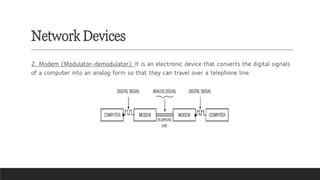
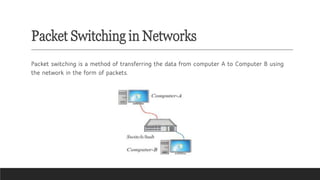
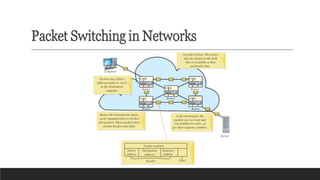
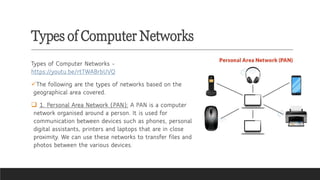
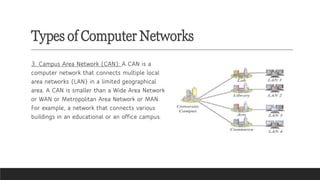
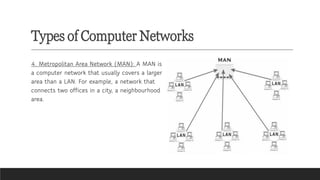
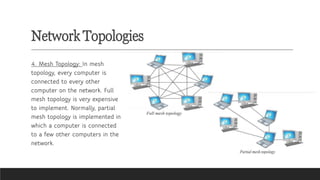
Learn the fundamentals of computer science with our video on exciting networking concepts for CBSE Grade 8 students! In this video, we'll explore the basics of networking, including protocols, devices, and architectures that will help you build a strong foundation in computer science. From understanding how data is transmitted over the internet to learning about different types of networks, our video is designed to make complex concepts easy to understand. Whether you're a student looking to ace your computer science exam or a teacher seeking to supplement your classroom teaching, this video is perfect for you. So, watch now and discover the exciting world of networking concepts for CBSE Grade 8 computer science!


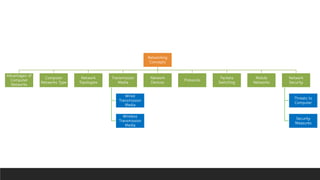








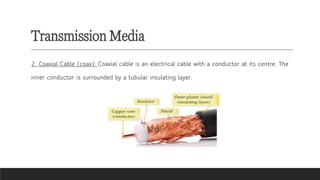


![Transmission Media
4. Bluetooth technology: It is used for exchanging data over short distances using radio waves.
This technology uses low power, has a short range [30 feet (approx.)] and medium
transmission speed.
5. WiFi technology: WiFi technology also makes use of radio waves to transmit and receive data.
This technology requires more energy but enables the signal to go farther (300 feet approx.)
with a faster rate of transmission.
6. WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access): Its technology is similar to WiFi,
but it operates at higher speeds and can cover greater distances and greater number of users
as compared to WiFi.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkingconcepts-mindmap-250814165250-5923762f/85/CBSE-Grade-8-Computer-Science-Ch-1-Networking-Concepts-Mind-Map-19-320.jpg)