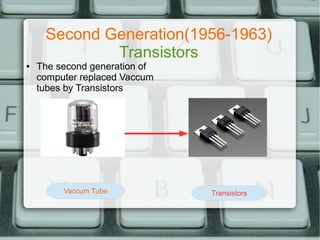
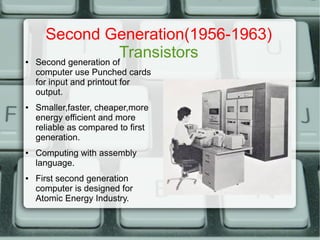
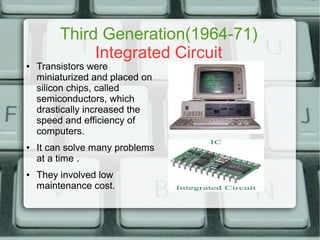
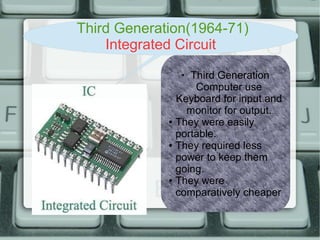
The document discusses the history of computer generations from the 1940s to present. It explains that the first generation used vacuum tubes, the second used transistors, the third used integrated circuits, the fourth used microprocessors, and the fifth generation focuses on artificial intelligence. It also provides details about different types of computer mice like wireless, optical, trackball, and mechanical mice. Finally, it defines some key computer hardware components like motherboards, switched mode power supplies, and random access memory.