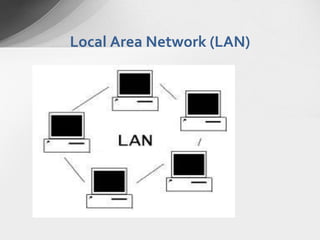
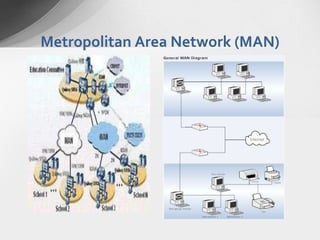
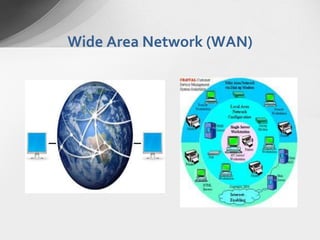
There are several types of computer networks depending on their geographical reach: local area networks (LANs) which span a small area like a home or building, metropolitan area networks (MANs) which connect devices within a city or campus, wide area networks (WANs) which connect LANs over large distances like countries or continents, and personal area networks (PANs) for connecting devices within a few meters of an individual.