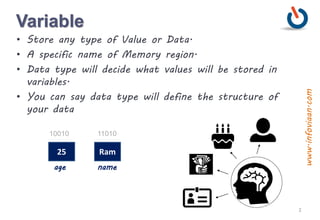
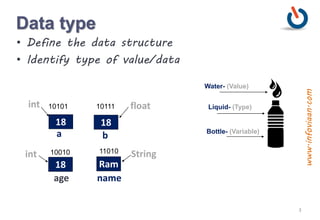
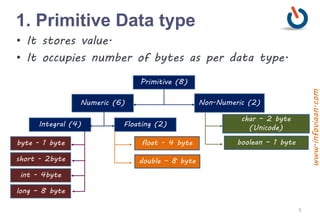
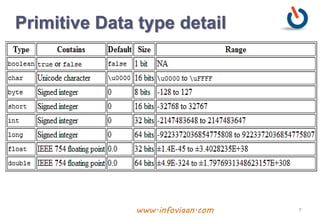
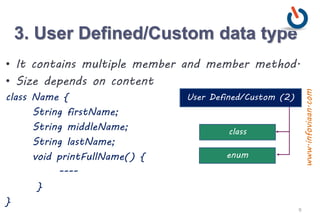
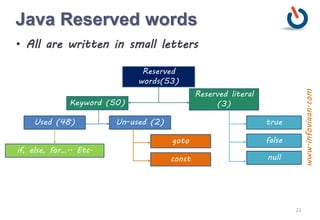
The document provides an overview of variables and data types in Java, including definitions and examples of primitive, reference, and user-defined data types. It explains the memory storage of variables, their declaration, and includes sample programs demonstrating basic operations like sum and division. Additionally, it discusses naming conventions, reserved keywords, and common Java syntax for documentation and comments.



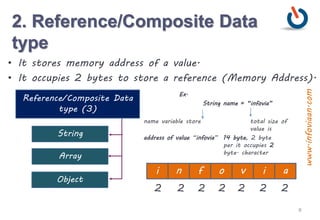
![Program - Sum of two numbers
10
public class Sum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int firstValue, secondValue, resultOfSum;
firstValue = 25;
secondValue = 15;
resultOfSum = firstValue + secondValue ;
System.out.println(“Sum Result is = ”+ resultOfSum);
}
}
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java2-variableanddatatype-200312084553/85/Variables-and-Data-Types-10-320.jpg)

![Program - Division
13
public class Division {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float a, b, c;
a = 25.678f;
b = 15;
c = a / b;
System.out.println(“Division Result is = ”+ c);
}
}
/* Output
Division Result is = 1.7118666
if use double data type then result is =
1.7118666330973307
*/
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java2-variableanddatatype-200312084553/85/Variables-and-Data-Types-13-320.jpg)
![Program - DataTypeExercise
14
public class DataTypeExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i =50;
float f = 25.5f;
double d = 89.789;
boolean b = true;
System.out.print(“ ”+ i + b + f + d)
;
}
}
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java2-variableanddatatype-200312084553/85/Variables-and-Data-Types-14-320.jpg)

![Program –Constant Area of
Circle
16
public class AreaOfCircle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final double PI = 3.1415;
double area;
float radius = 3.5f ;
area = PI* radius * radius ;
System.out.println(“Area of Circle = ”+
area);
}
}
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java2-variableanddatatype-200312084553/85/Variables-and-Data-Types-16-320.jpg)

![Identifier
• A name in java program is identifier, which can be
used for identification purpose.
• It can be method name, variable name, class name or
label name.
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int x = 25;
}
}
18
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java2-variableanddatatype-200312084553/85/Variables-and-Data-Types-18-320.jpg)

![Naming convention rules
class Test{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int number = 10;
int Number = 20; //ok, but use with class (first
character of class name is capital)
int NUMBER =30; //ok, but use with Constant
declaration(All Caps)
int String =78; // ok, no error, but - wrong it is
predefine class
int Runnable = 78; // ok, no error, but - wrong predefine
Interface
} // we can differentiate
with case
} //case sensitive programming
language 20
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java2-variableanddatatype-200312084553/85/Variables-and-Data-Types-20-320.jpg)

![Literals
int x = 20;
[Data typevariable constant | literal ]
int x= 10; //decimal value
int x= 010; //octal value -> 8 (octal to
decimal)
int x= 0X10; //hexadecimal value-(base -16)
int x = 10; //ok
int x = 0788; // no CE
int x = 0777 // ok
int x = 0XFace; // ok
int x= 0XBeef; //ok
int x = 0XBeer; //no
23
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java2-variableanddatatype-200312084553/85/Variables-and-Data-Types-23-320.jpg)


