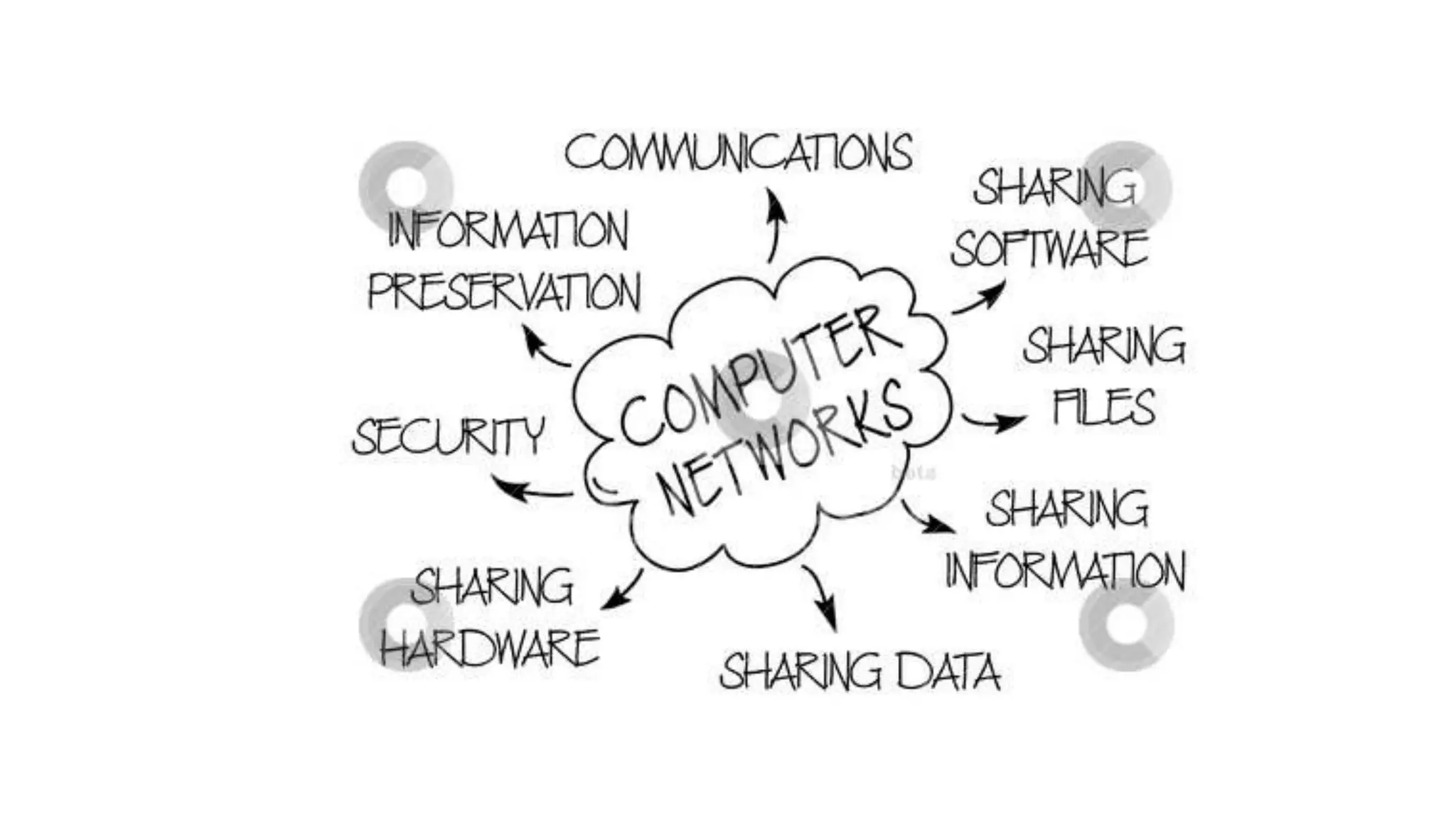
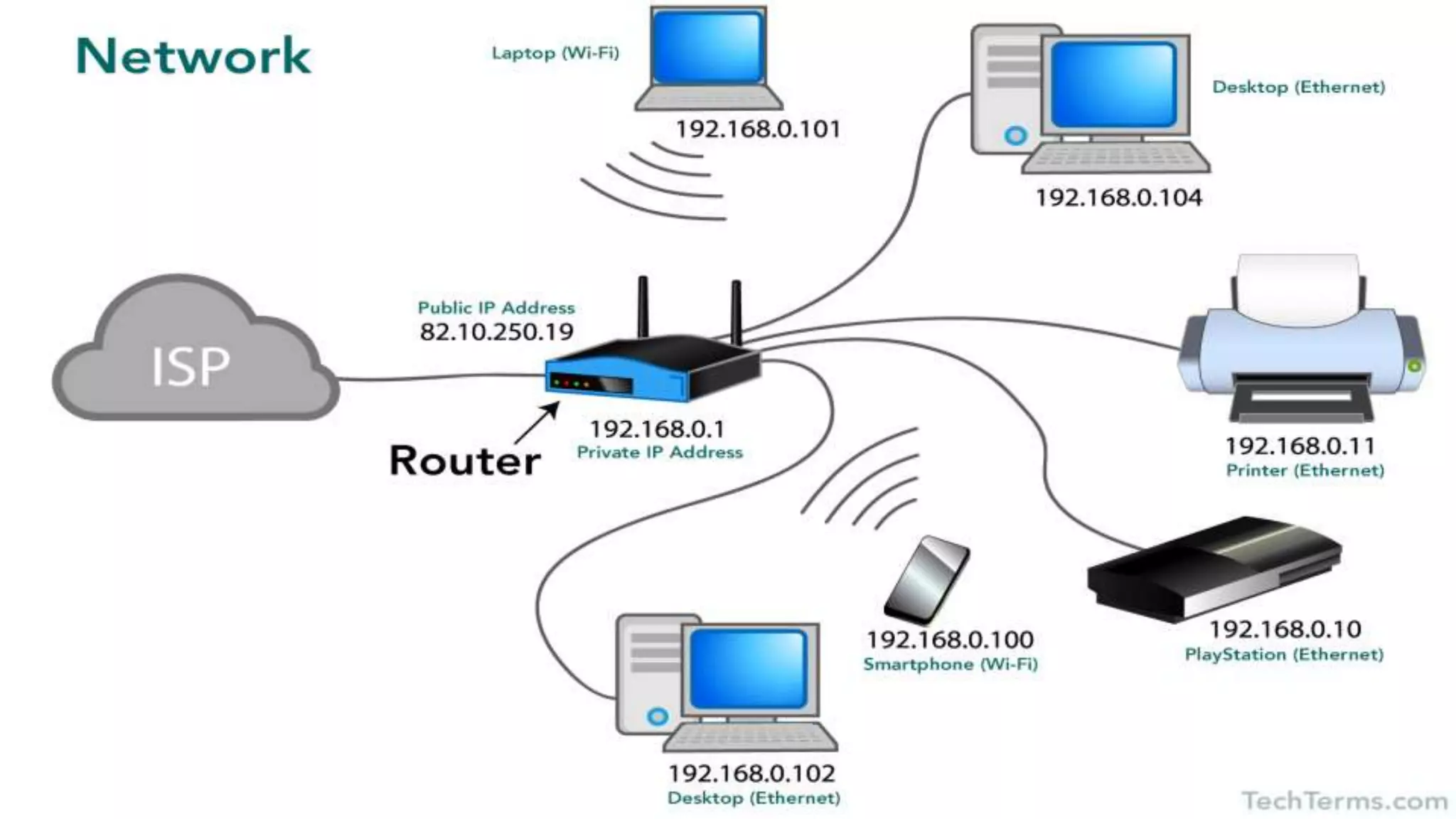
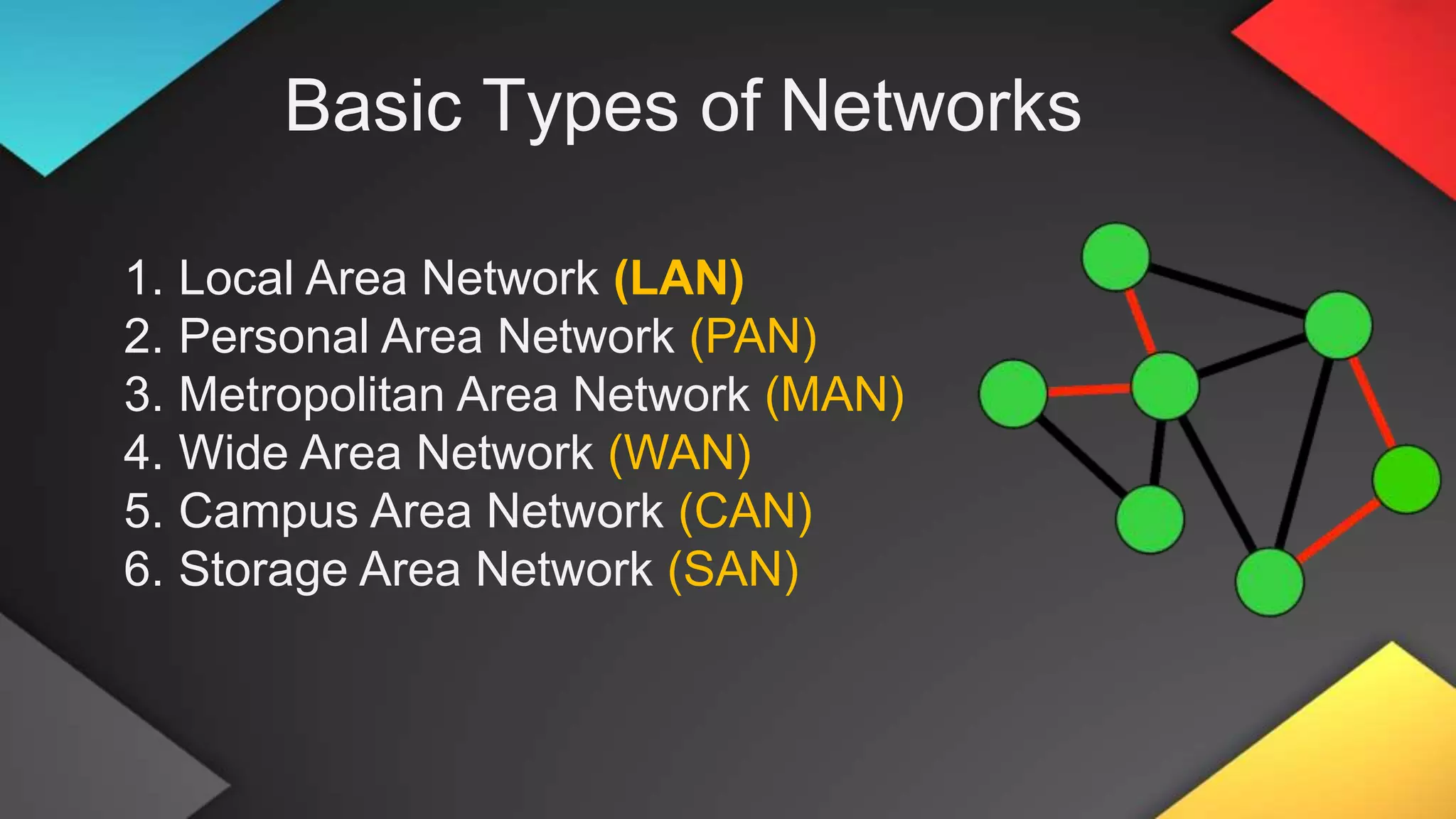
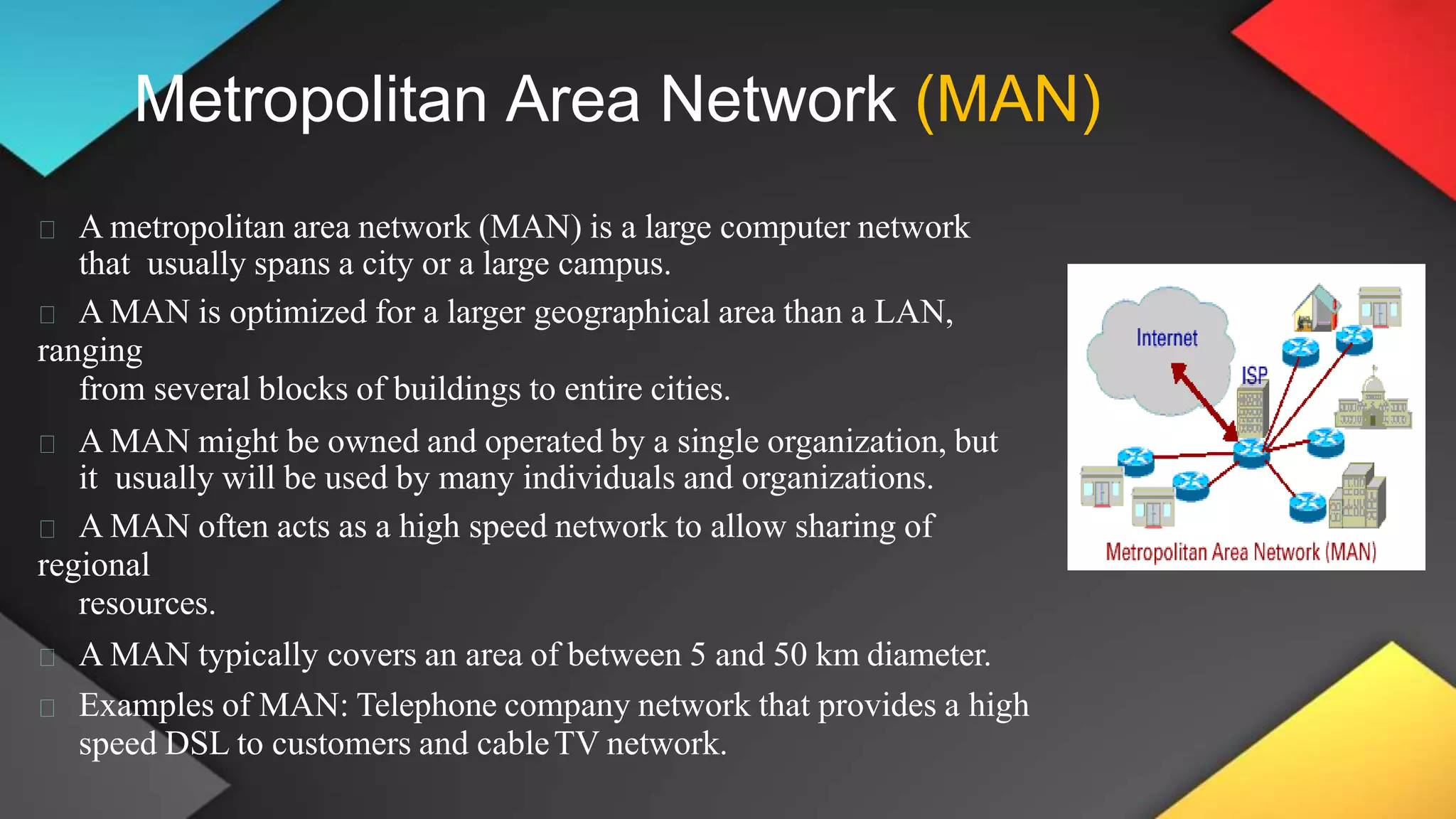
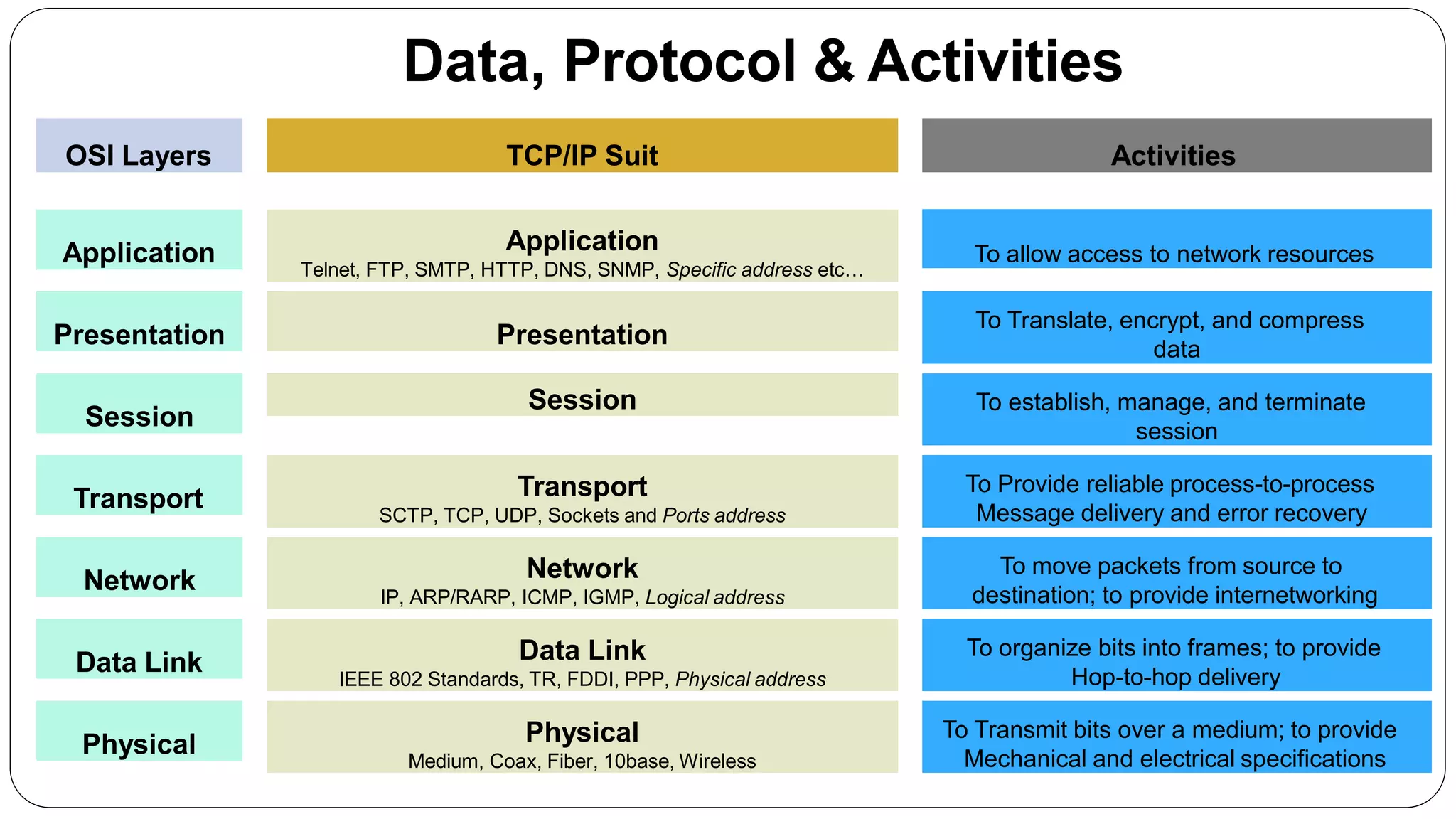
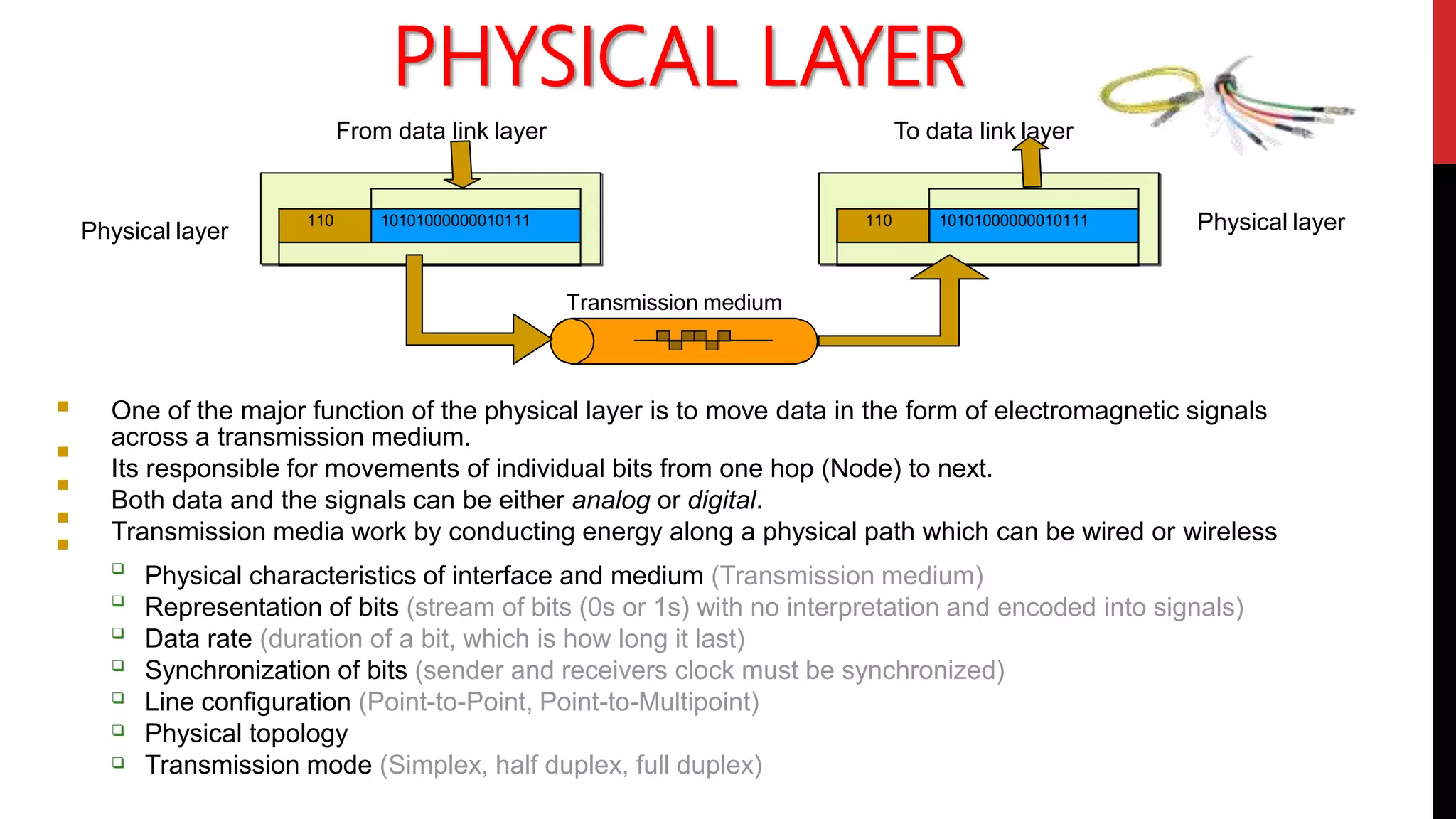
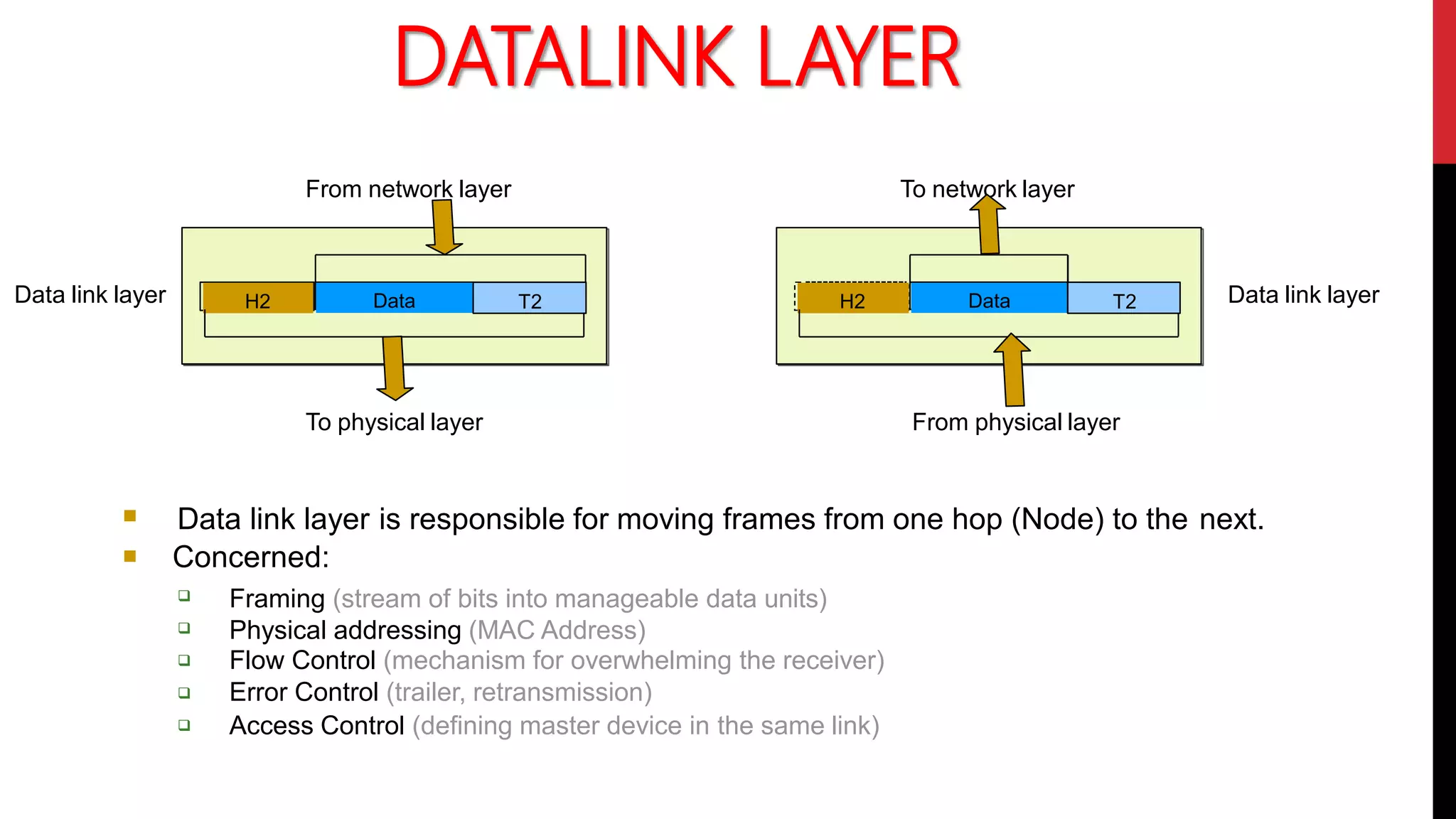
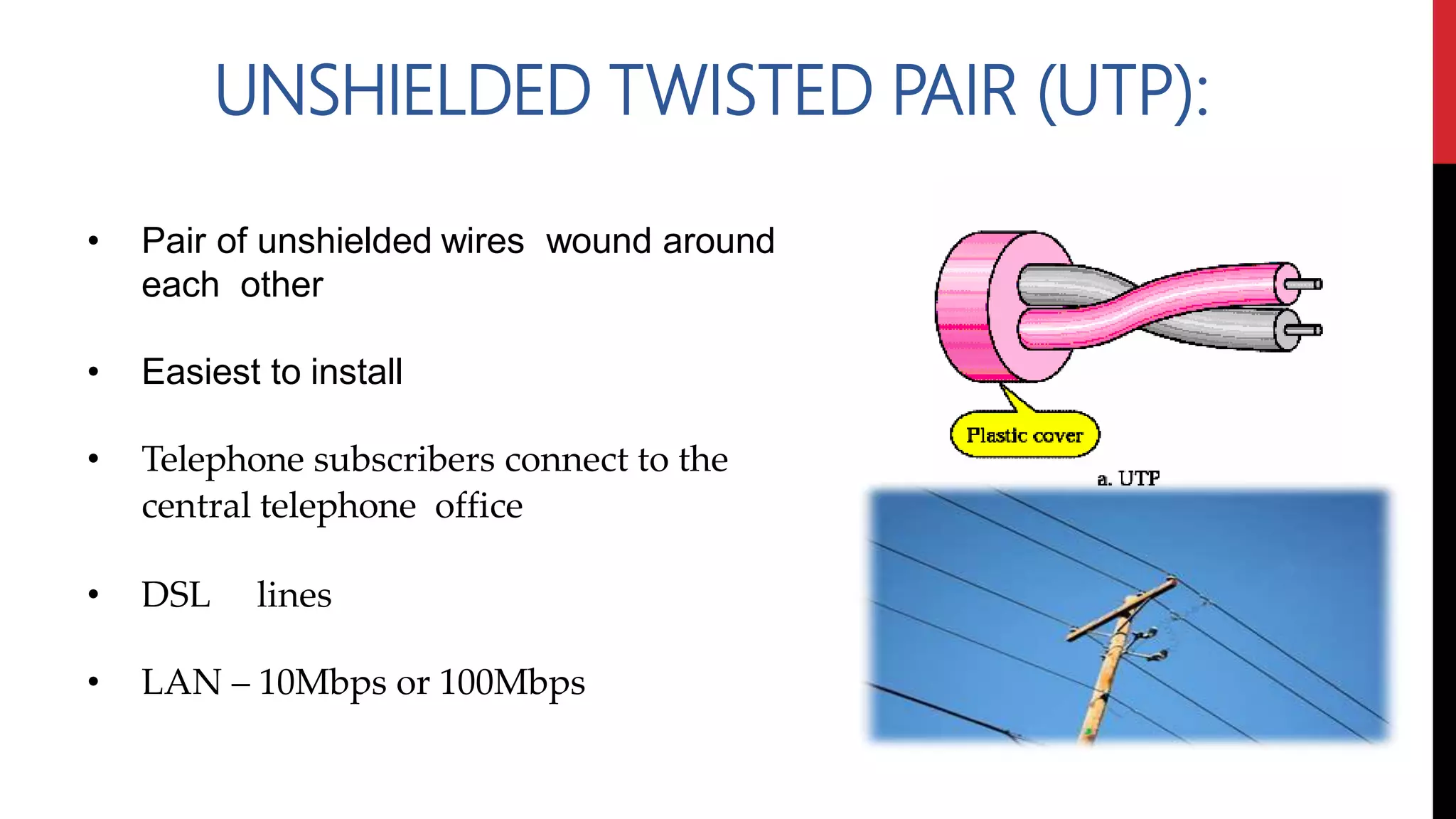
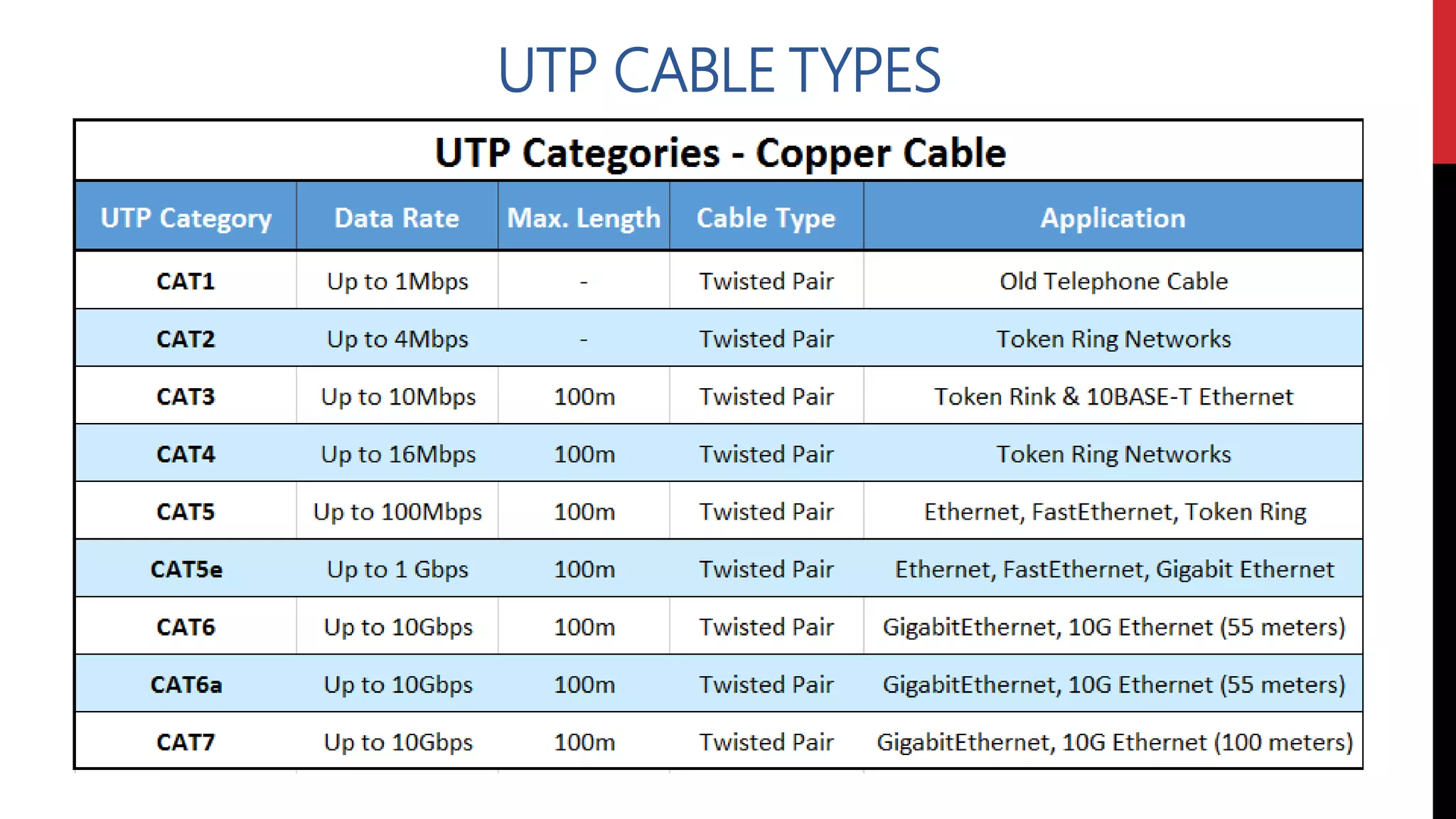
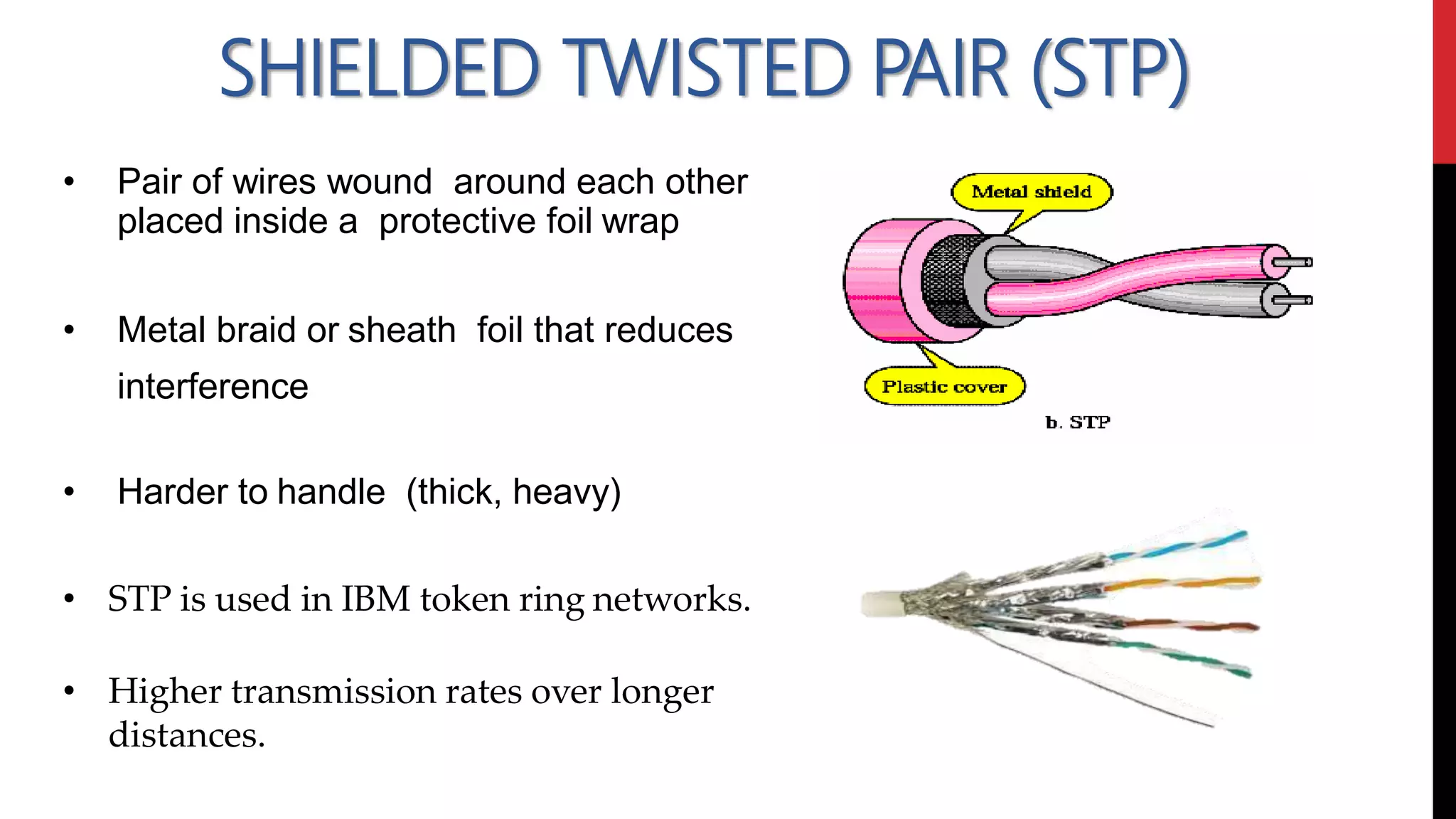
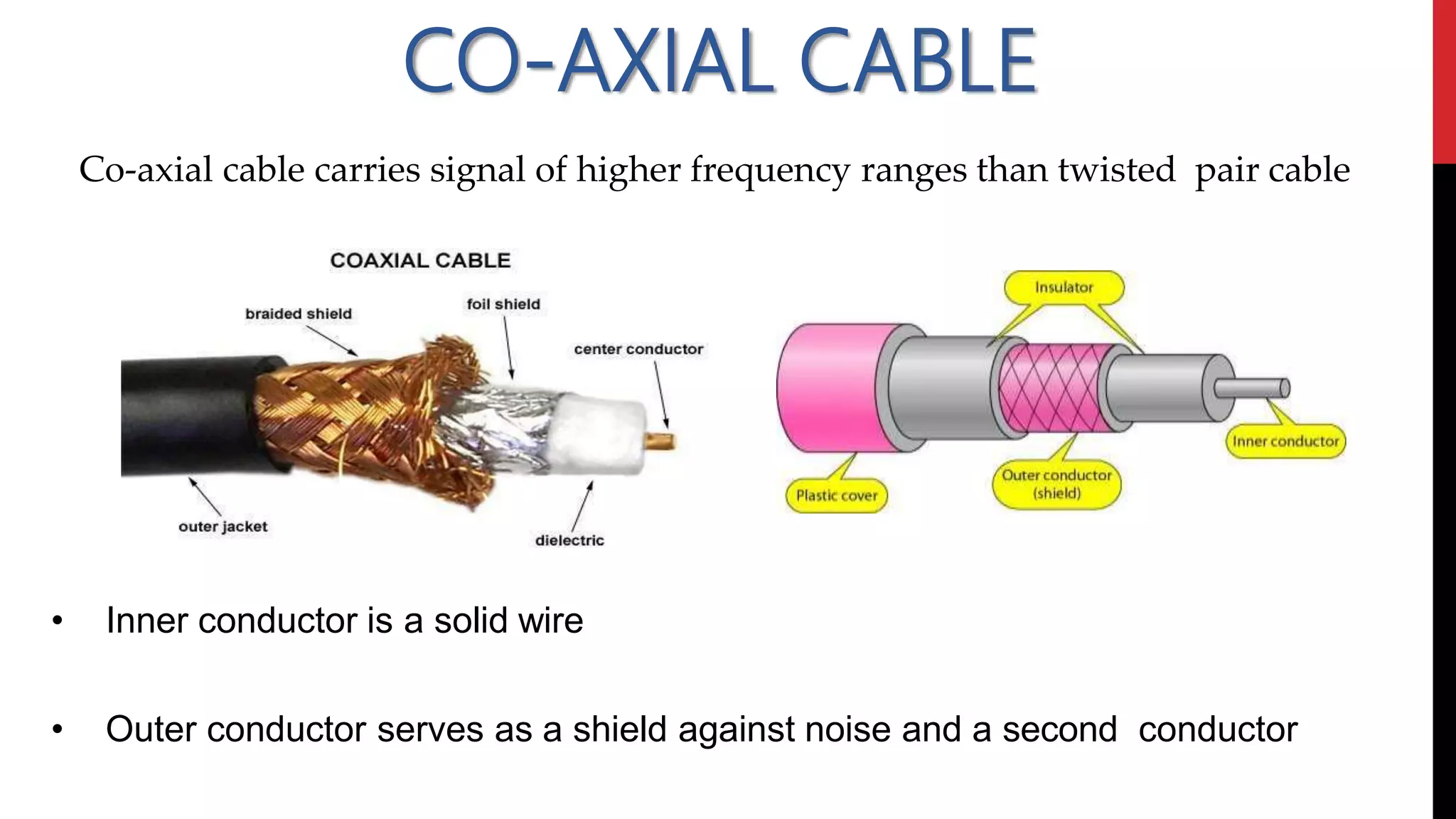
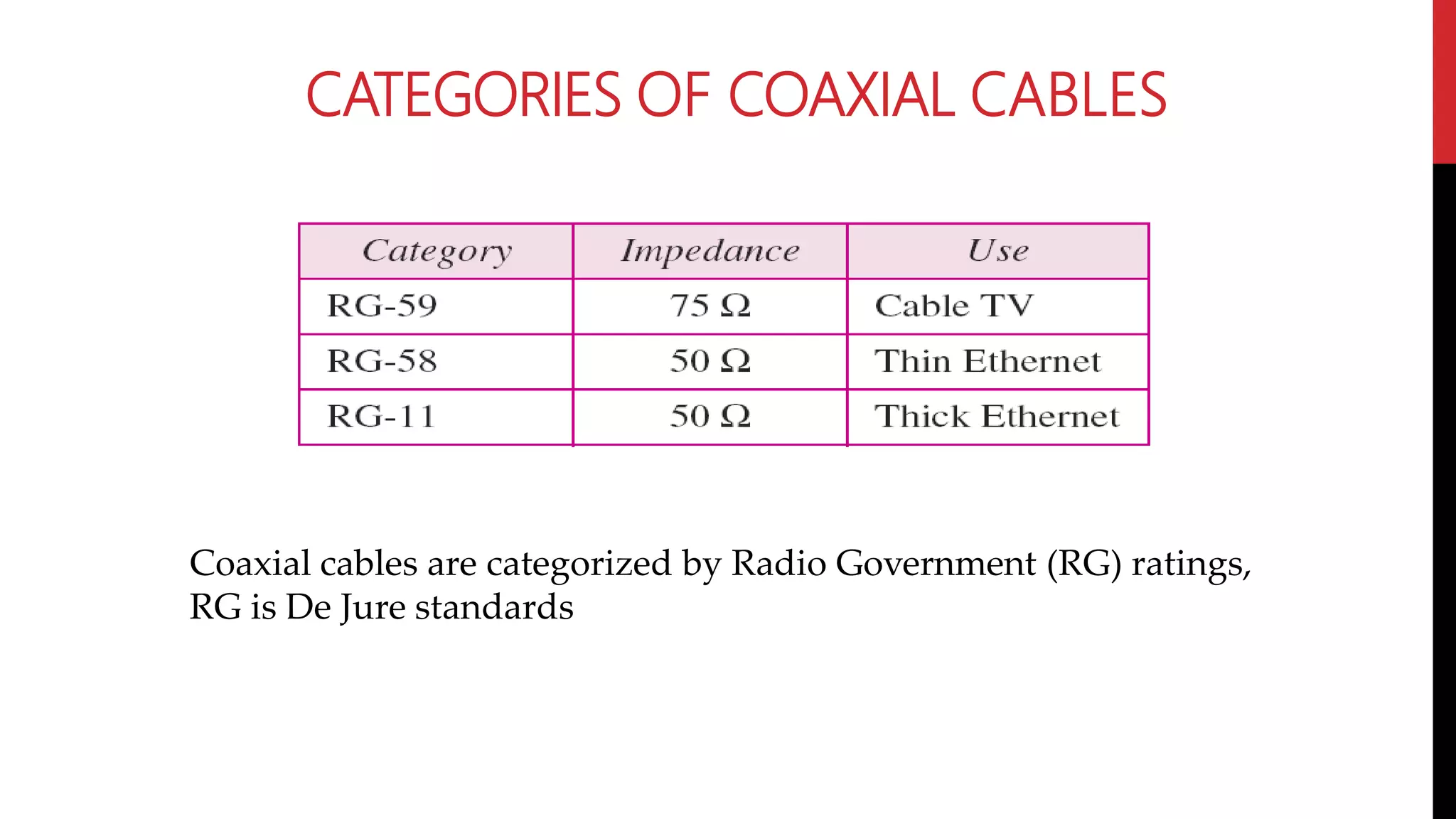
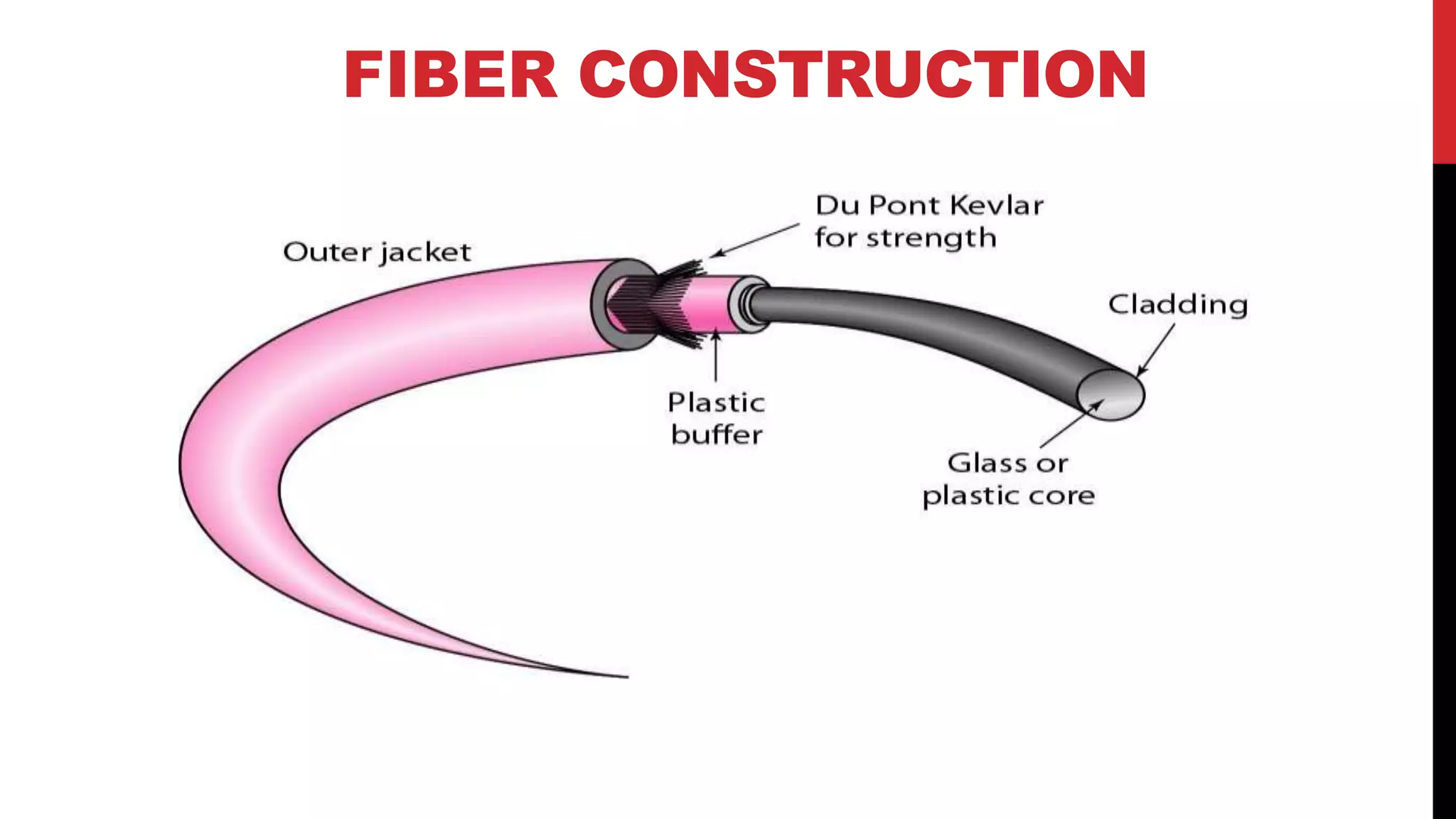
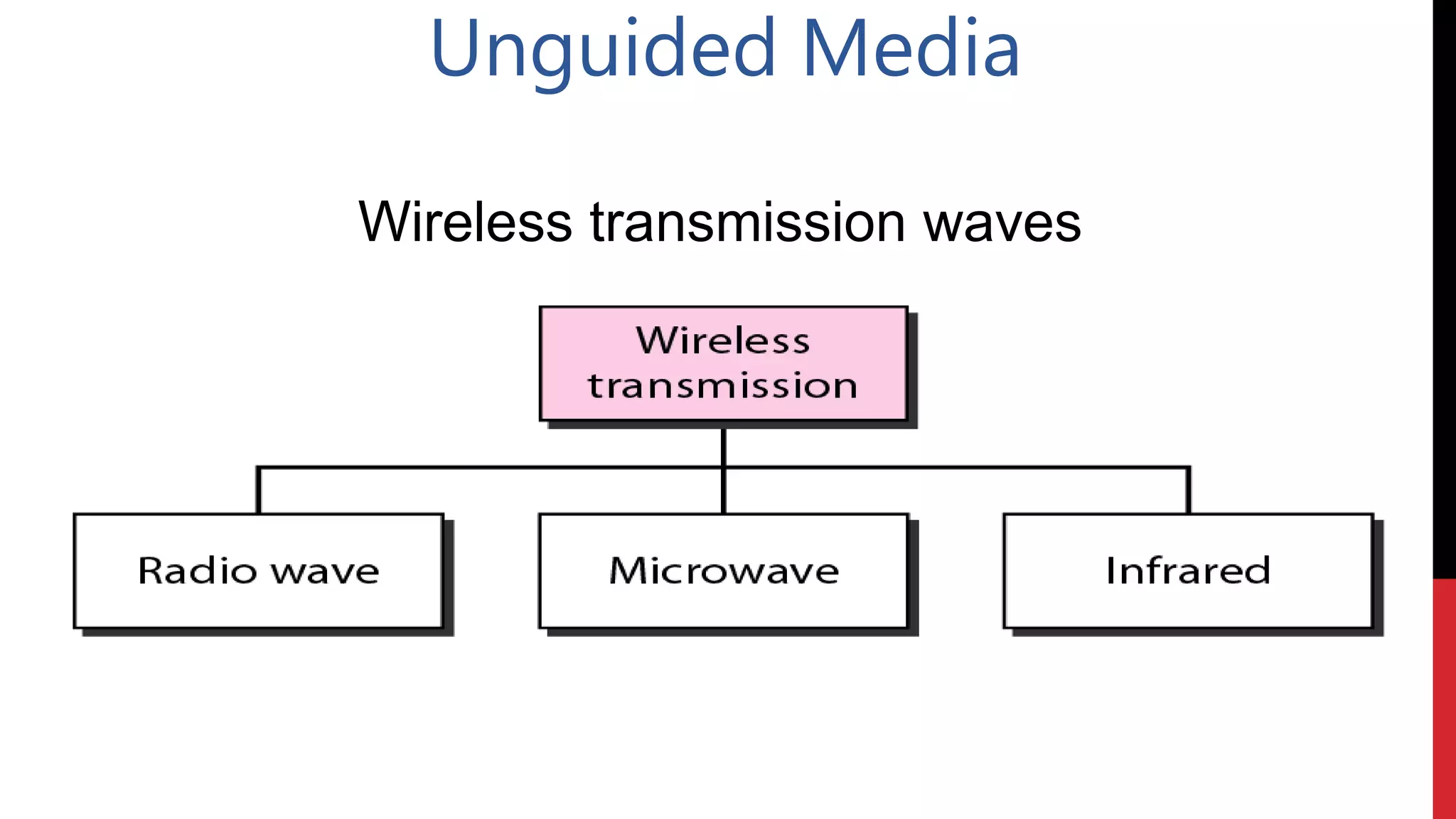
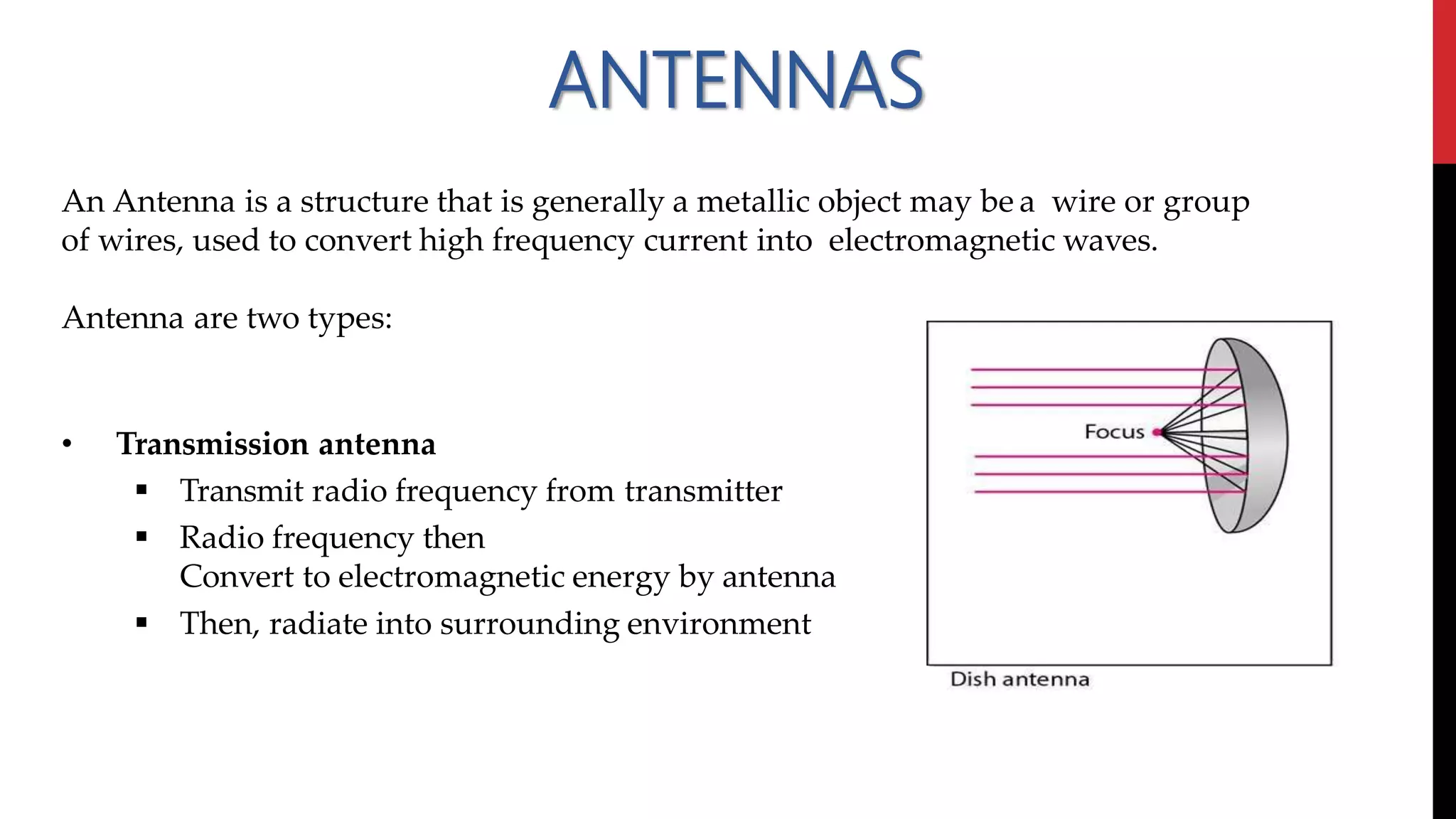
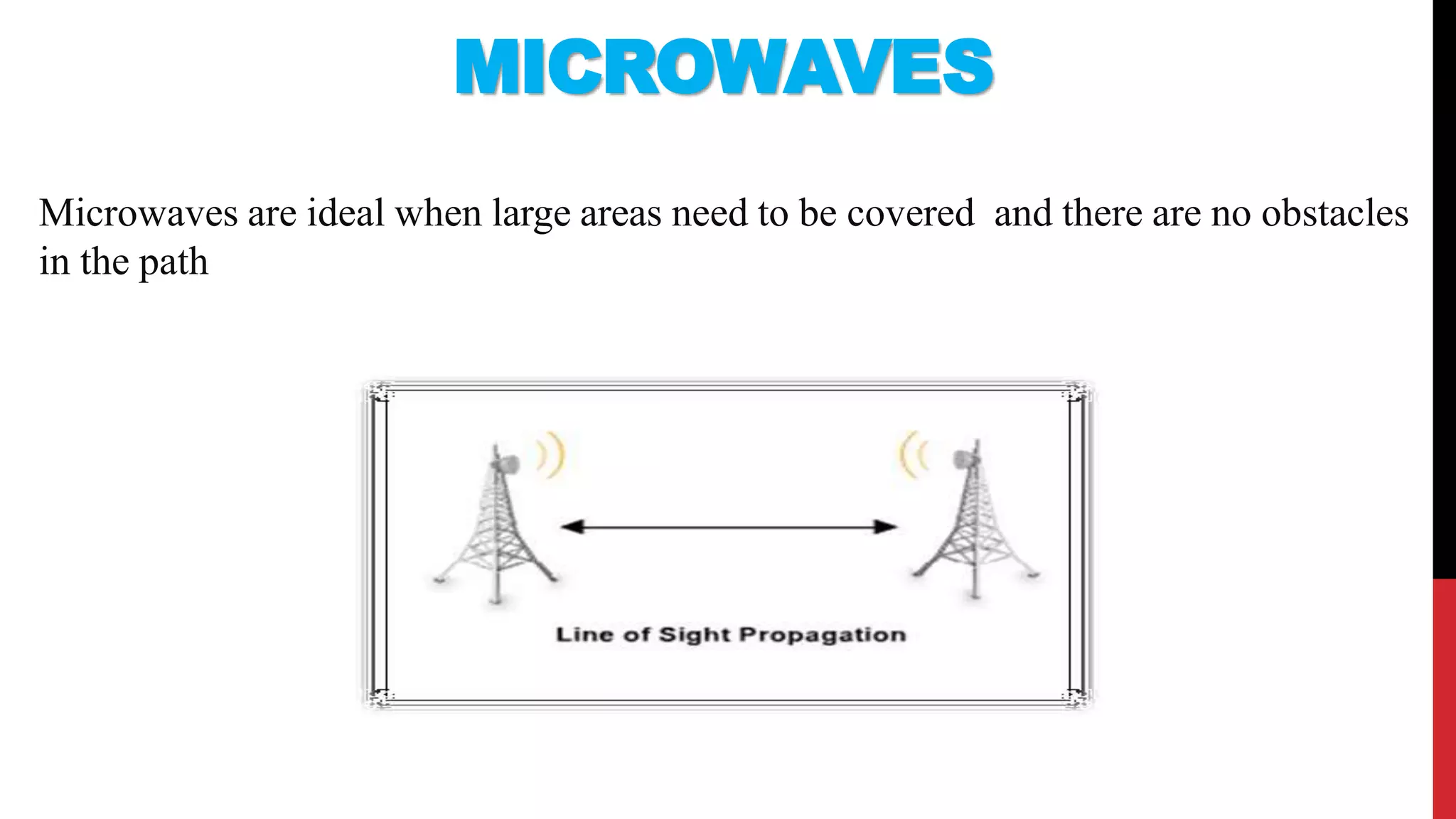
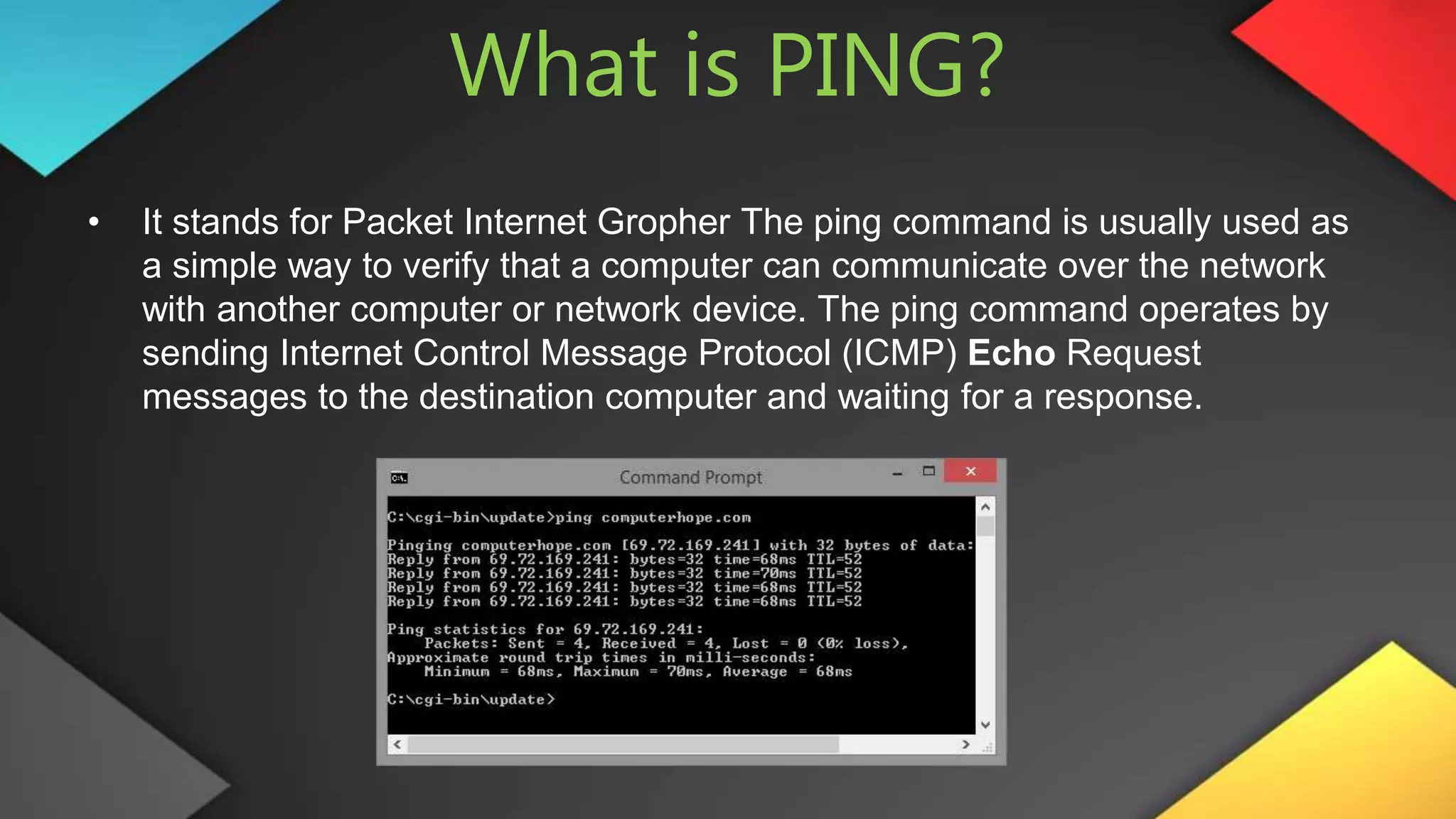
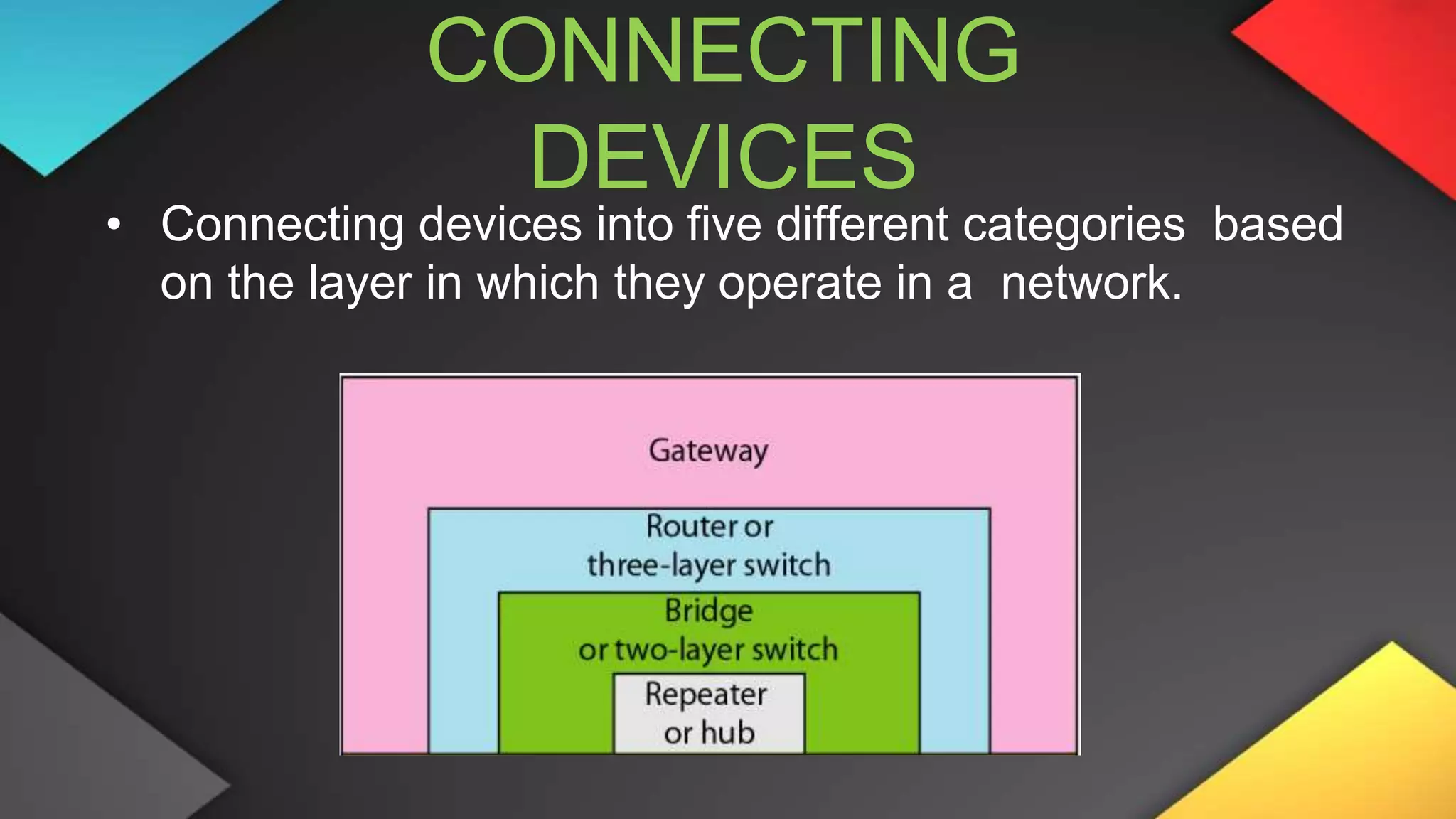
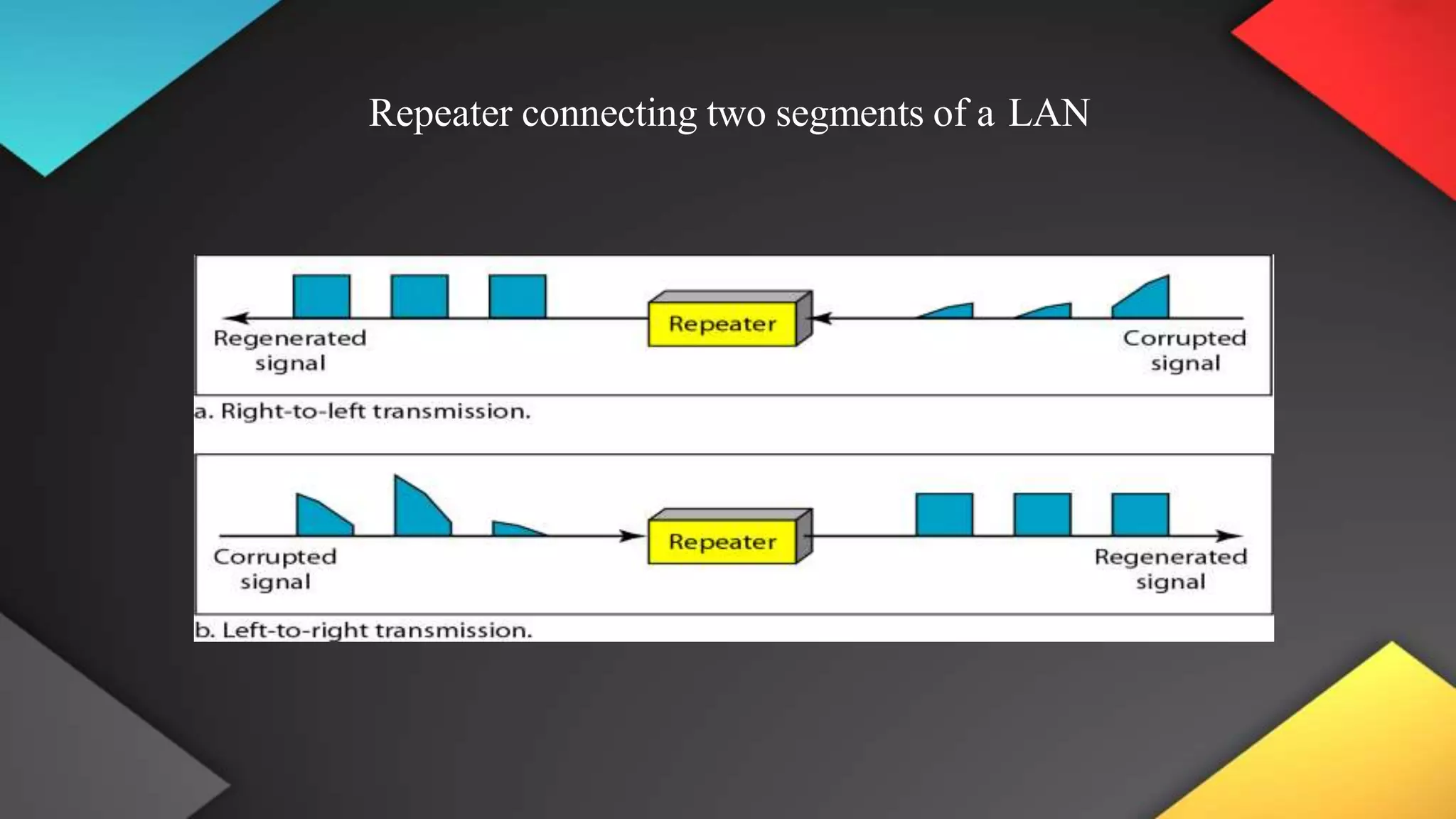
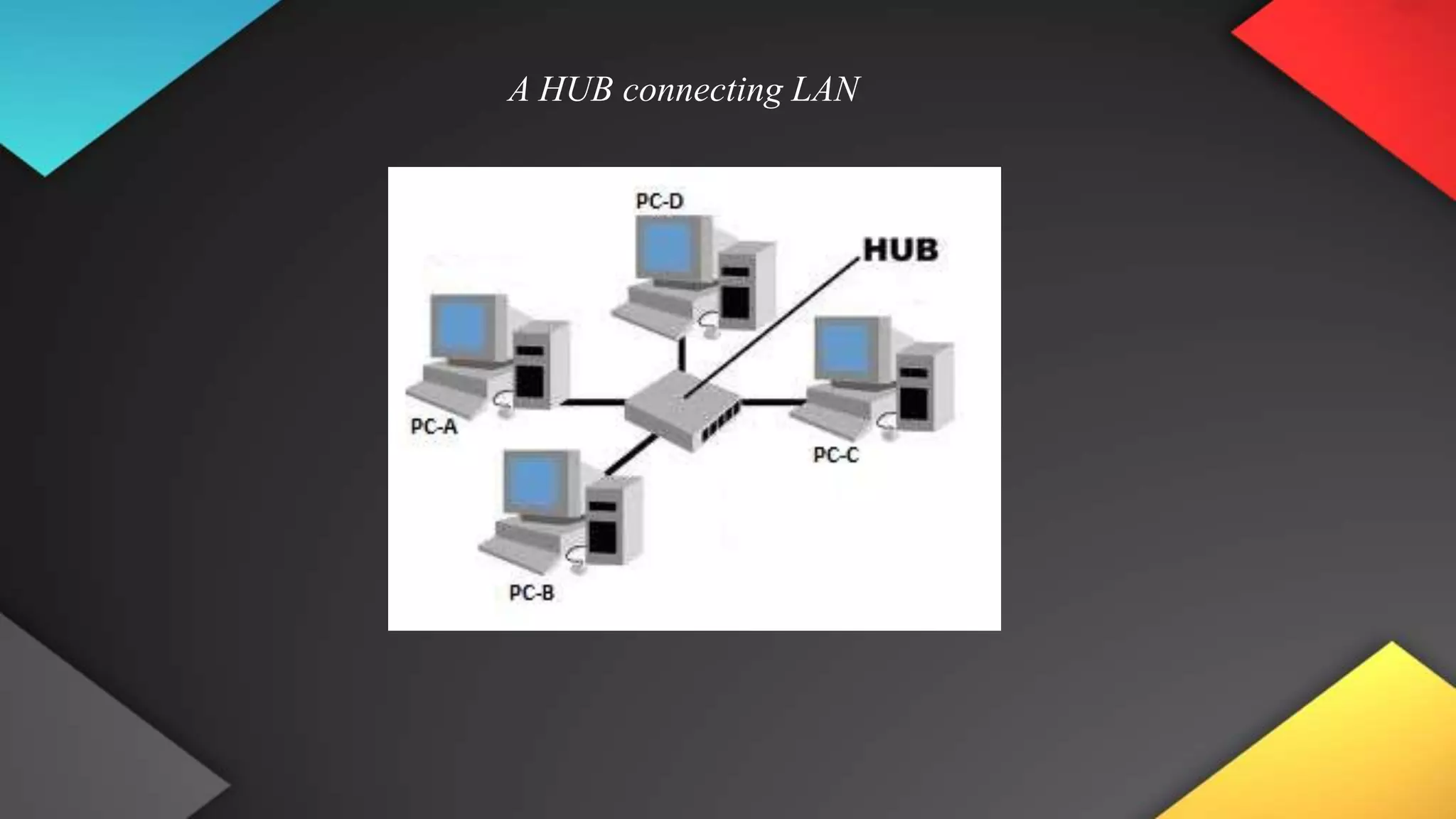
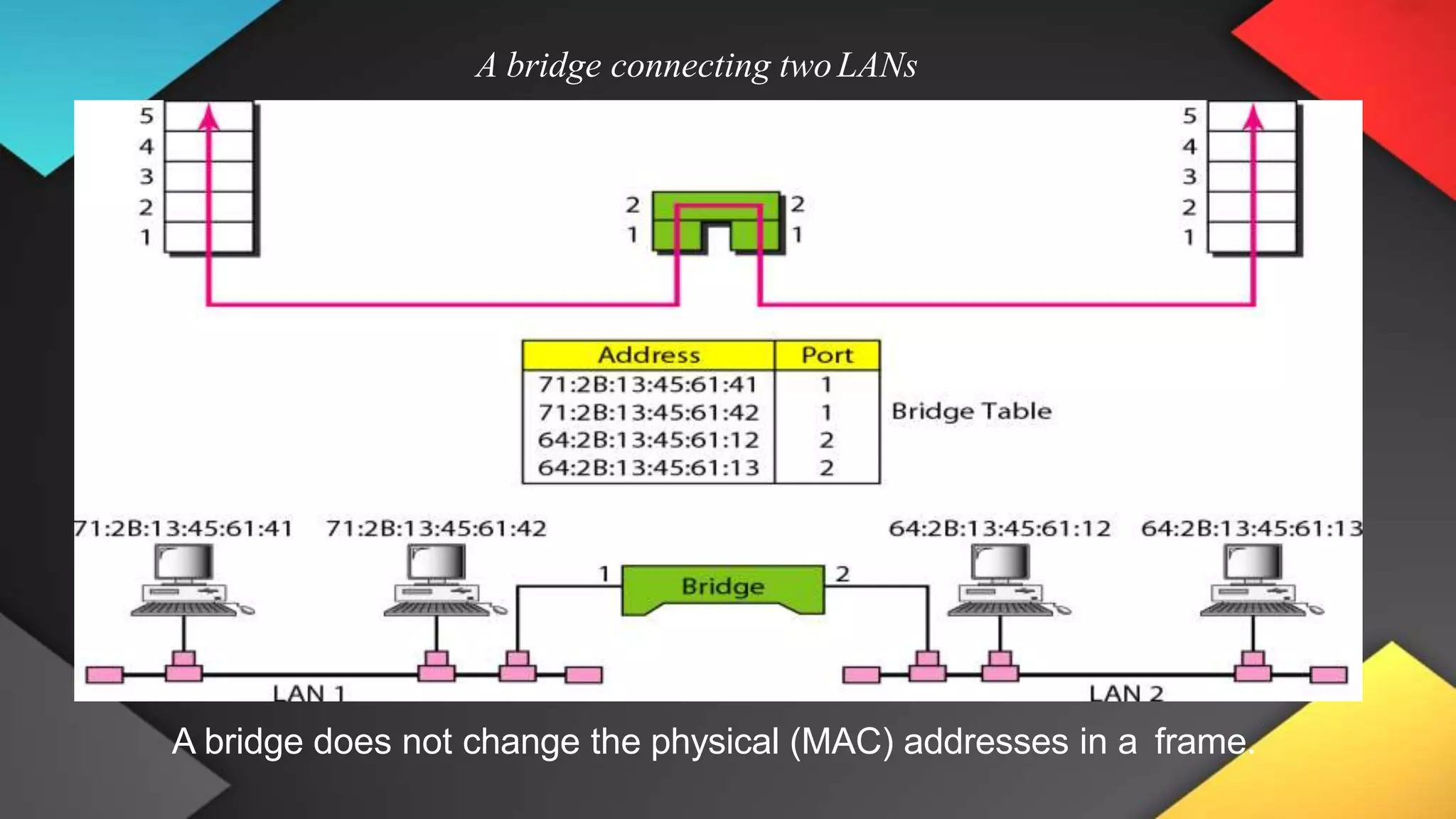
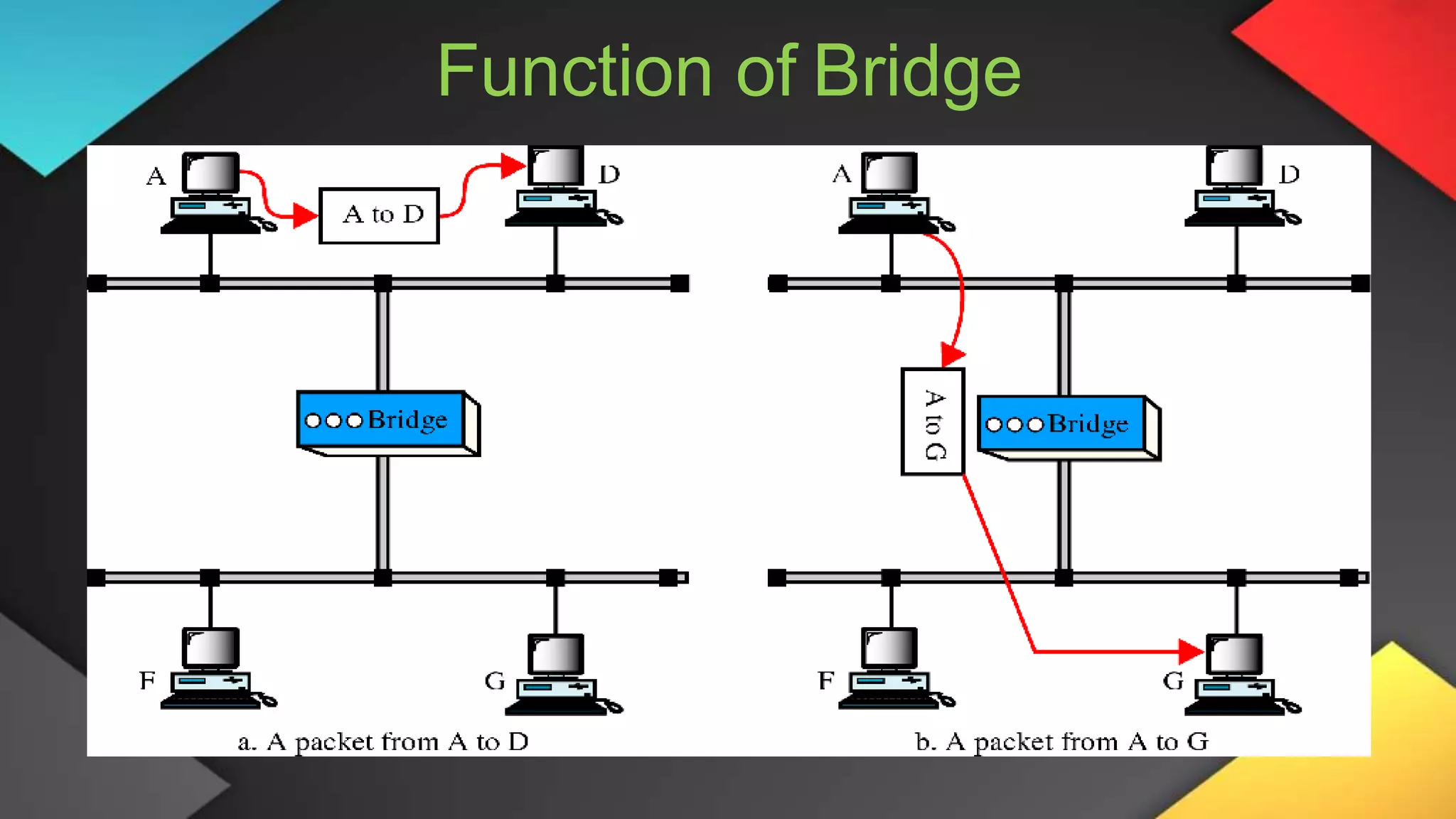
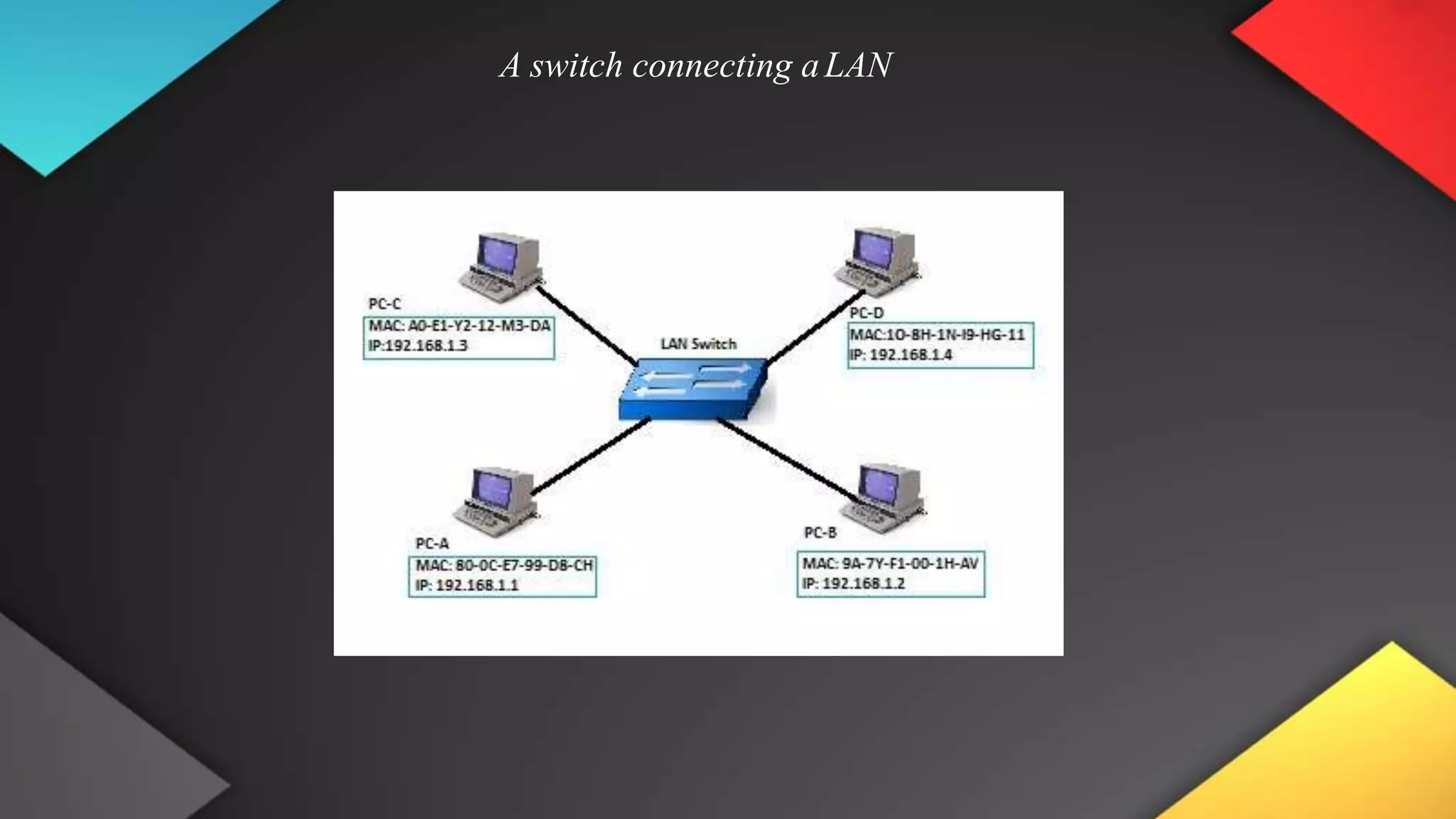
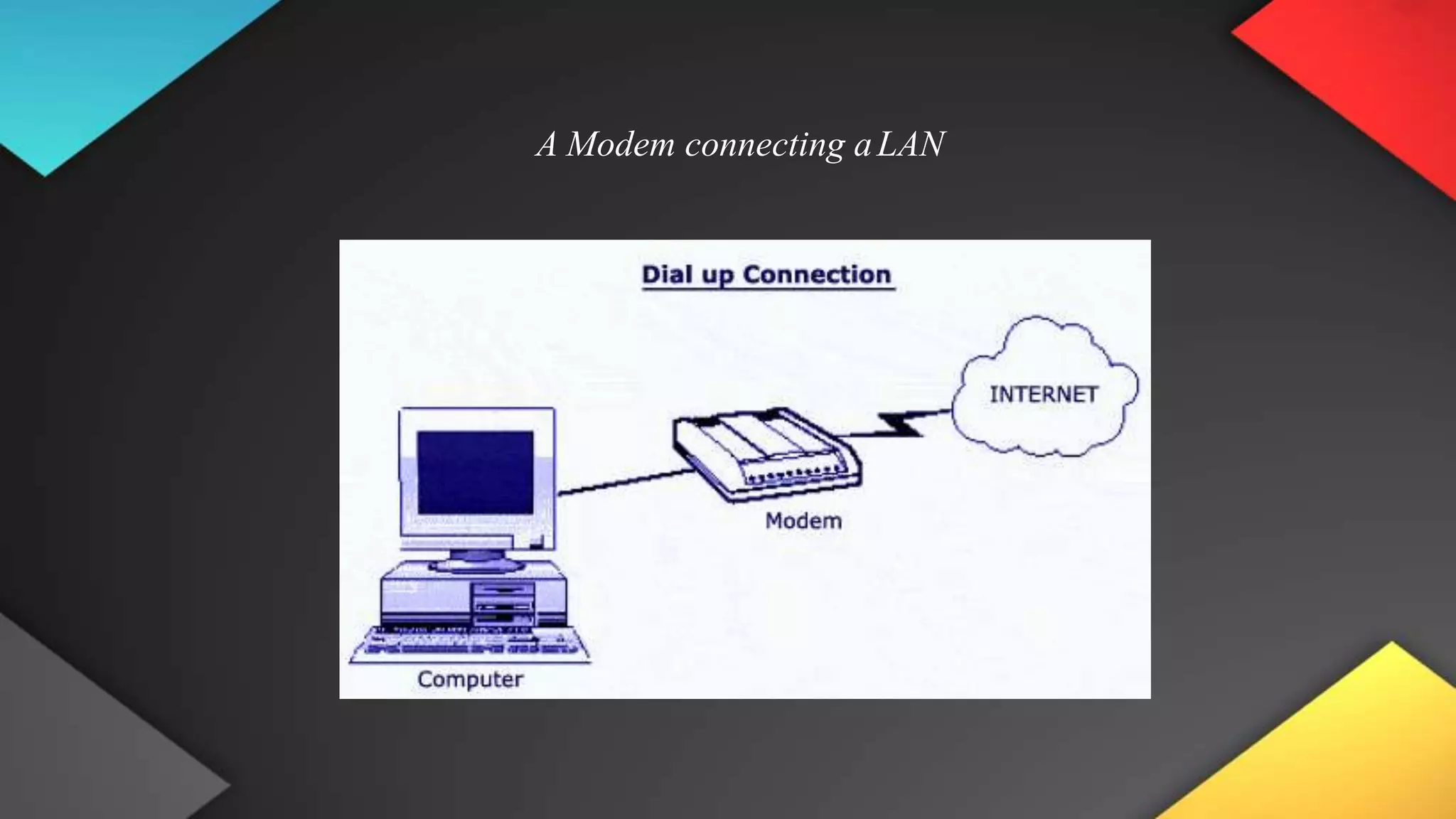
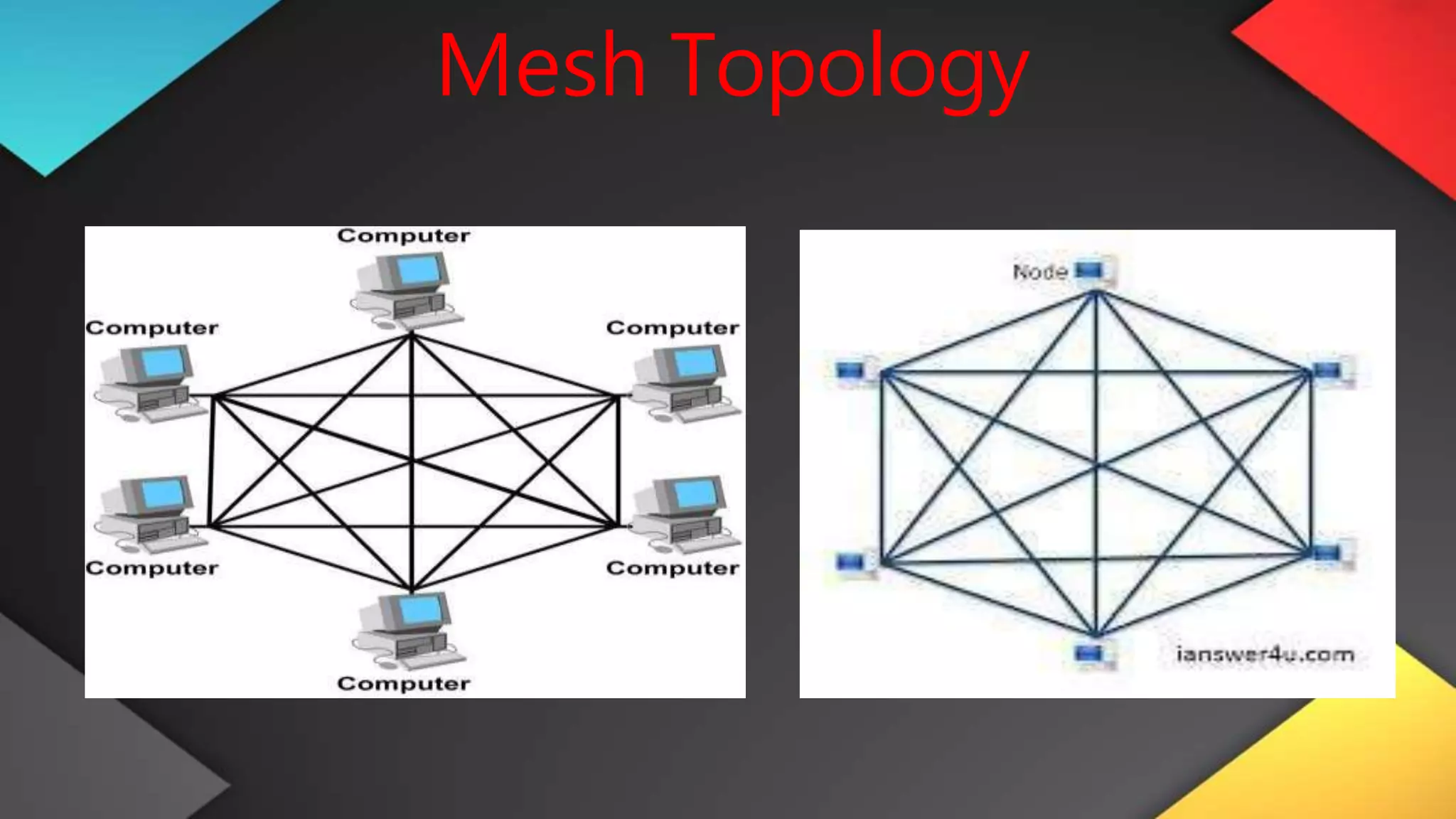
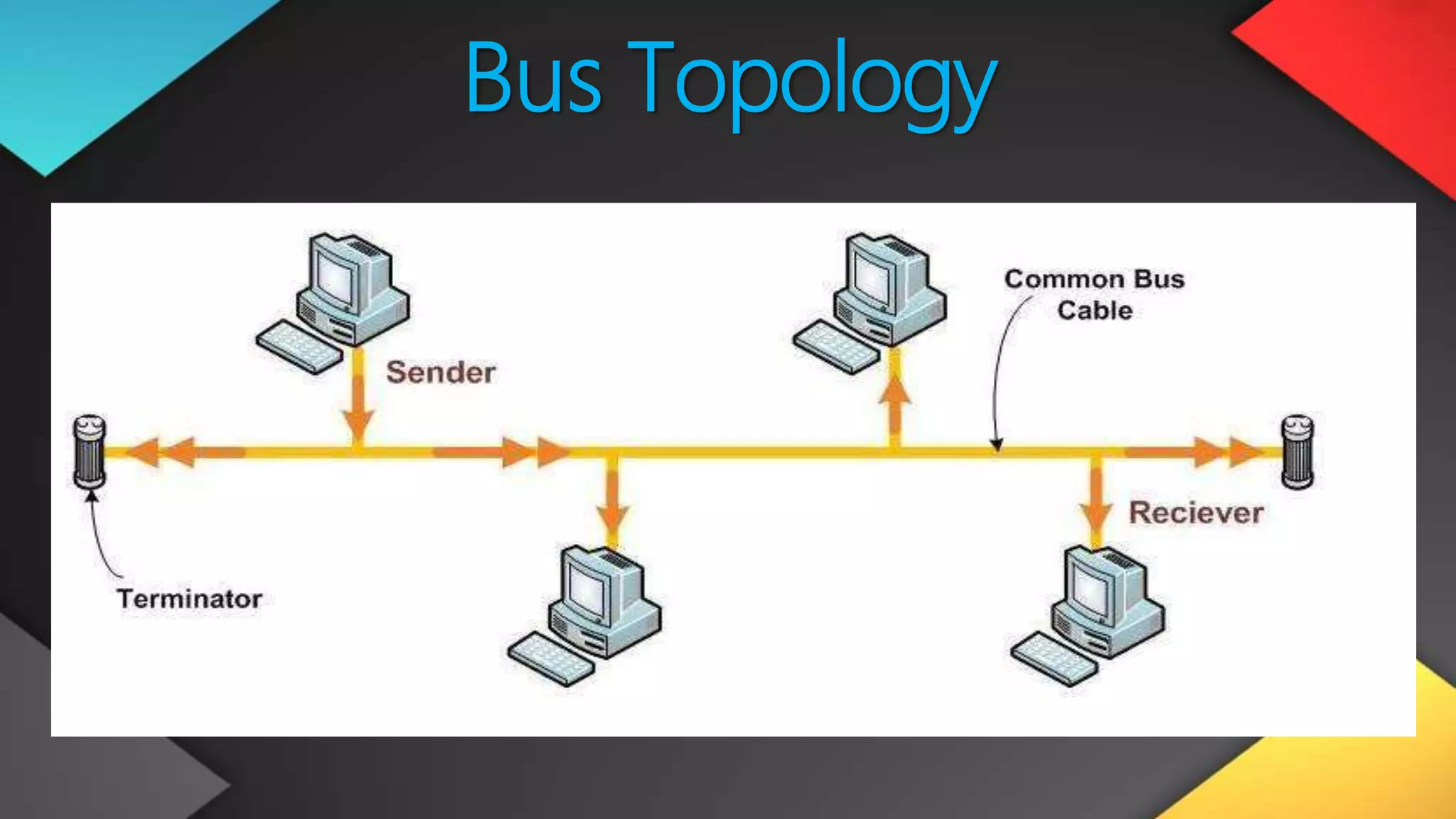
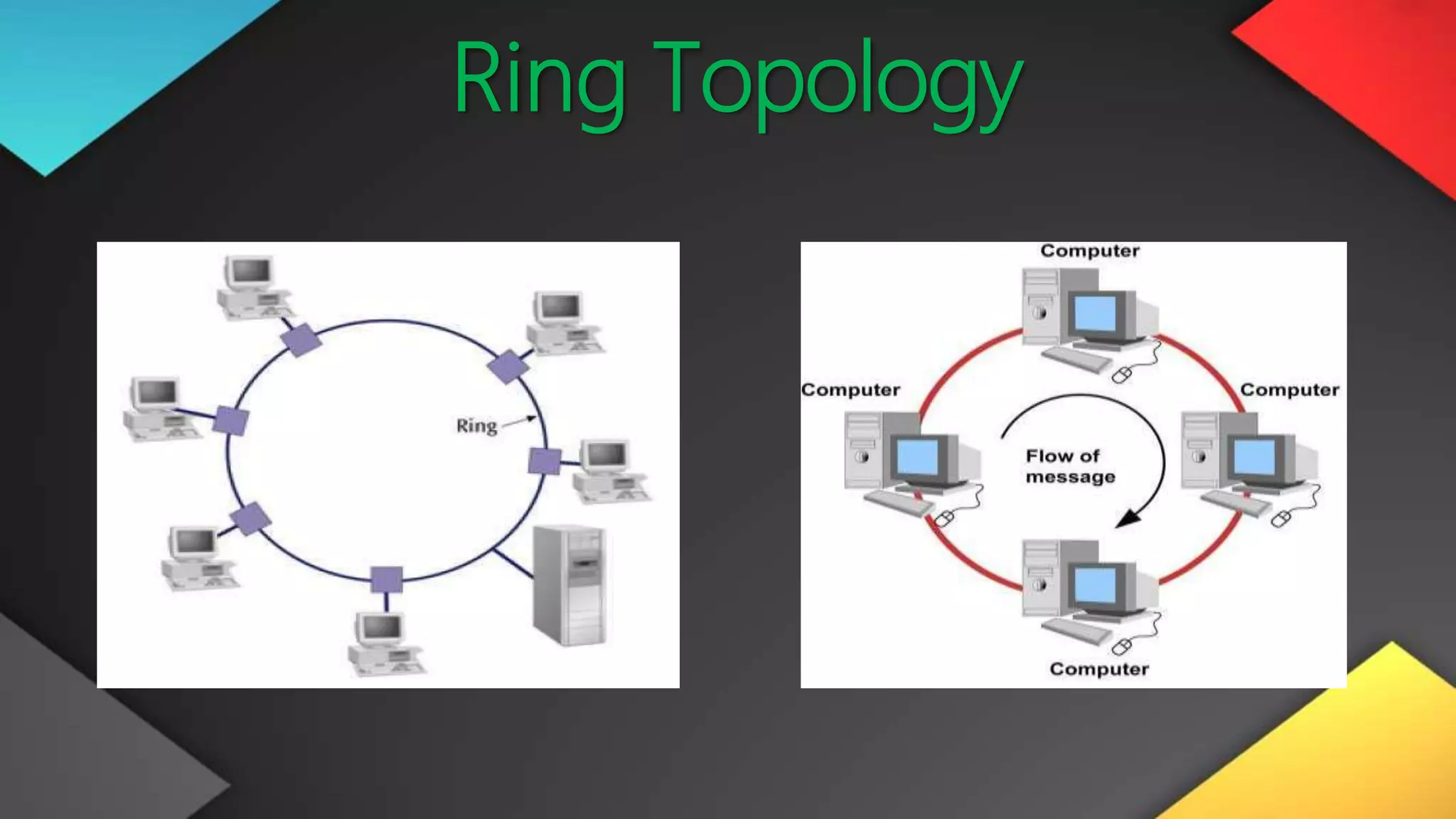
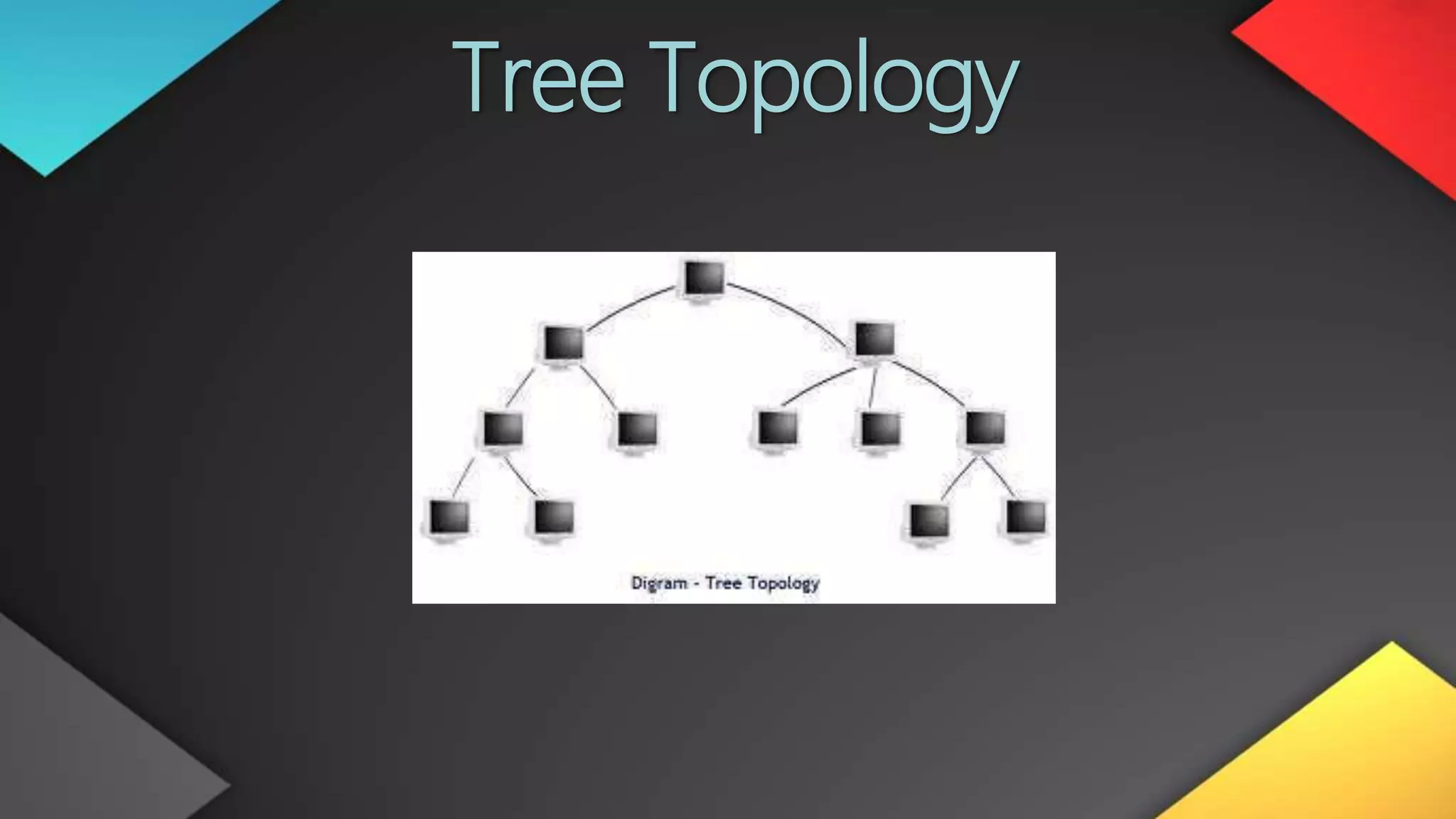
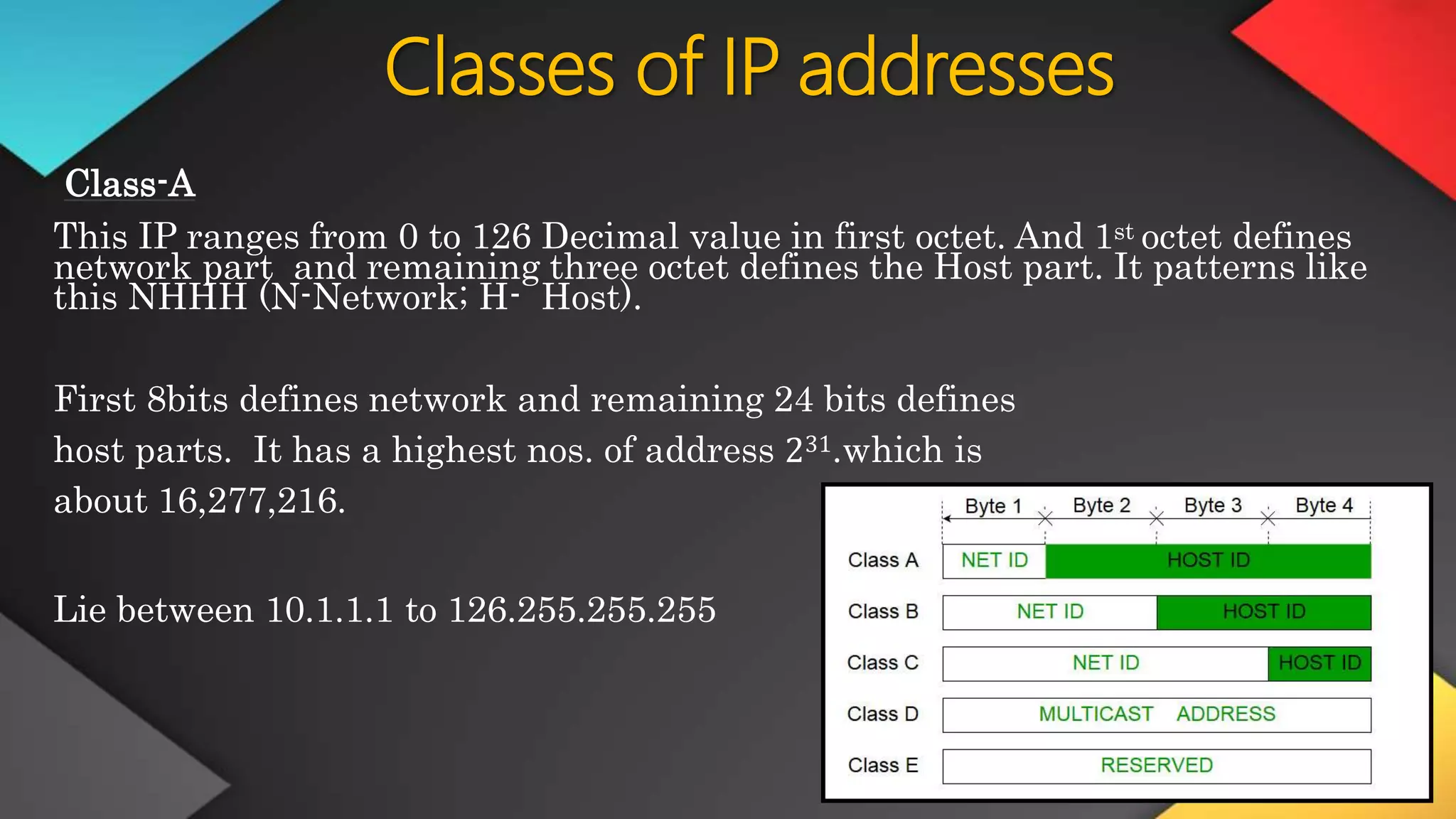
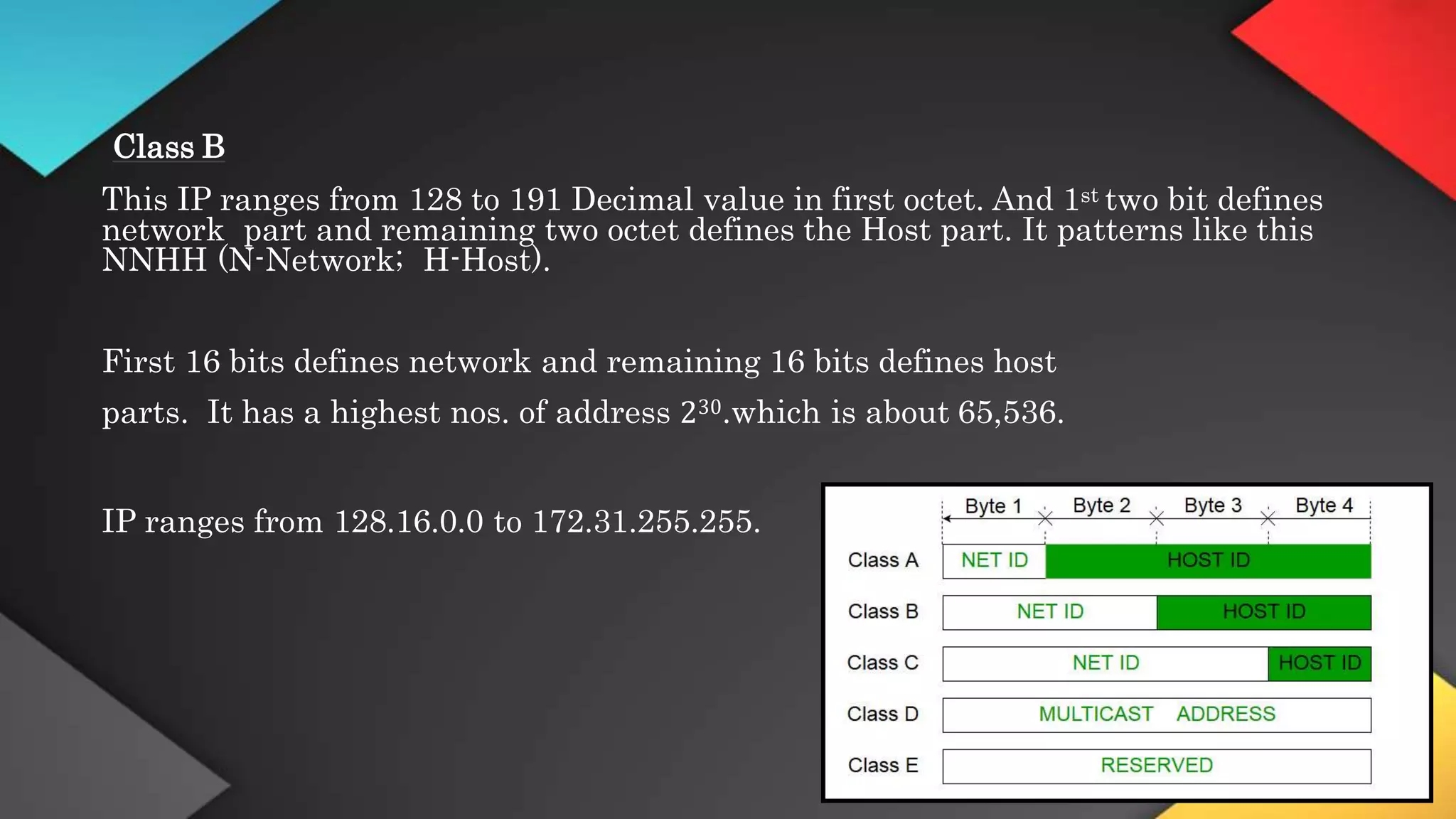
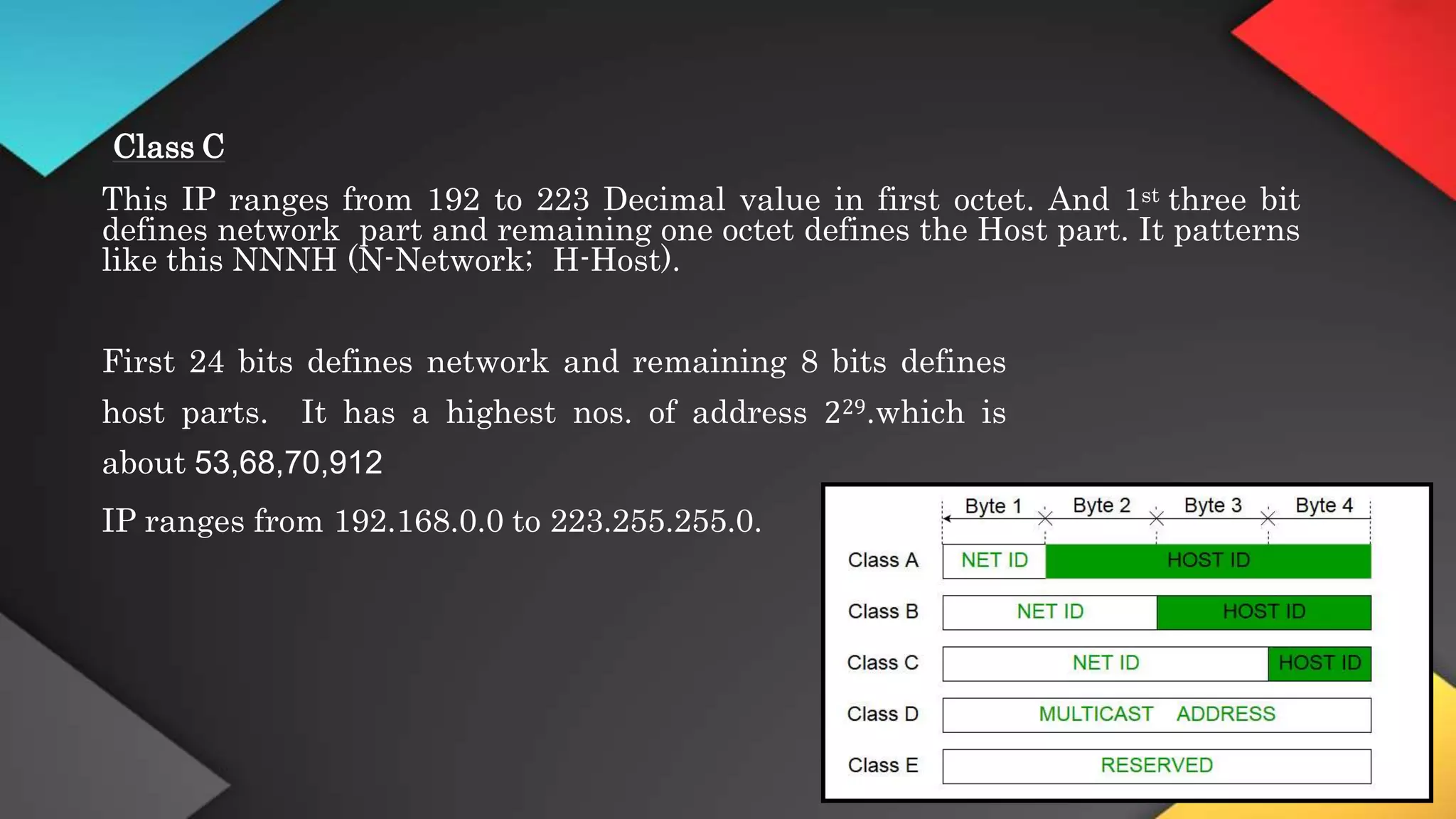
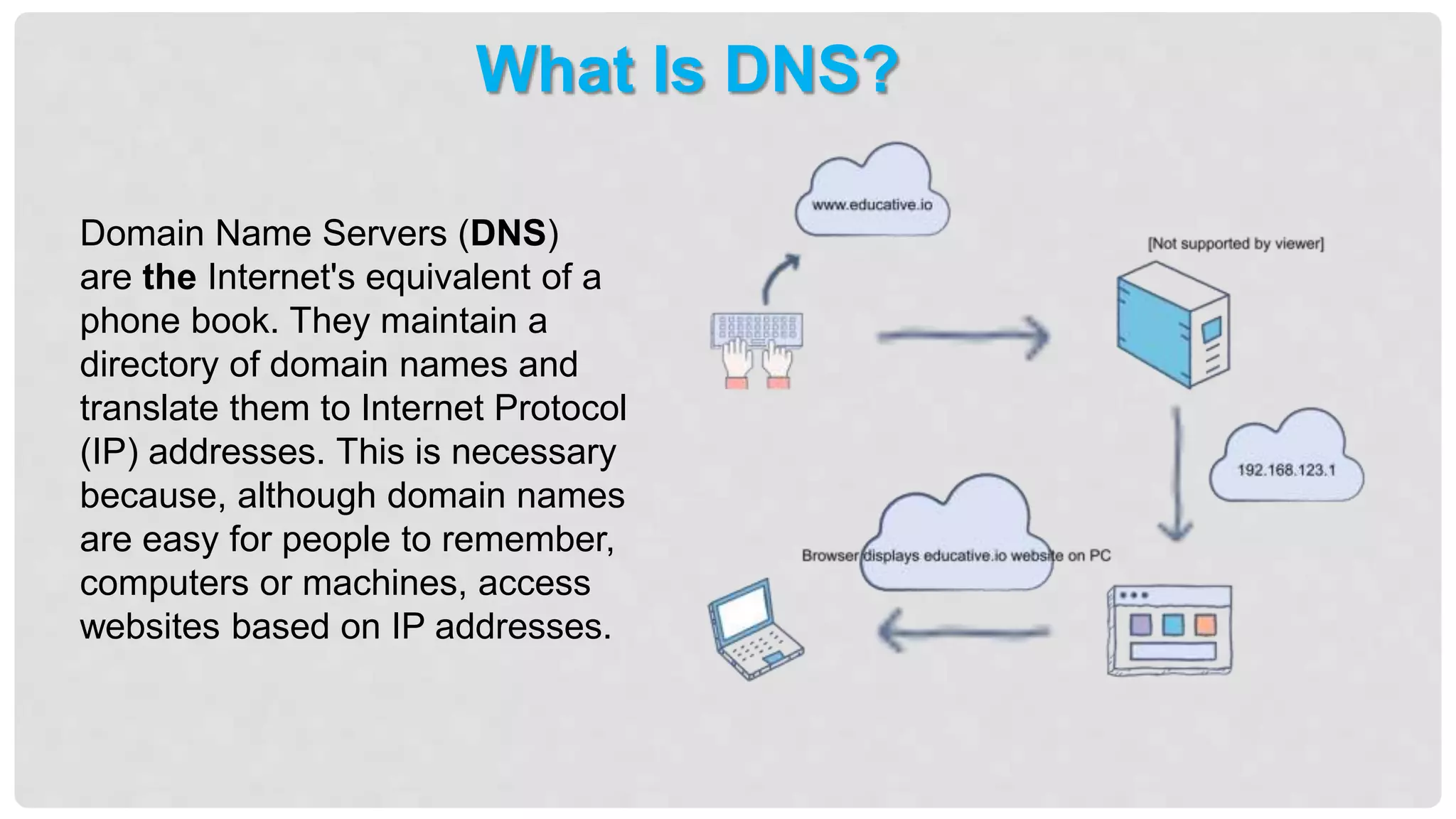
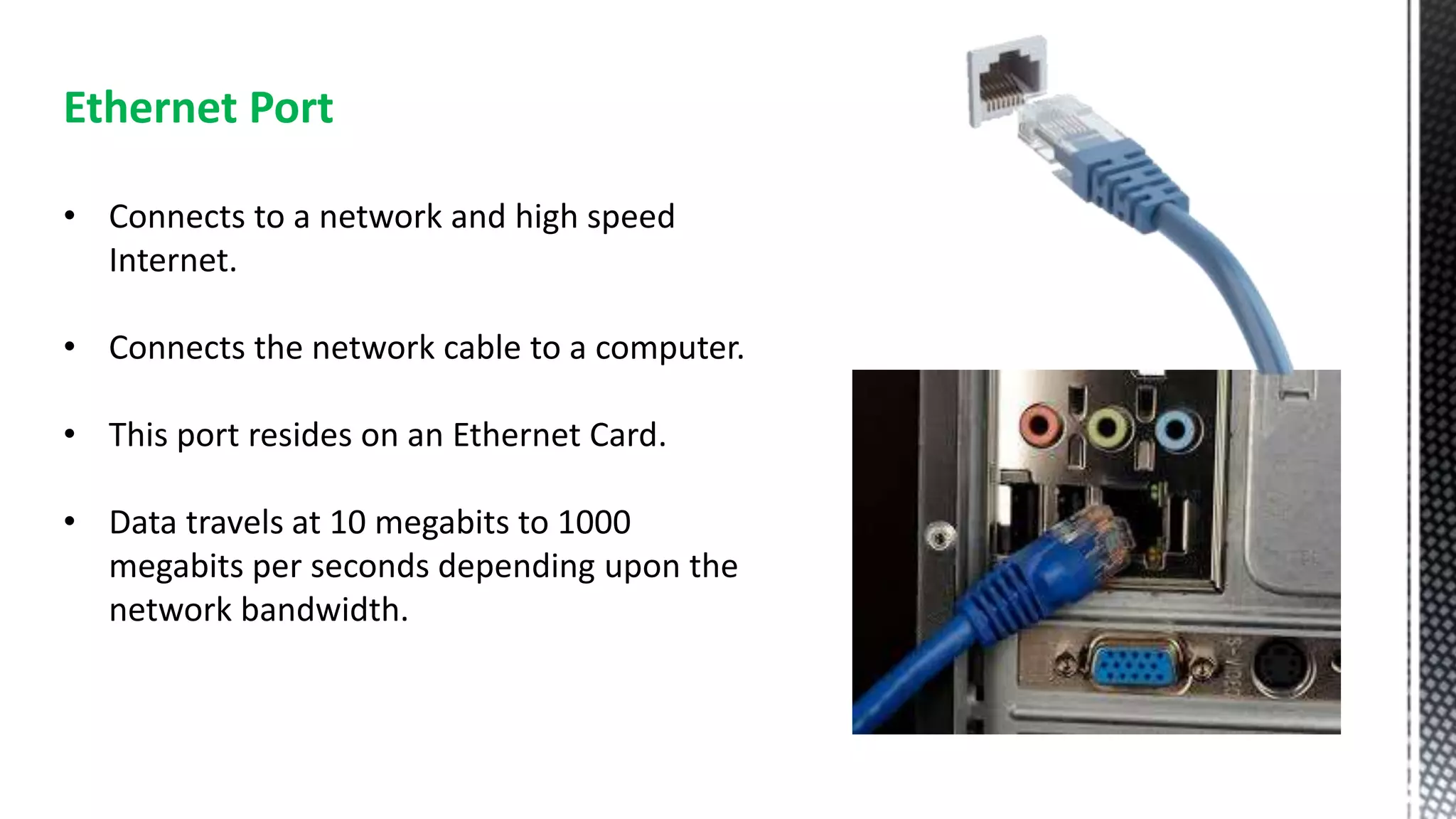
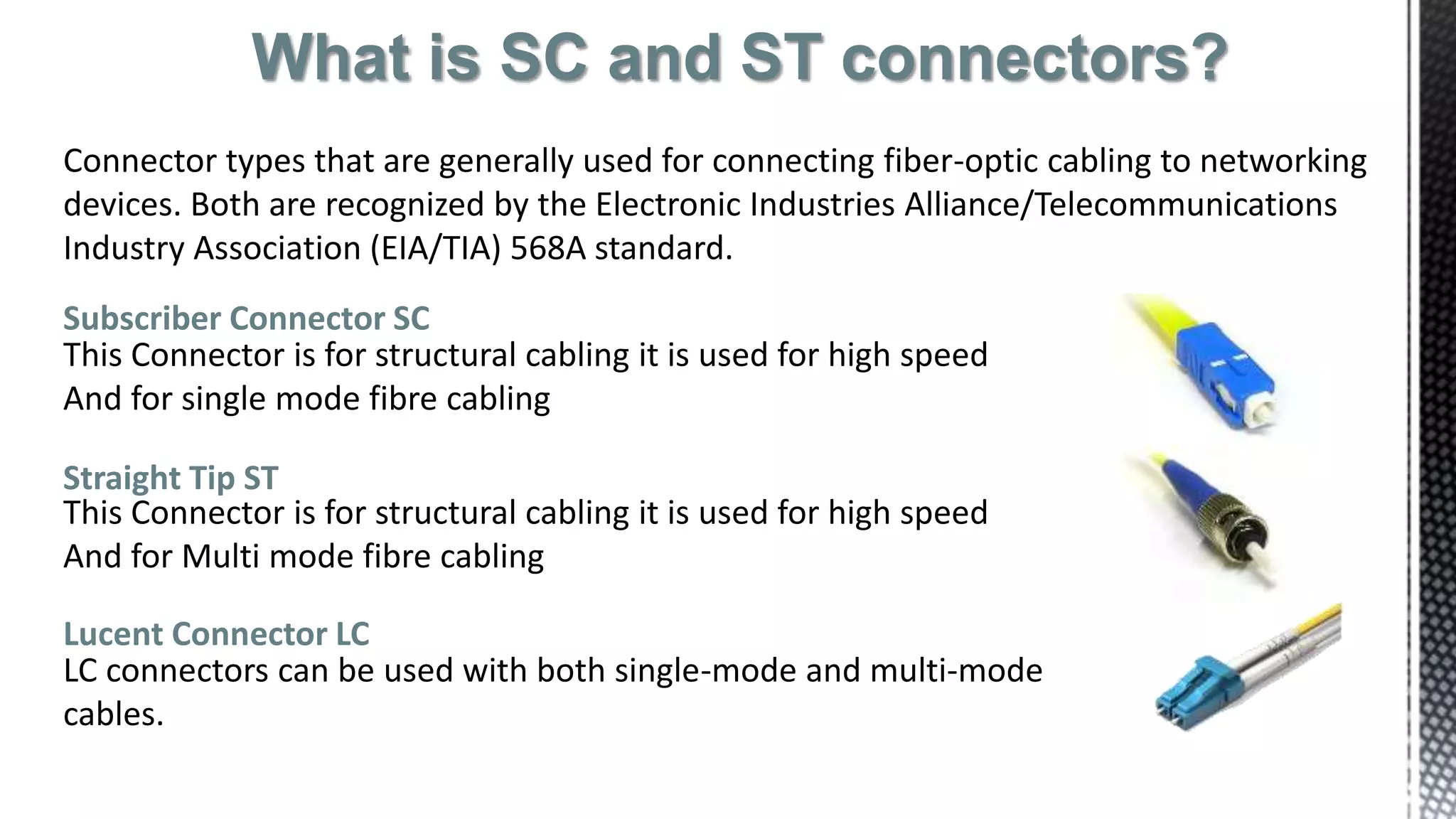
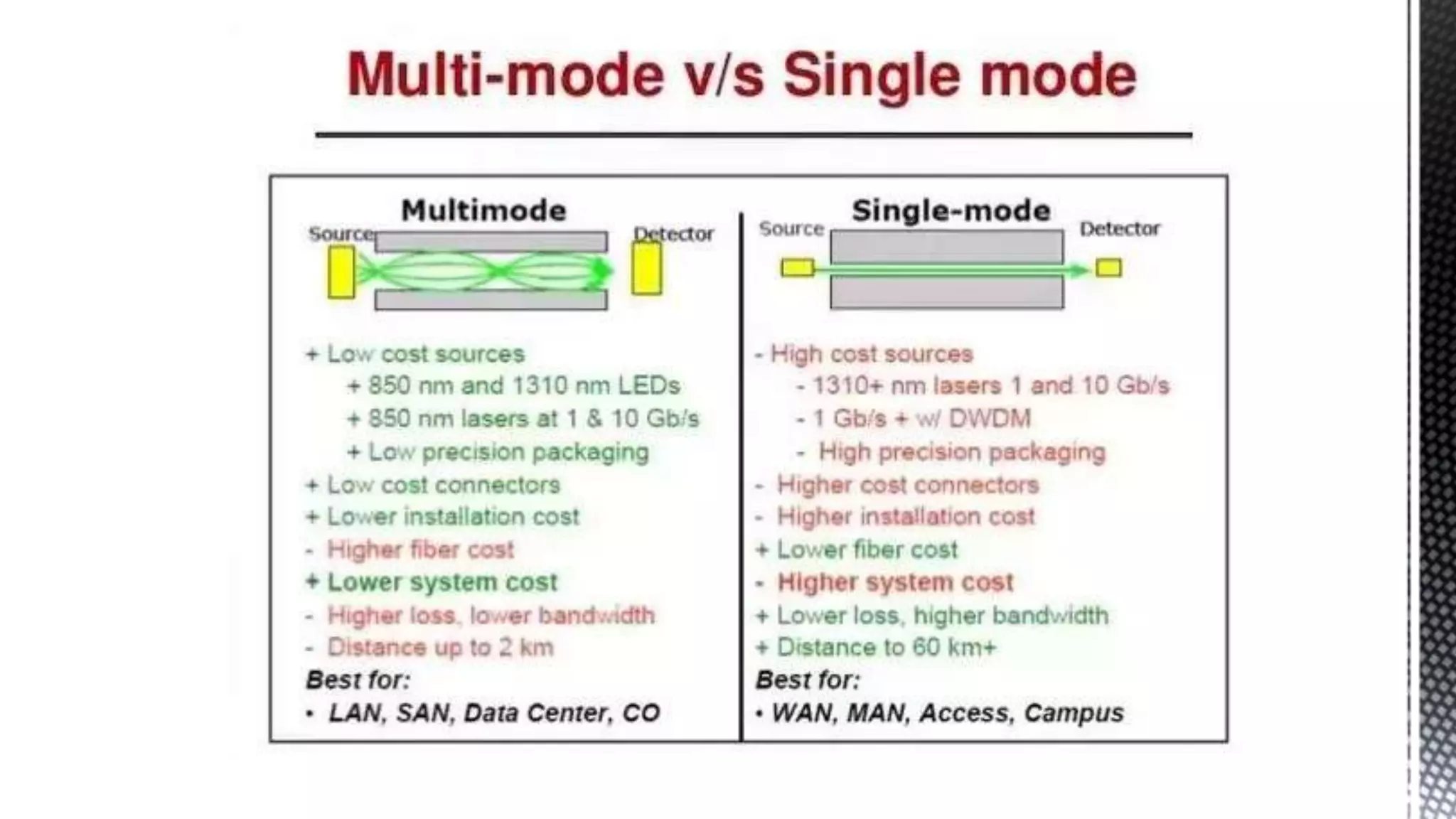
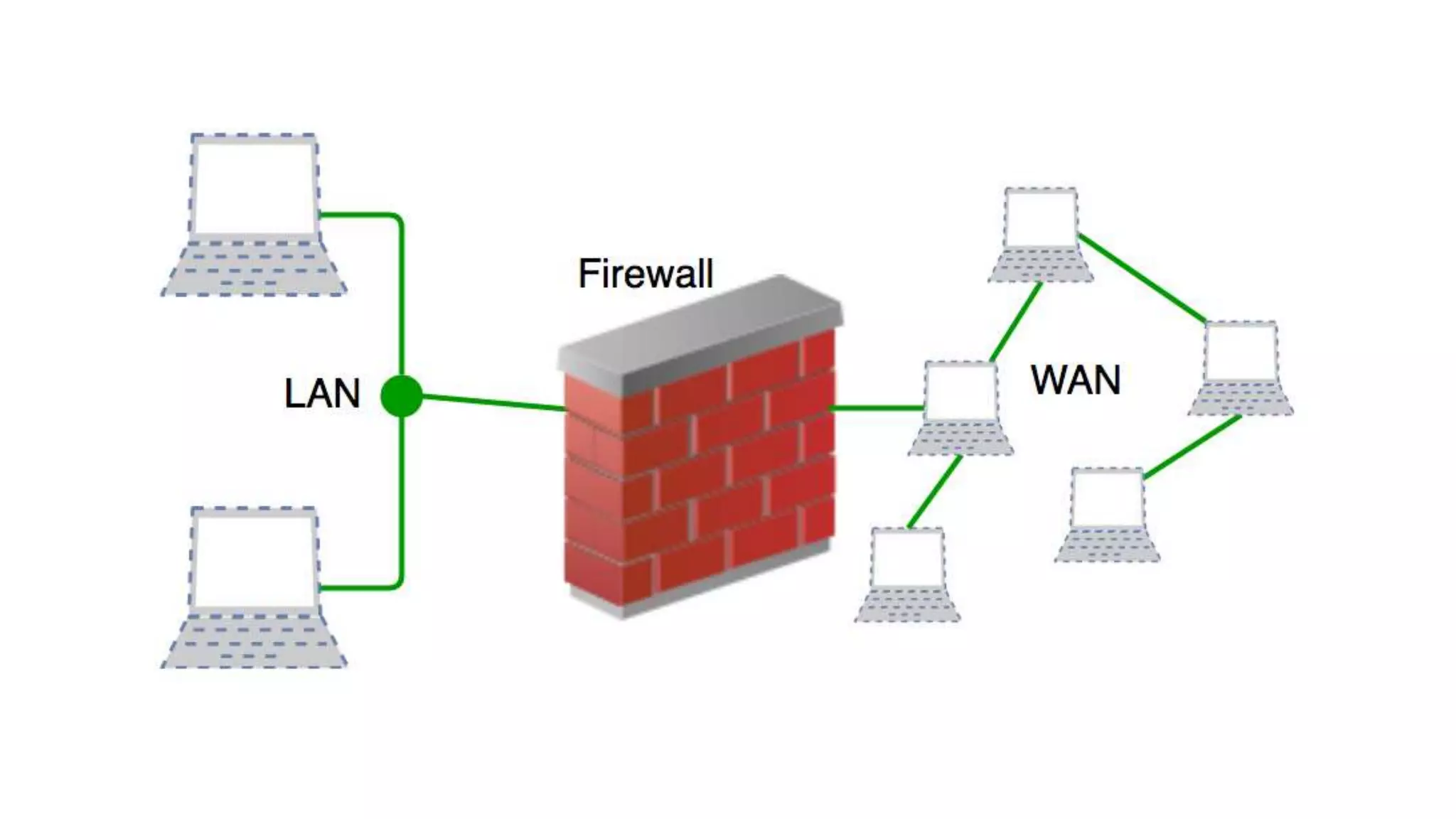
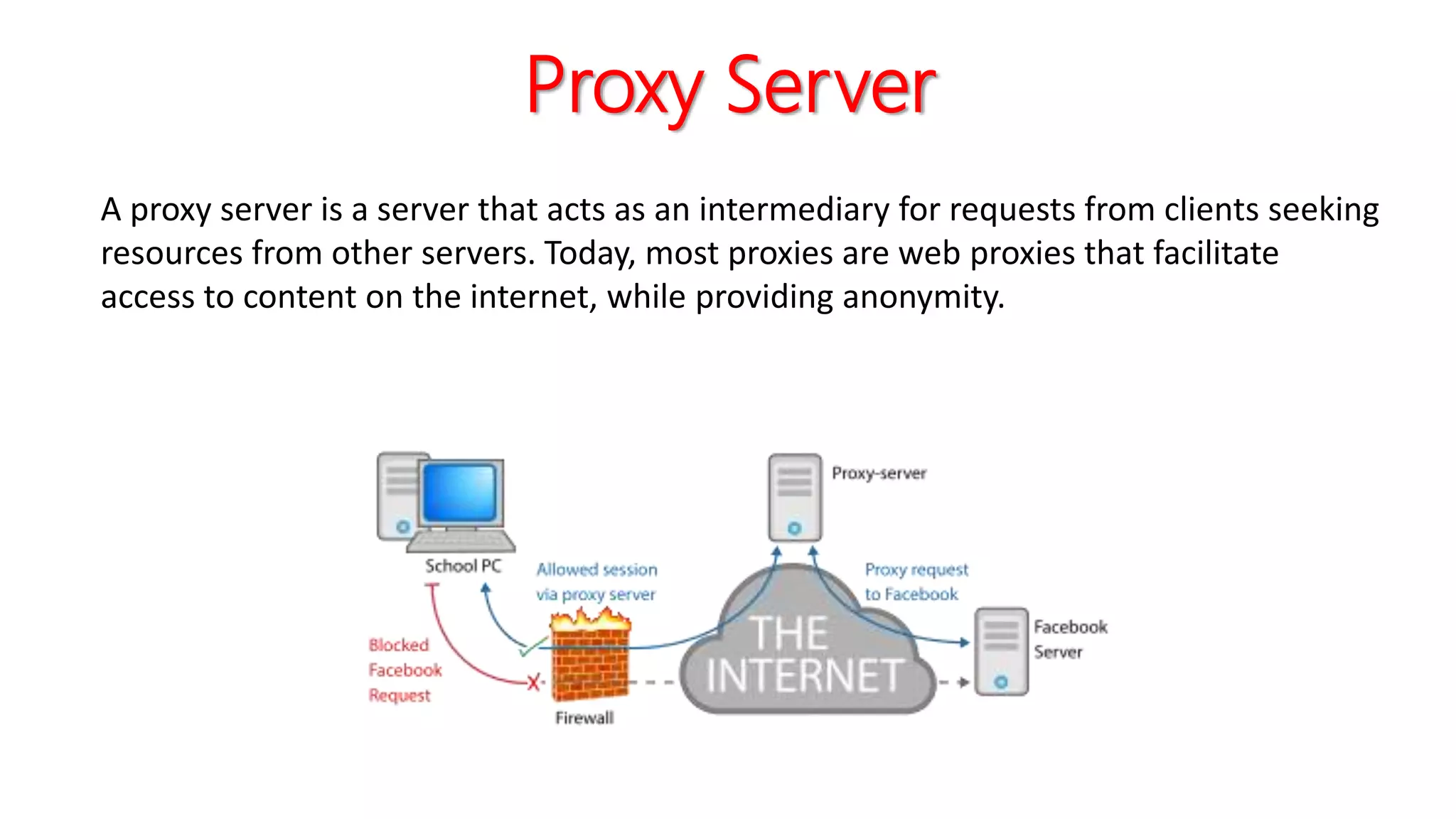
This networking course document discusses the key topics covered in a networking course including why networking is important, common network types, the OSI model, and networking devices. The document provides details on local area networks (LANs), personal area networks (PANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), wide area networks (WANs), campus area networks (CANs), and storage area networks (SANs). It also summarizes the seven layers of the OSI model and their functions.