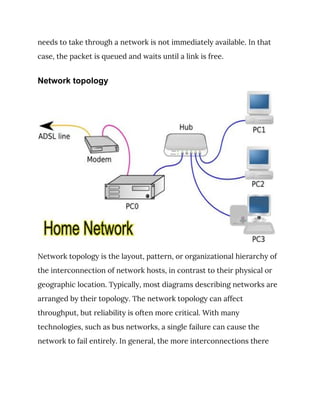
A computer network consists of interconnected computers that use common communication protocols to share resources, classified by various criteria including transmission medium and topology. The history of computer networking spans significant developments from the late 1950s through the 1990s, with key innovations like packet switching and Ethernet that shaped modern networks. Different network topologies, such as bus, star, and mesh, determine the organization and reliability of connections within a network.