1. Complex numbers can be represented as a sum of a real part and an imaginary part, written as a + bi, where a is the real part and b is the imaginary part.
2. Operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication on complex numbers follow the same rules as real numbers, with the exception that i2 = -1. Division of complex numbers involves multiplying the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator.
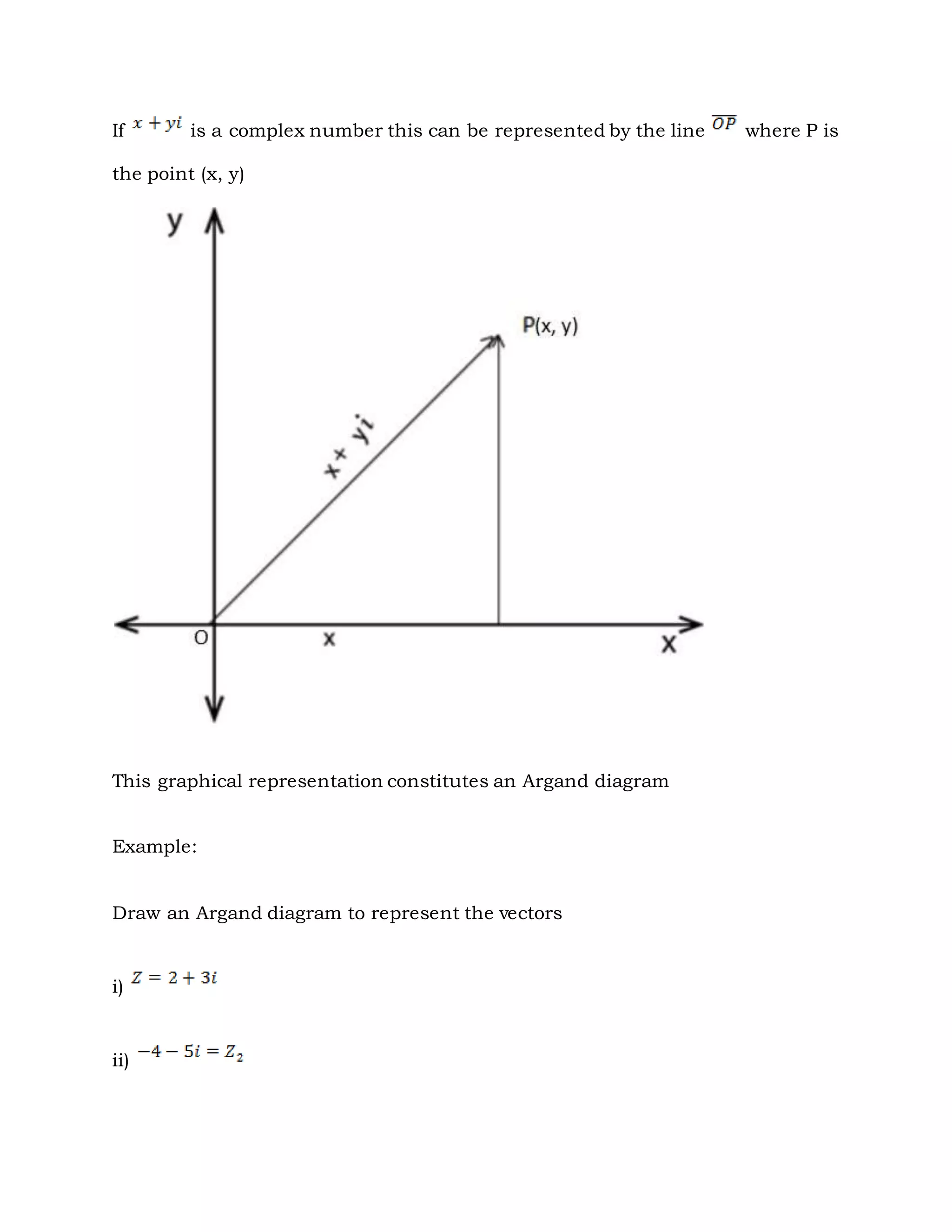
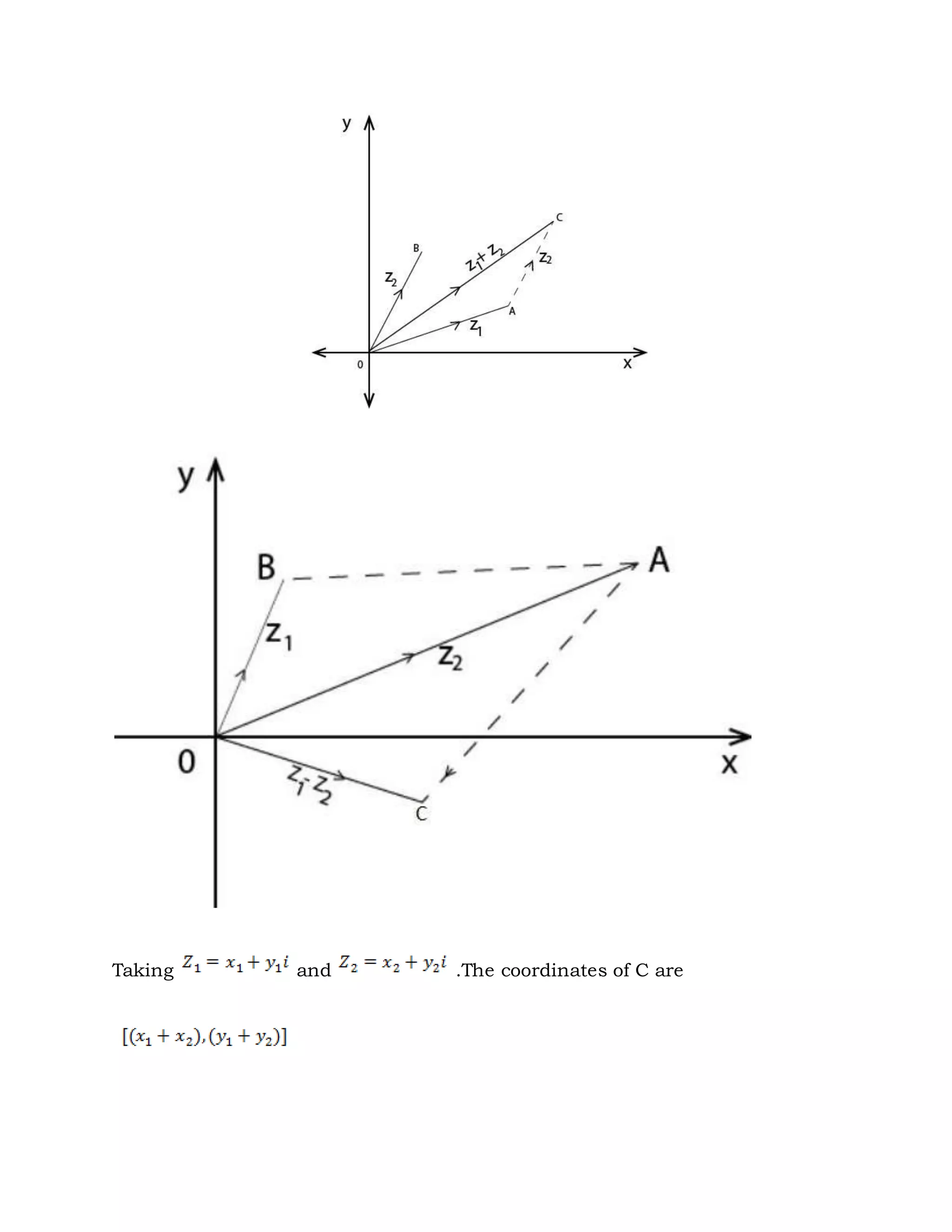
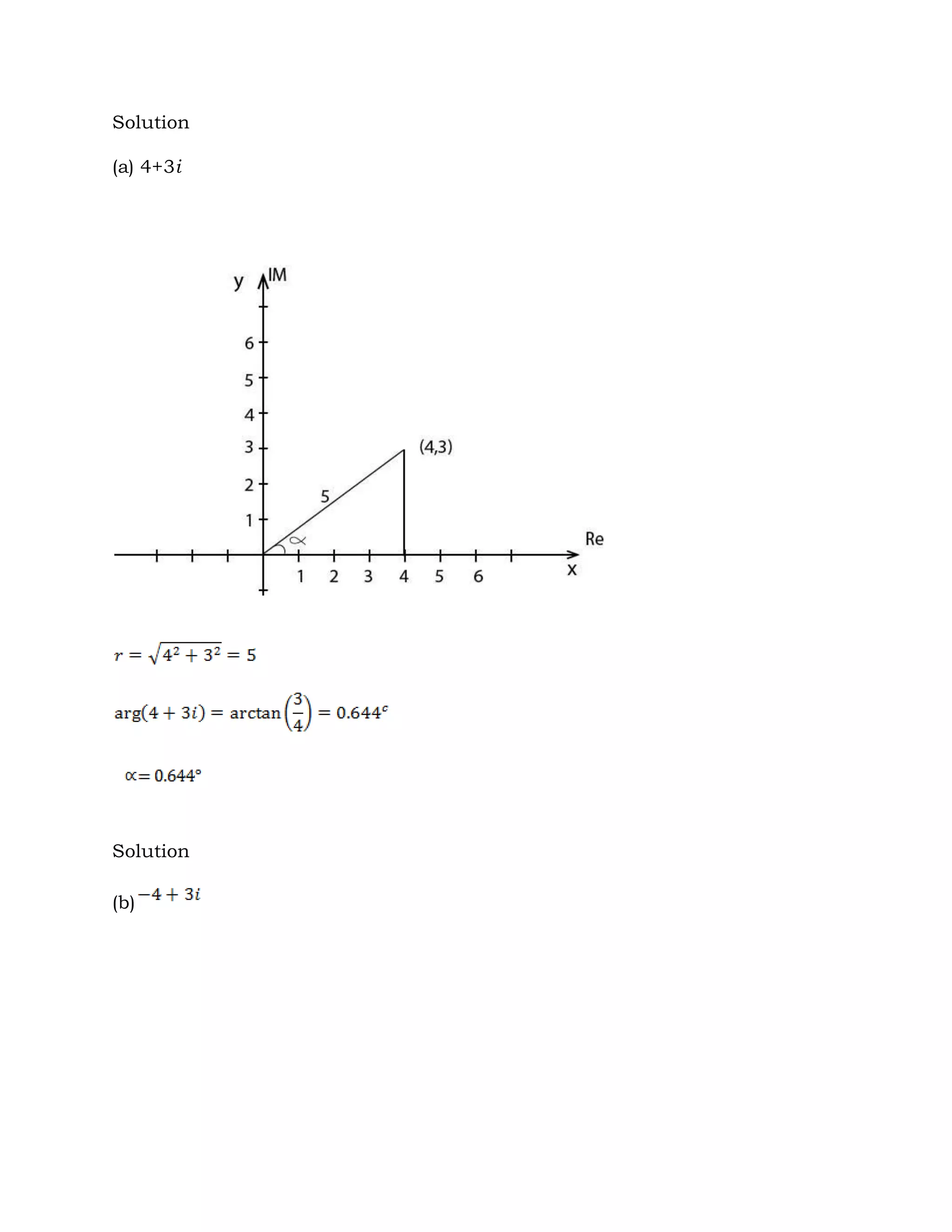
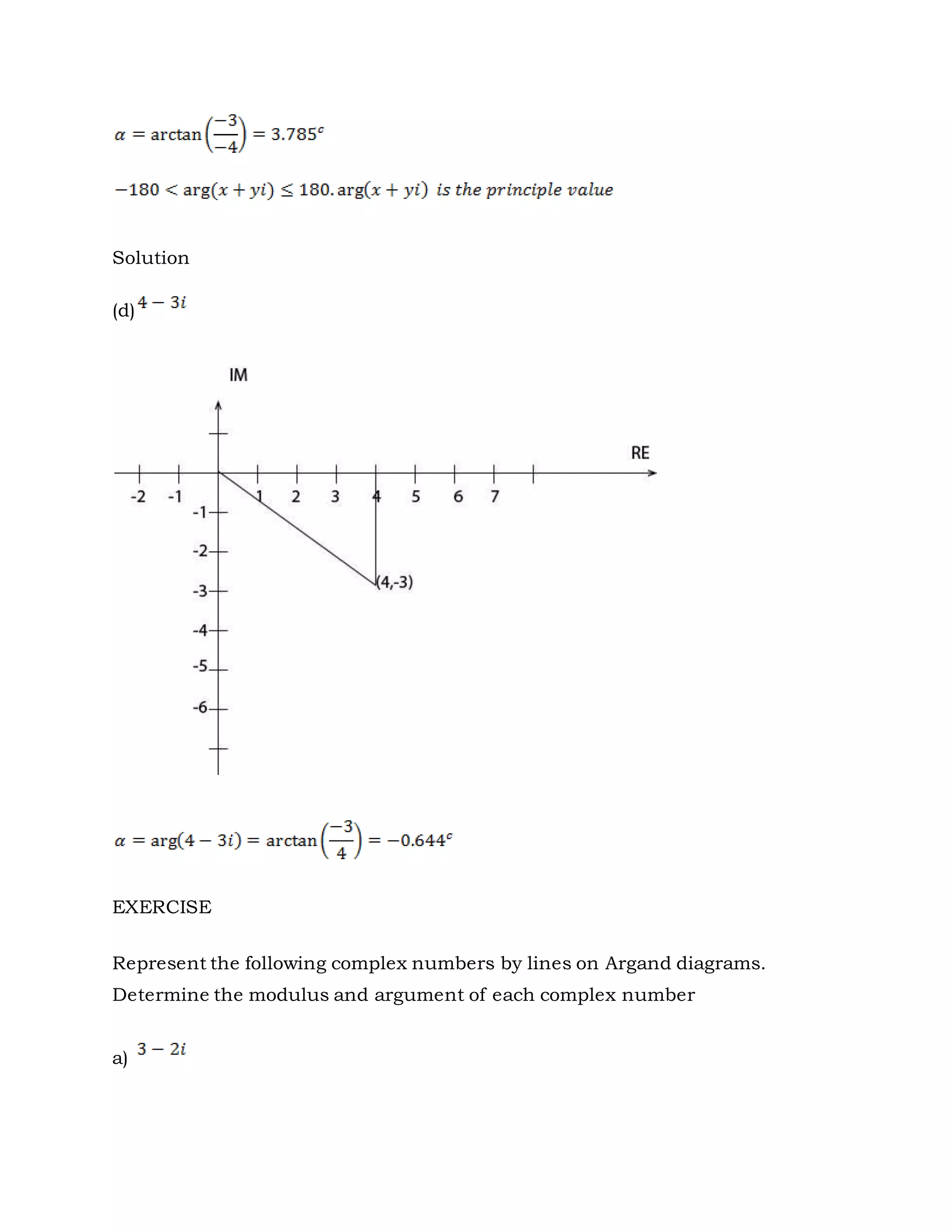
3. Complex numbers can be represented graphically on an Argand diagram, with the real part along the x-axis and imaginary part along the y-axis. The modulus and argument can then be used to describe the magnitude and angle of the complex number.