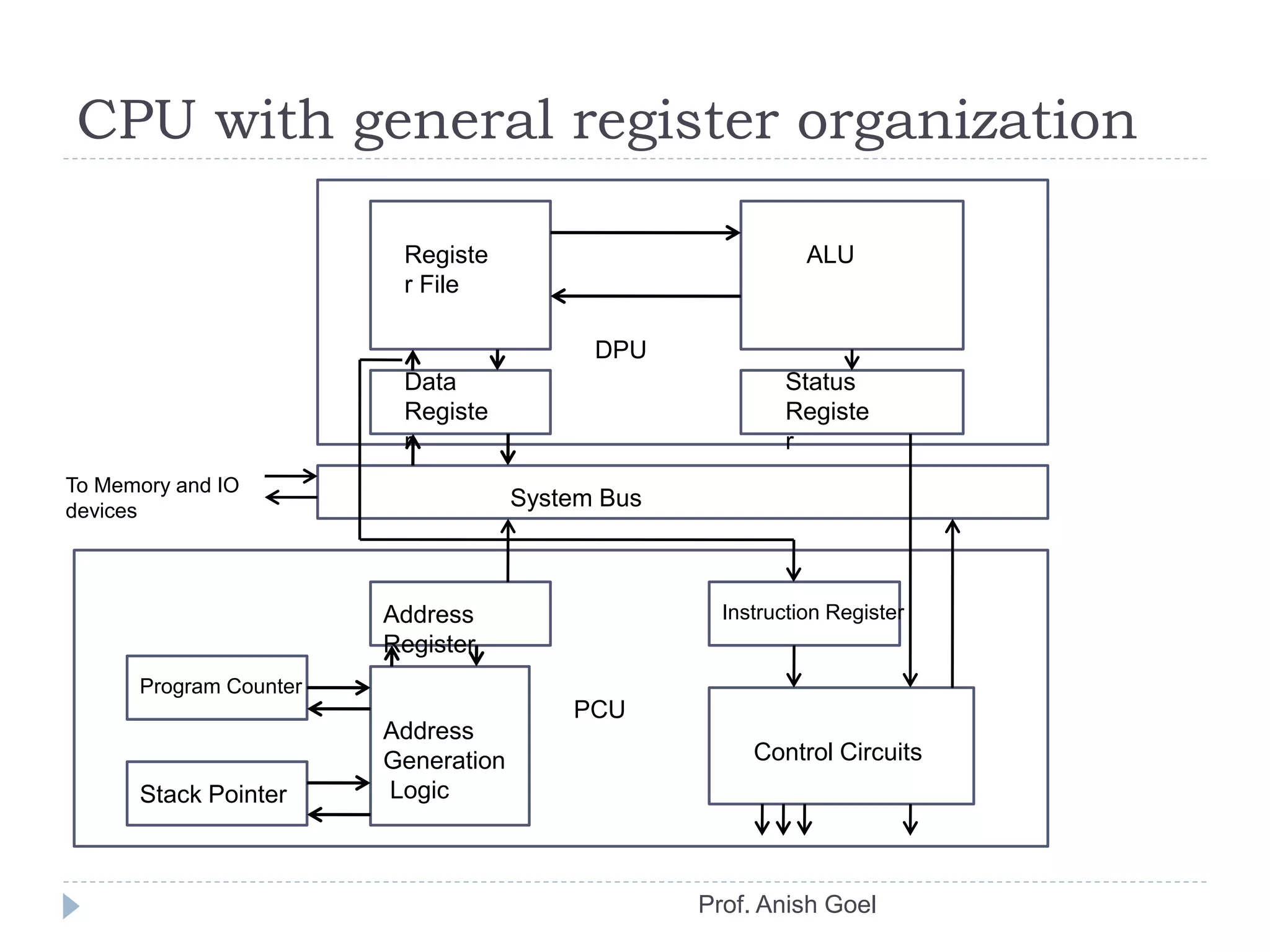
The document discusses the basics of CPU organization and behavior. It explains that the CPU transfers instructions and data between registers and main memory, executes instructions sequentially unless branching occurs, and transfers output data back to memory. It also describes user and supervisor modes, with user programs running applications and supervisor programs managing system routines. The accumulator-based CPU design is shown, including its instruction decoder, arithmetic logic unit, and program control unit. The document provides examples of instruction sets and types.