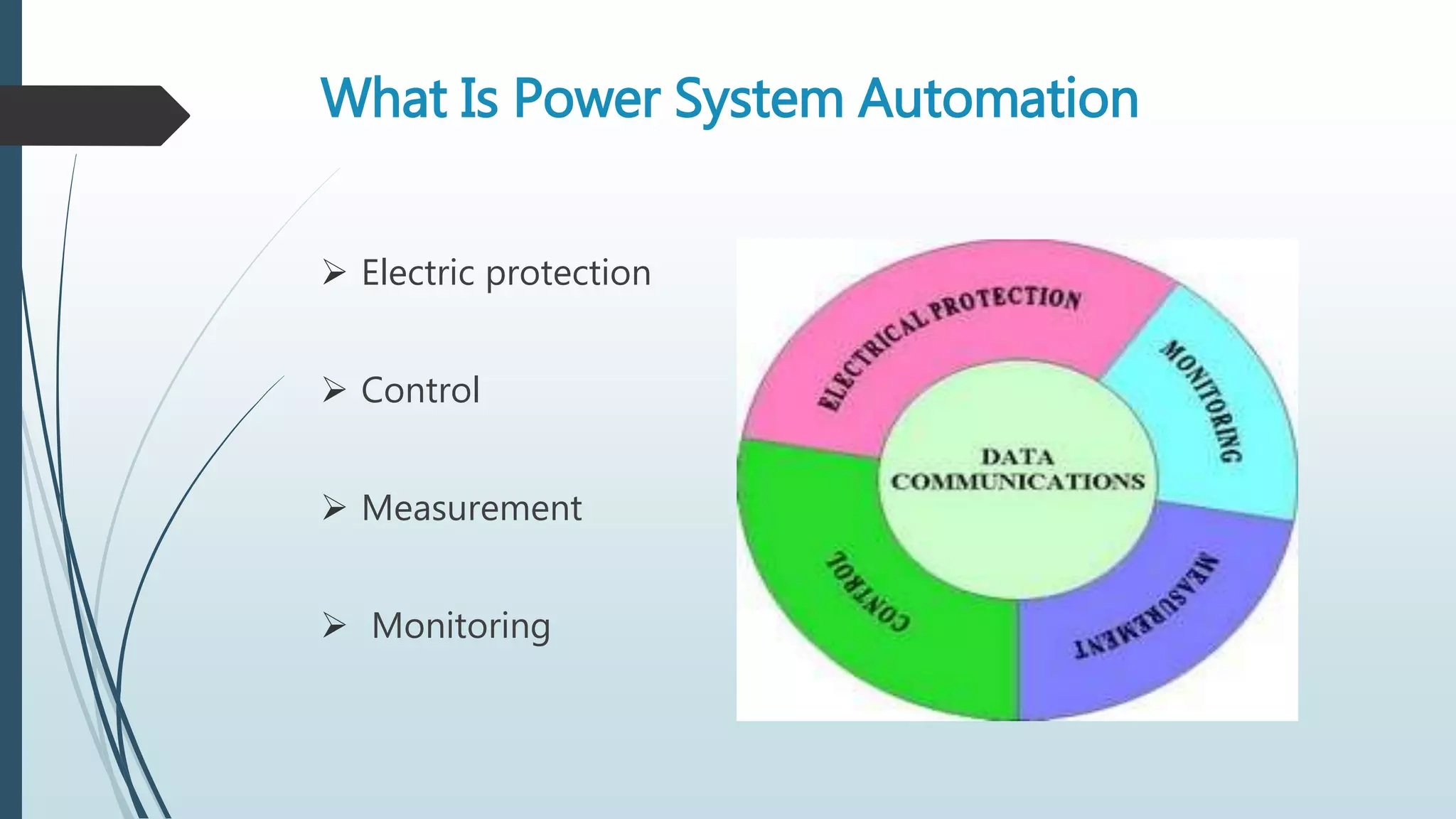
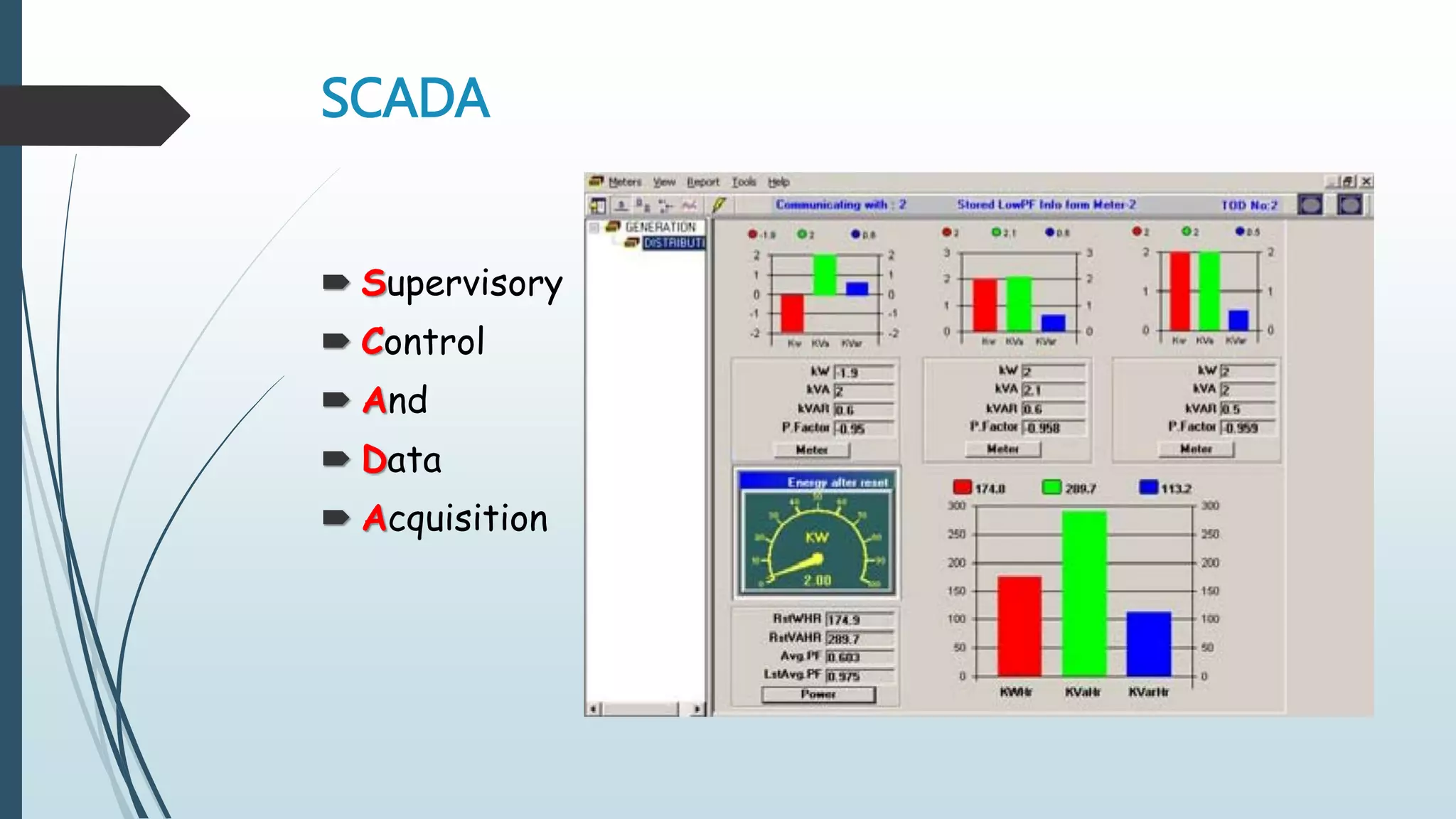
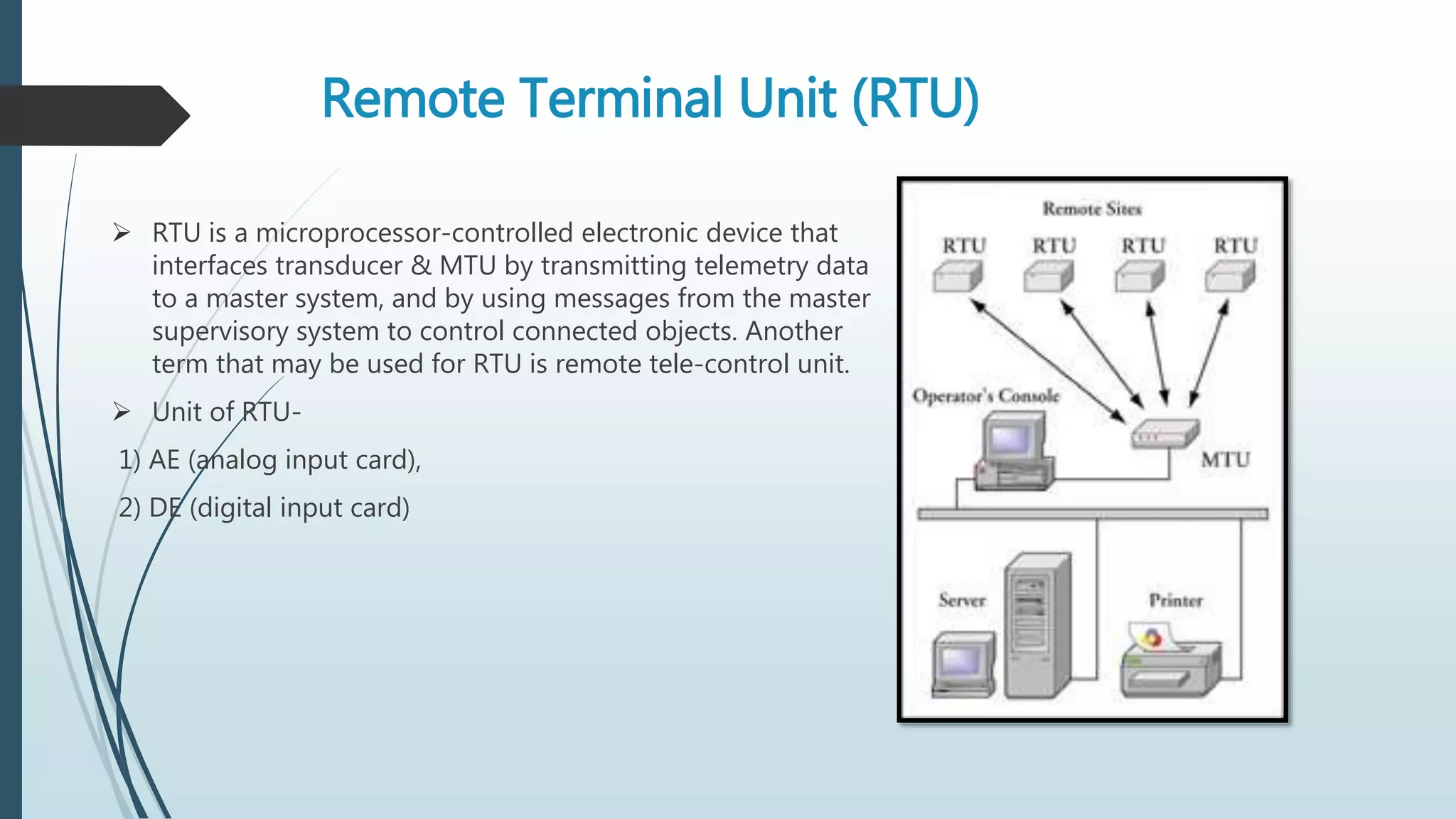
This document discusses power system automation and SCADA systems. It describes the key components of SCADA including instrument transformers, transducers, relays, RTUs, meters, digital fault recorders, PLCs and HMIs. The advantages of power system automation are that it makes the system more efficient with less manpower and is flexible, simple and reliable. The disadvantages include high initial costs and need for trained personnel. Power system automation has applications in smart grids, smart meters and automatic generation control. It concludes that automation increases efficiency and standardization of power utilities.