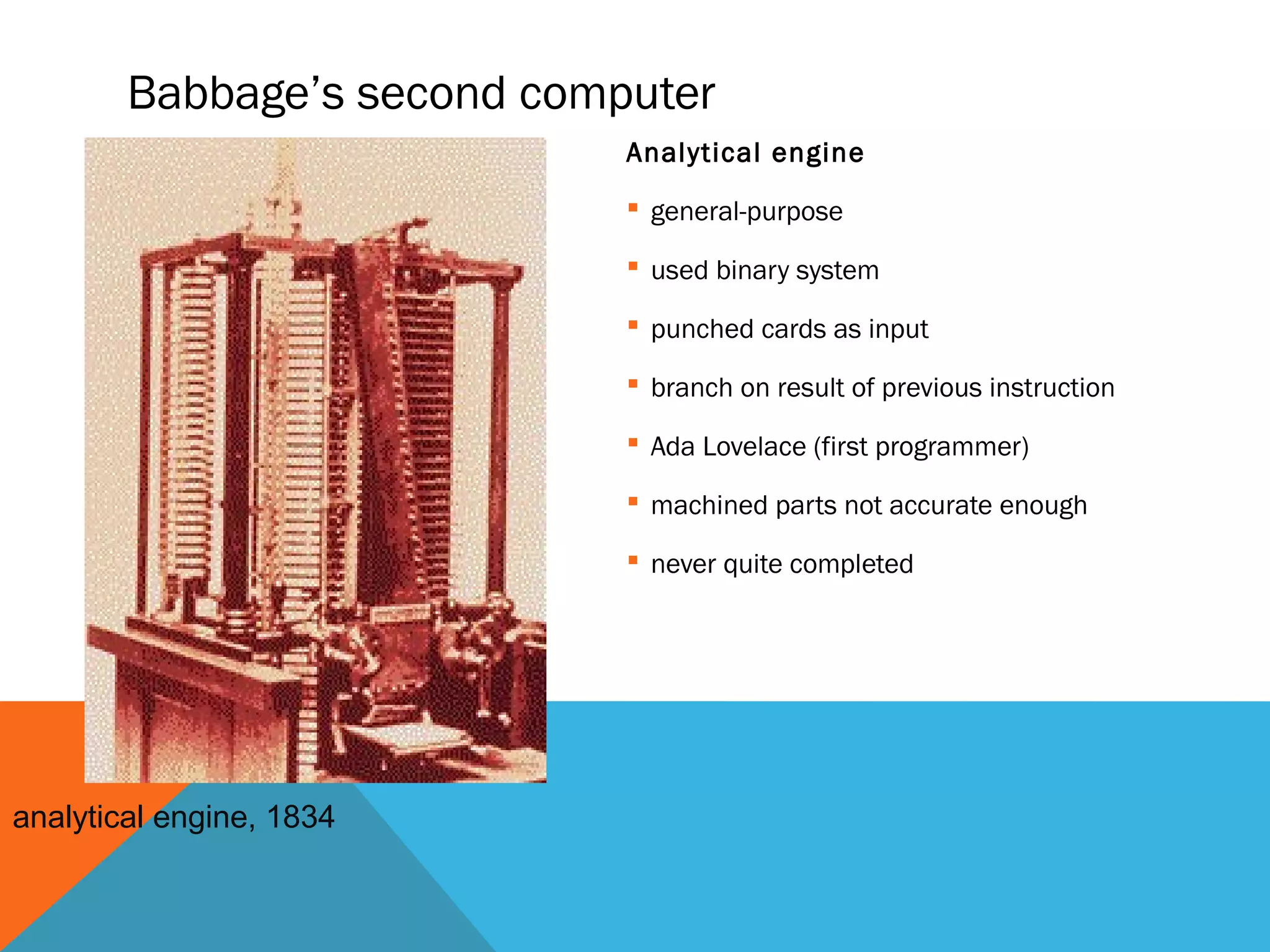
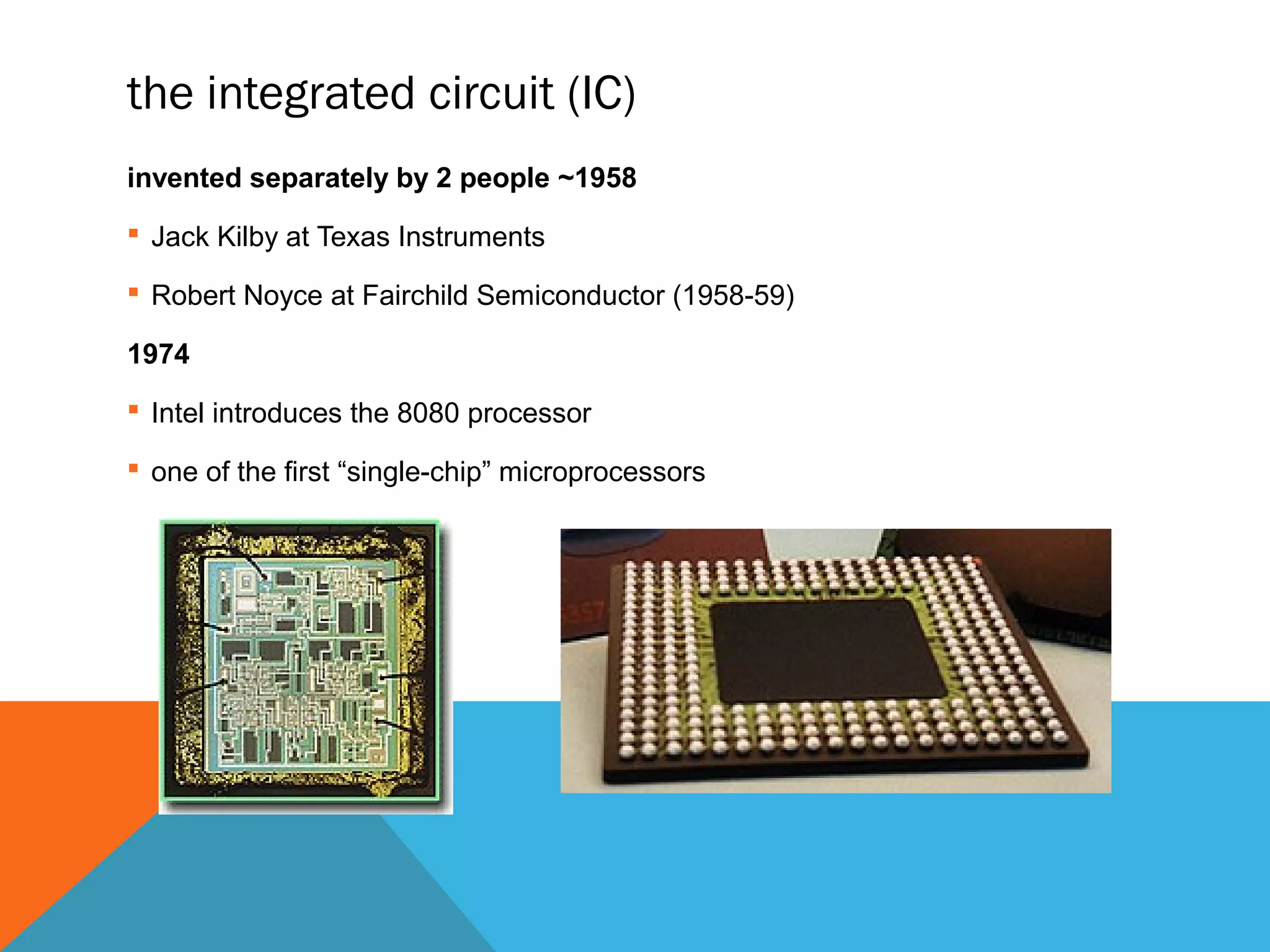
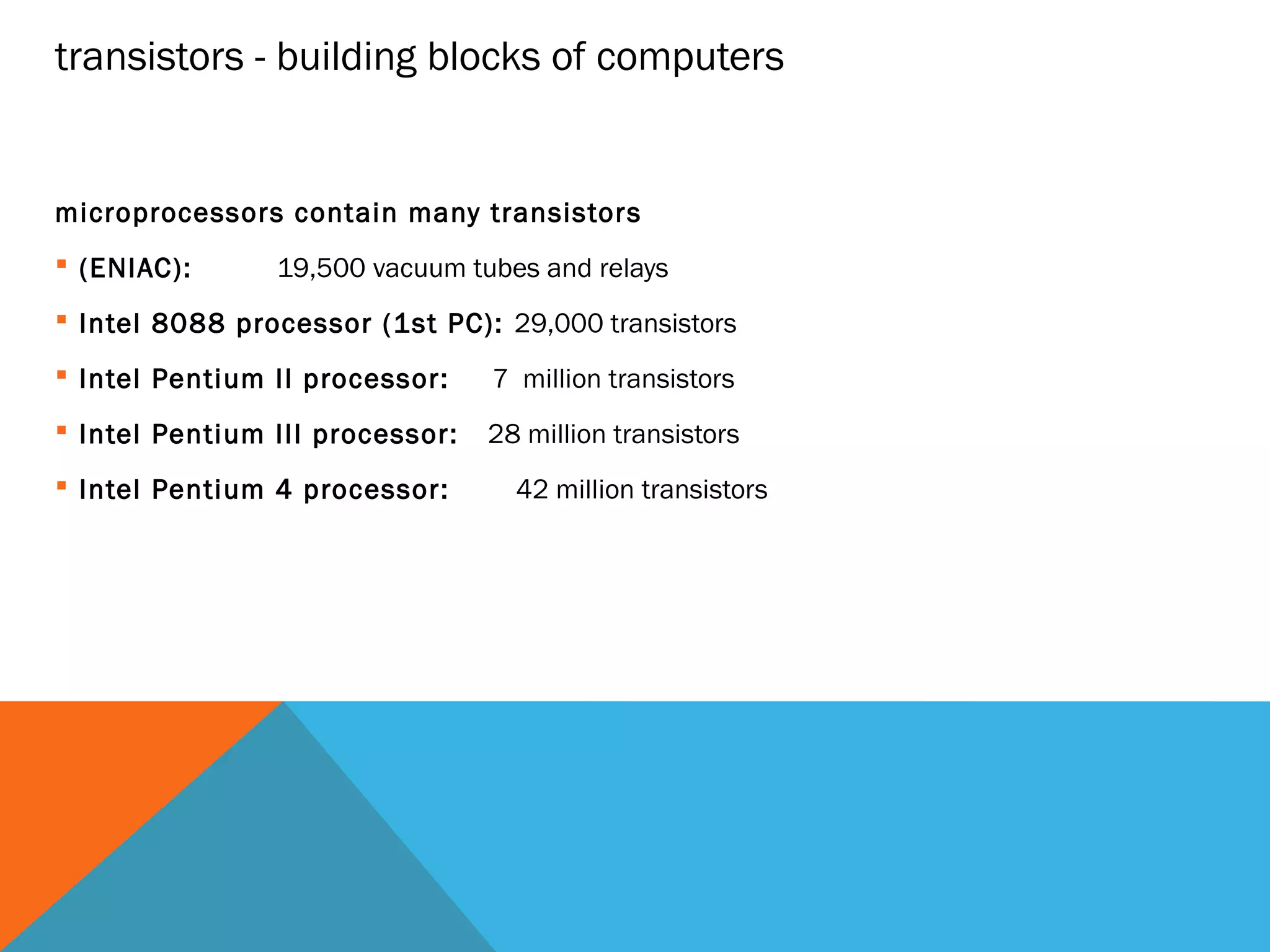
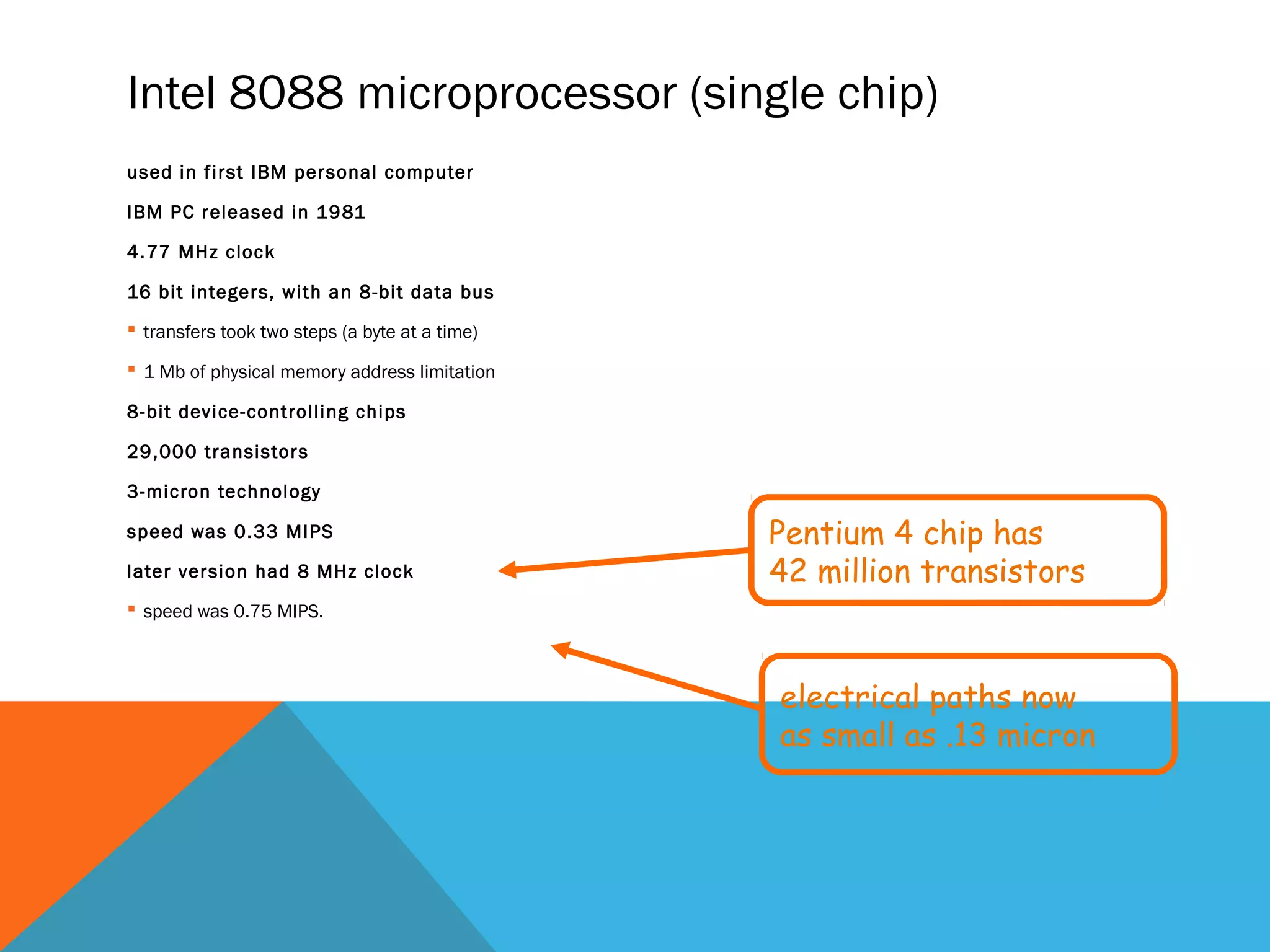
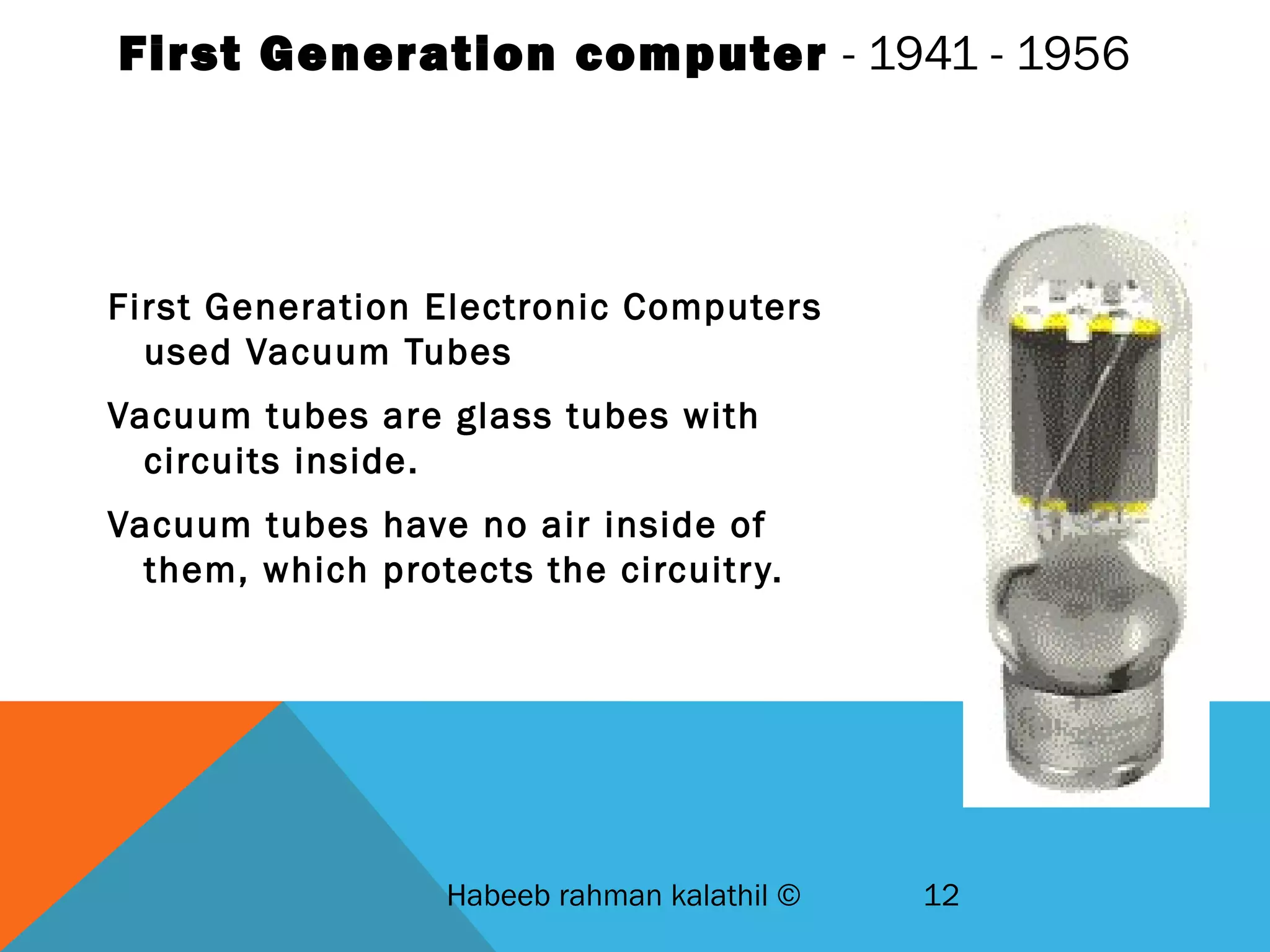
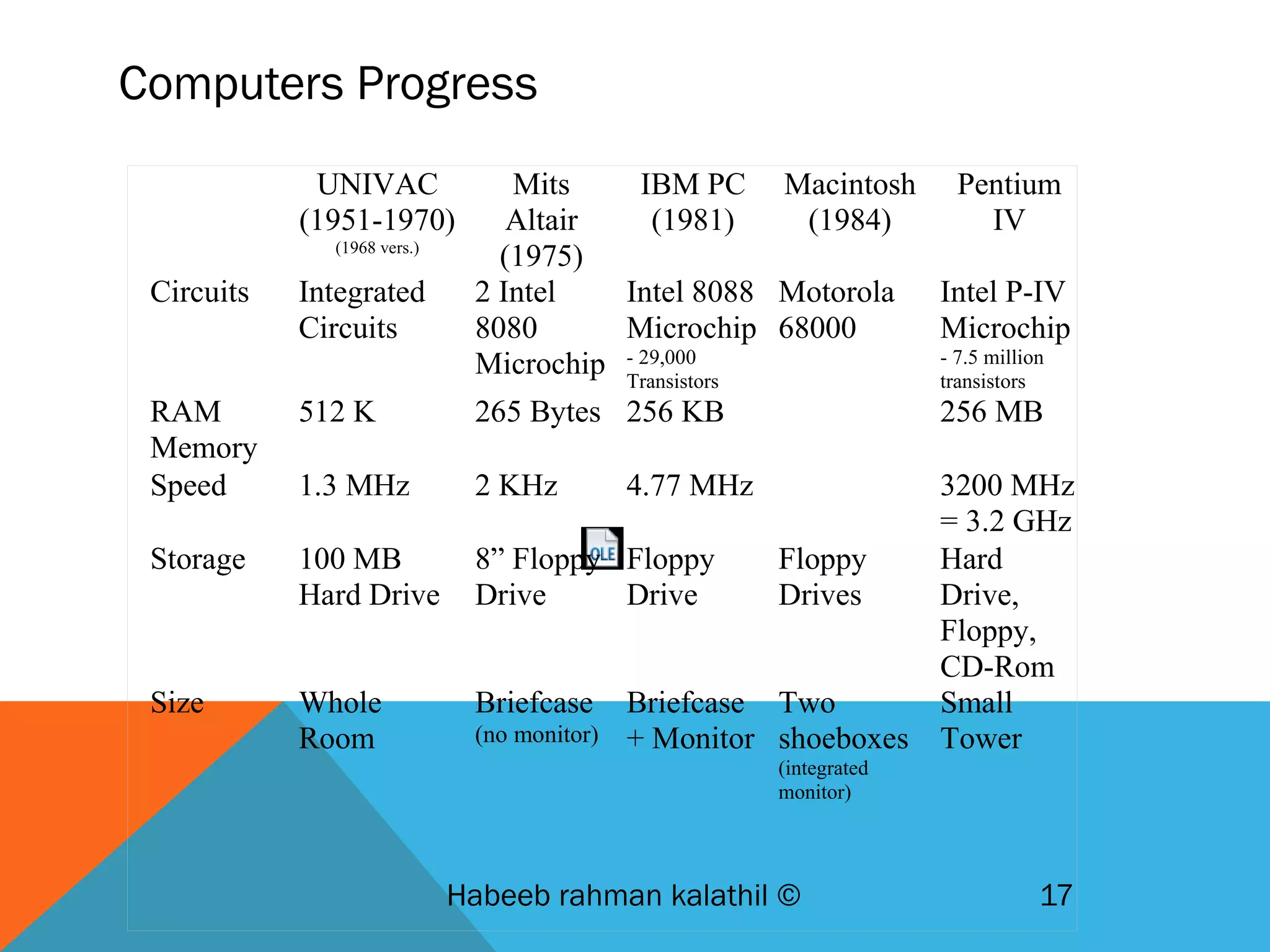
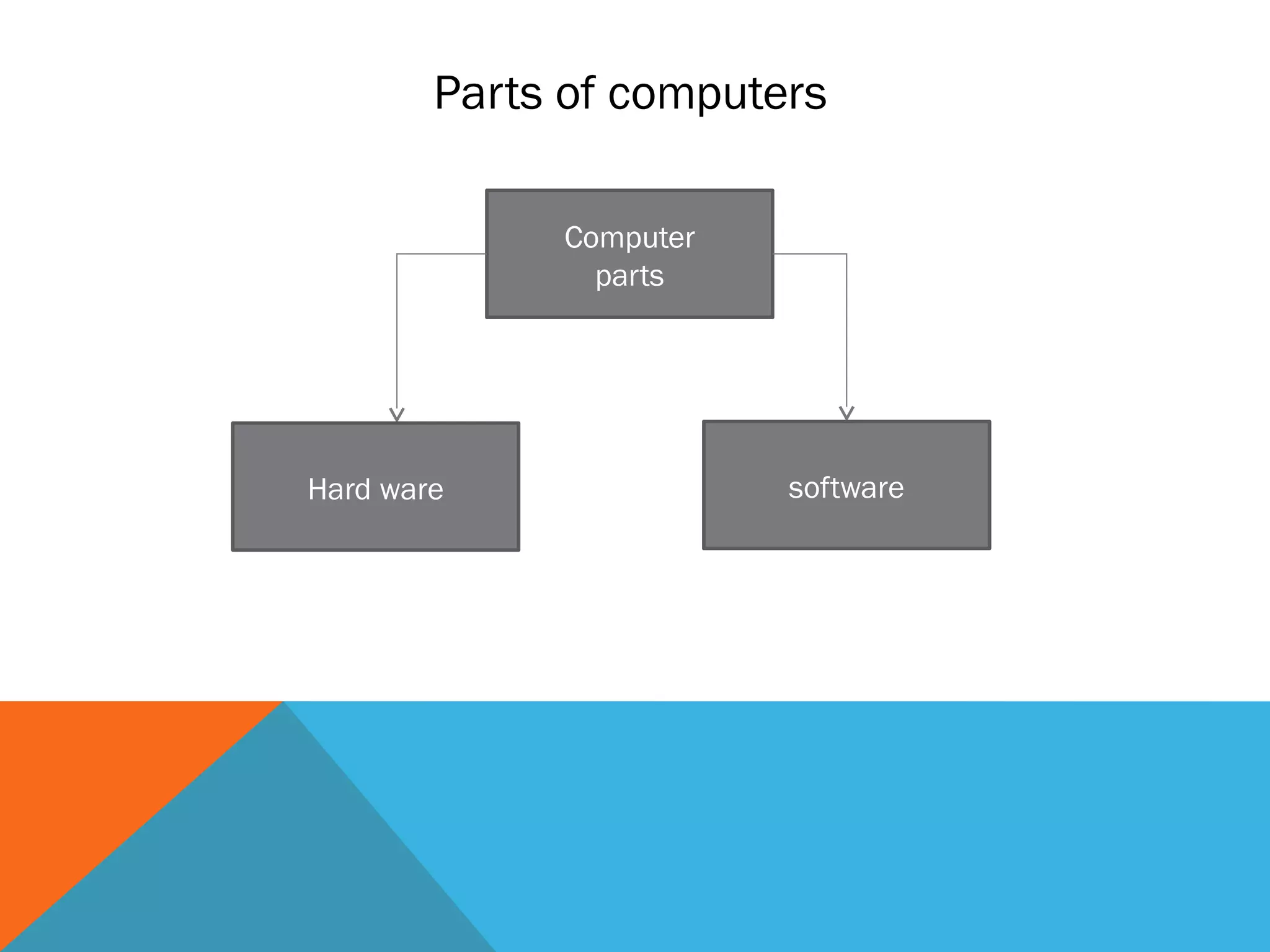
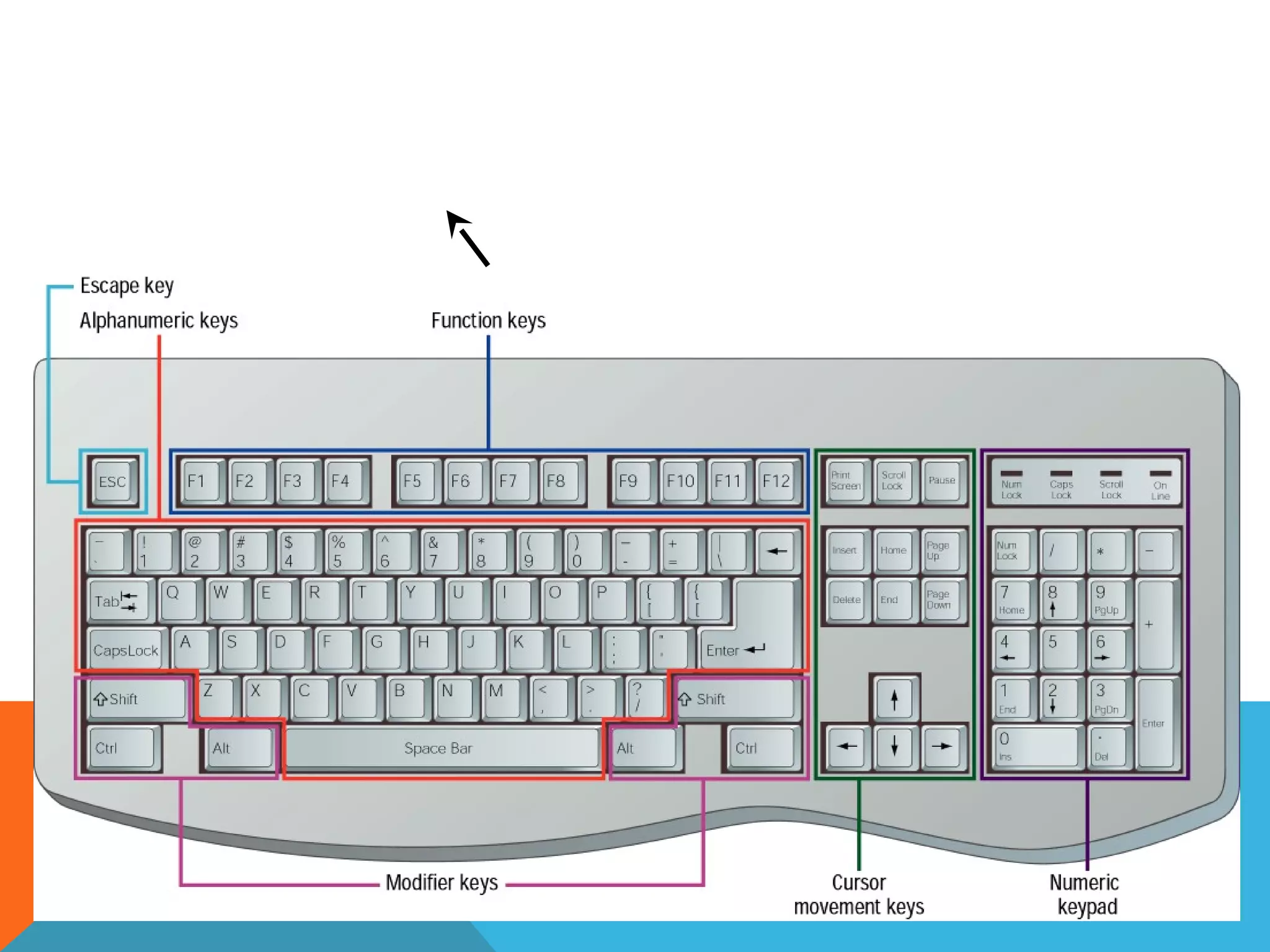
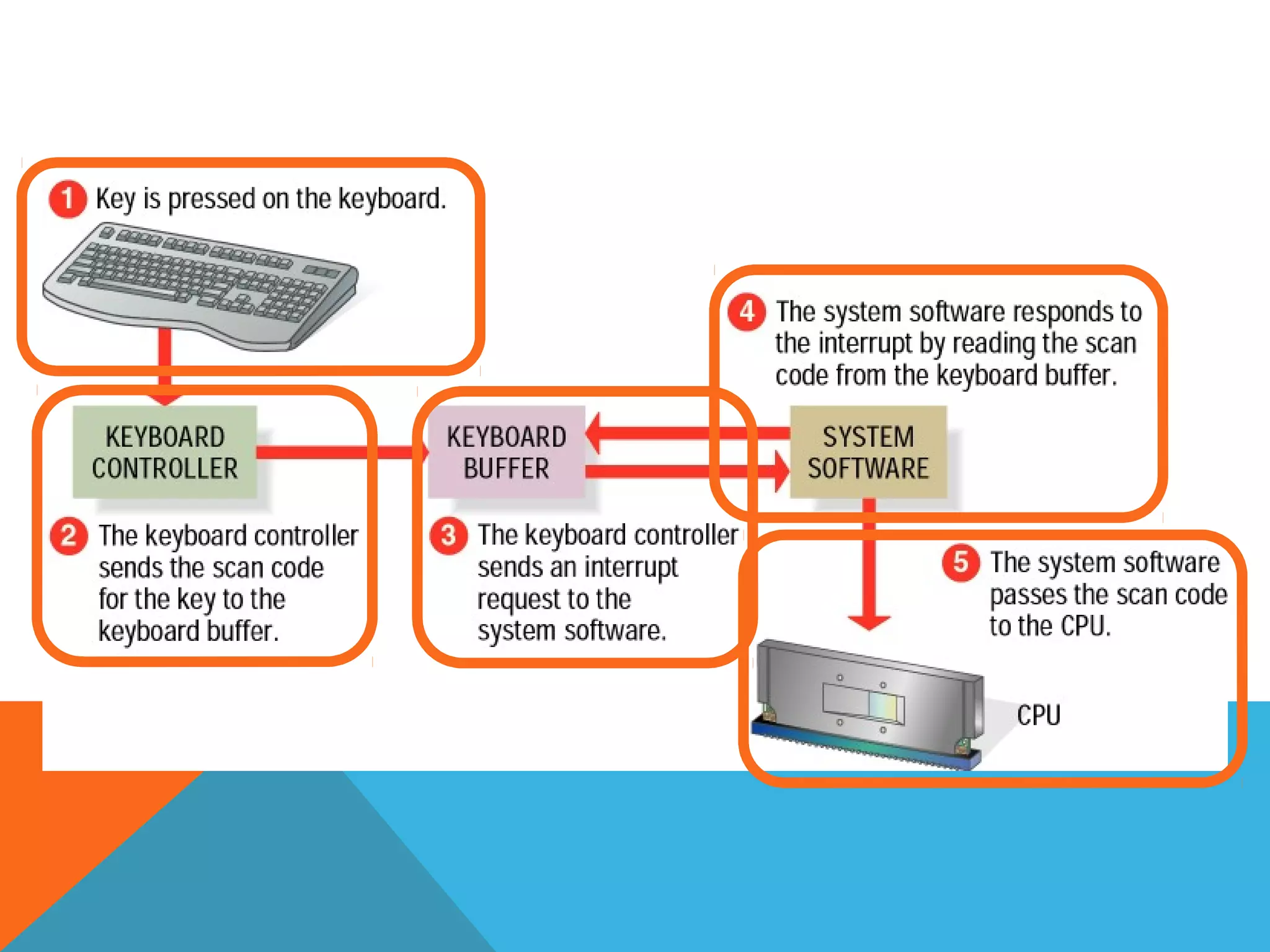
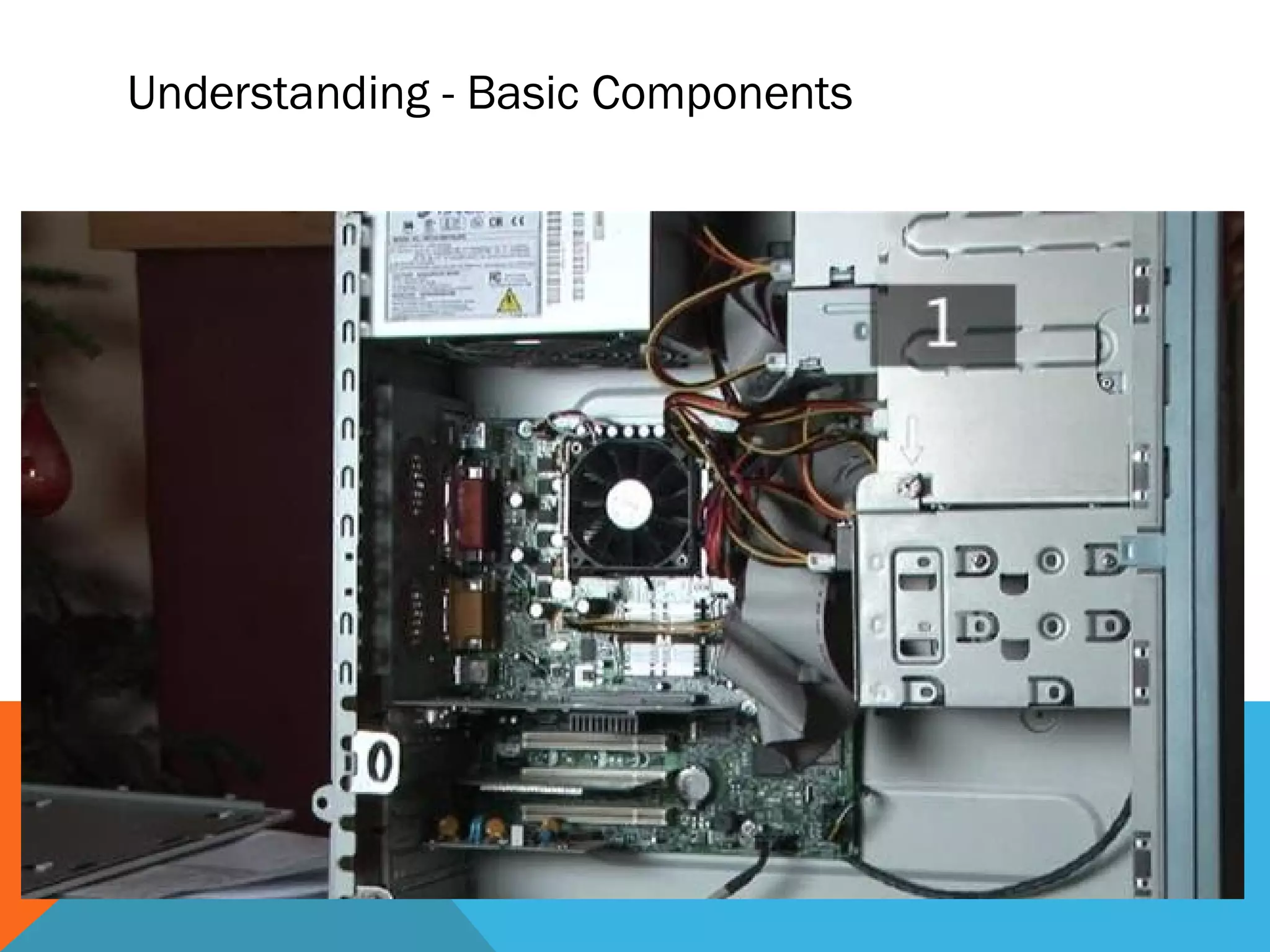
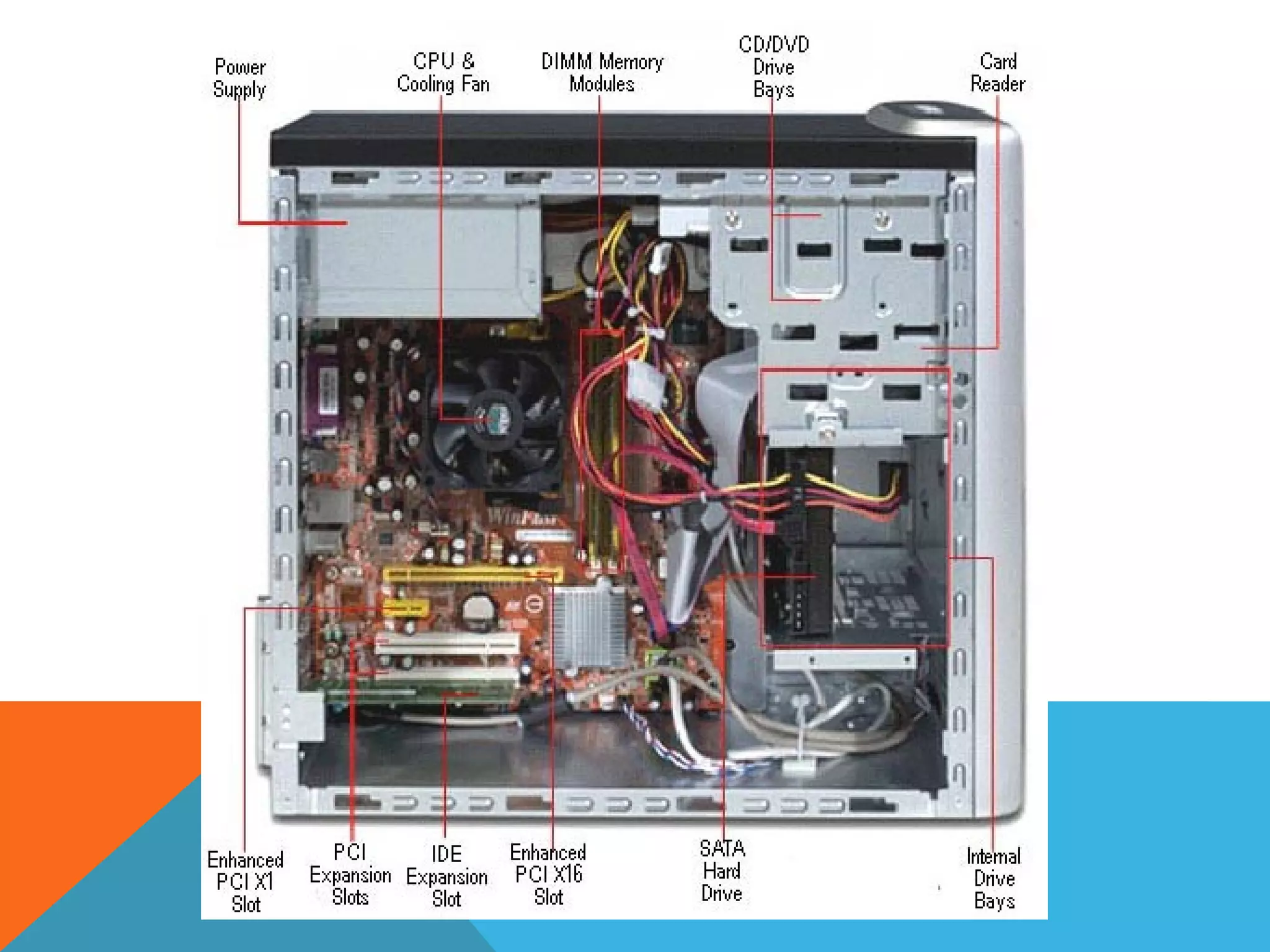
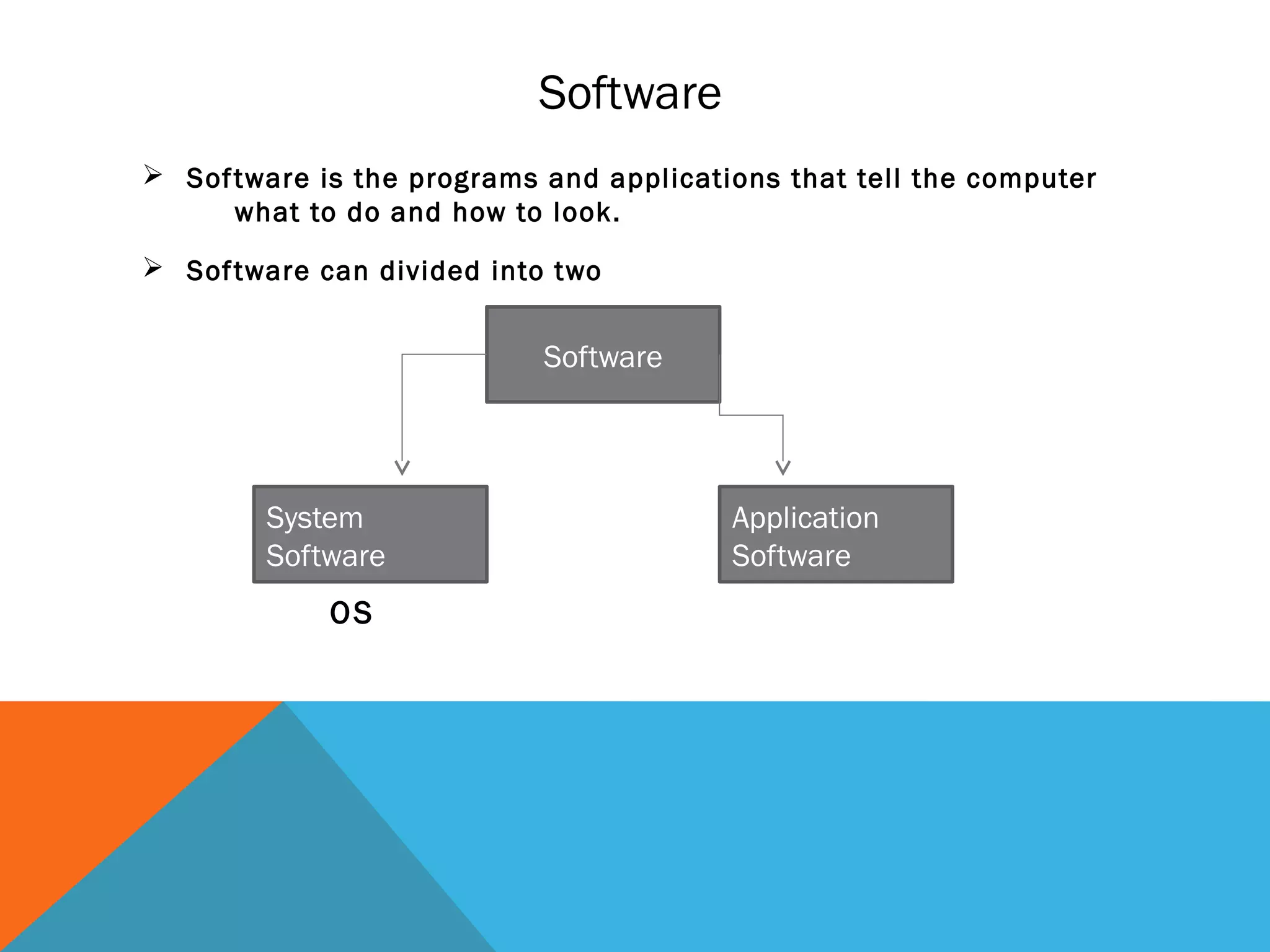
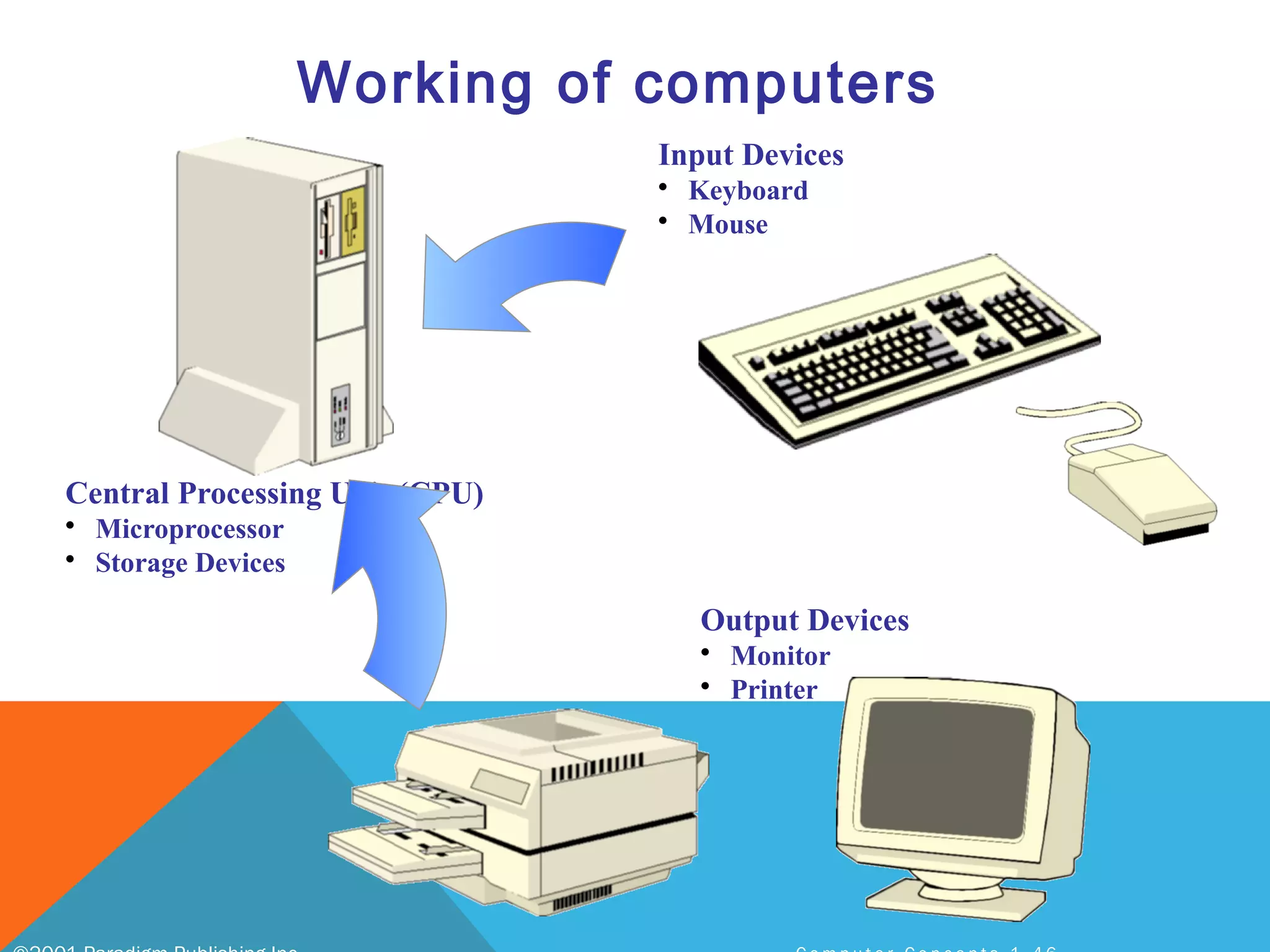
The document provides an overview of computers, including their history, basic components, and types. It outlines key milestones from early mechanical calculators to modern microprocessors and discusses various types of computers like microcomputers, desktops, laptops, mainframes, and supercomputers. Additionally, it describes key hardware and software components, including input and output devices, central processing units, and communication devices.