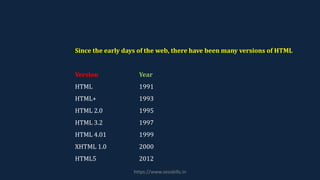
HTML, or Hypertext Markup Language, is the standard language for creating static web pages, understood by all browsers and developed by Tim Berners-Lee. It consists of text documents with markup tags that define content display and includes elements like headings, paragraphs, and images, structured within <html>, <head>, and <body> tags. The latest version is HTML5, which requires a proper doctype declaration for correct browser display.