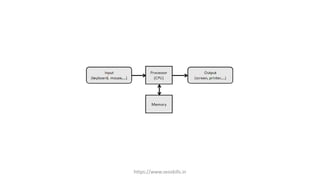
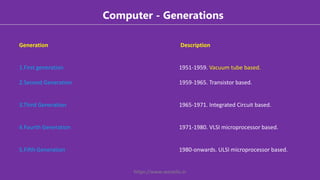
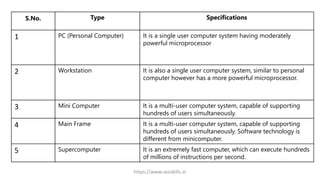
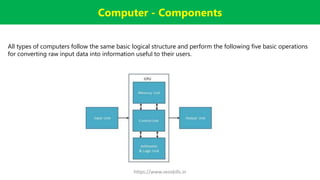
The document provides an overview of computers, defining them as electronic data processing devices that perform five essential functions: input, storage, processing, output, and control. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of computers, their applications in various fields, and outlines the five generations of computers from vacuum tubes to artificial intelligence. Additionally, it categorizes computers into types based on speed and computing power, and describes key components like the input unit, CPU, and output unit.