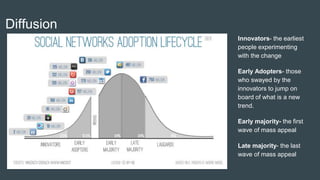
This document discusses theories related to computer-mediated communication (CMC). It defines CMC as human communication via computers using text, images, audio, and video. Early social networking sites from the 1980s and 1990s are mentioned, as well as how CMC allows for identity fabrication but also truth. Theories discussed include diffusion of innovation theory, uses and gratifications theory, and concepts of online culture and power. Characteristics of social networking sites and their relationship to communication theory are also summarized.