This document discusses performance management, talent management, and competency management. It provides information on:
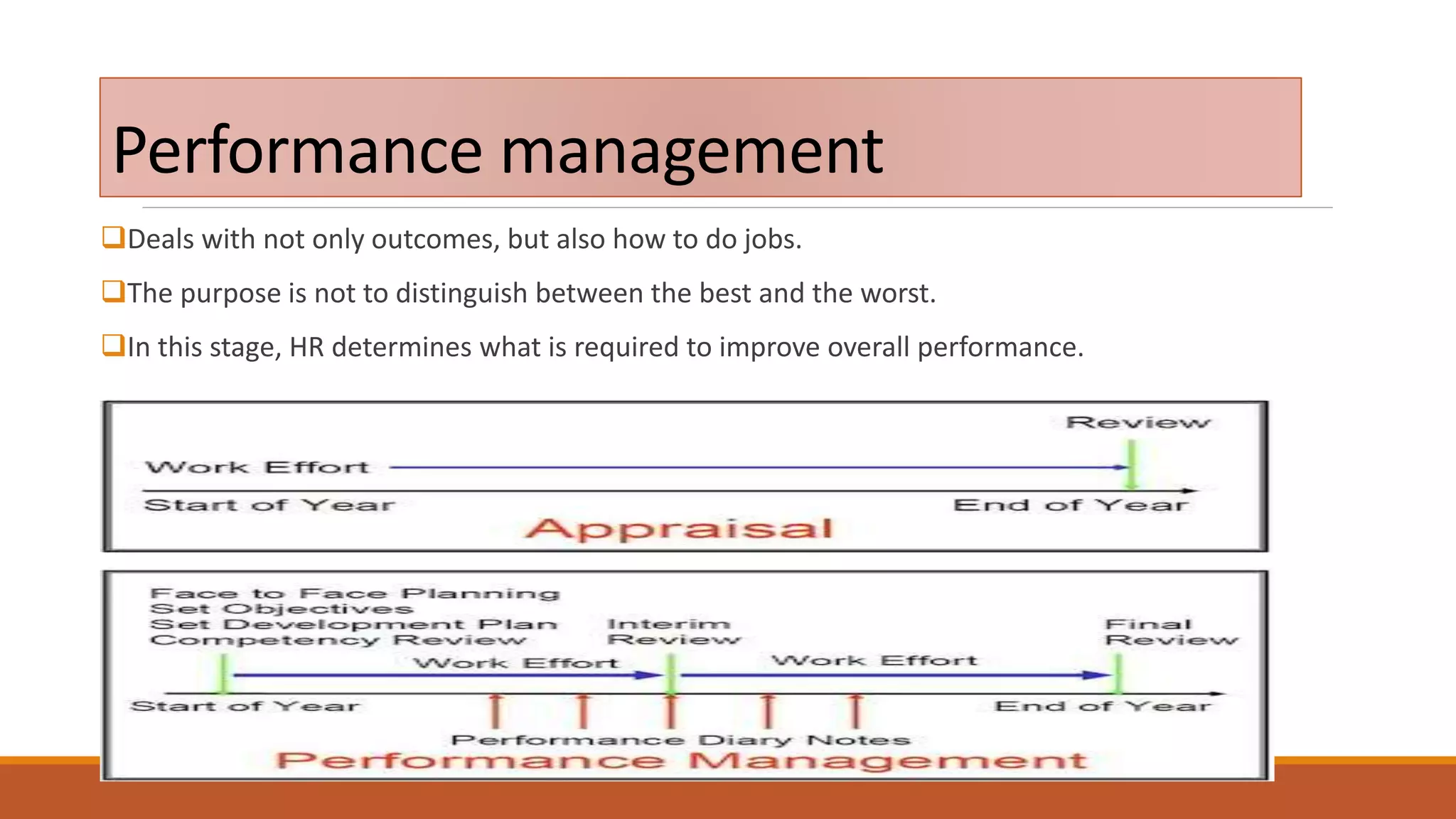
- Performance management includes ensuring goals are met effectively and efficiently, and can focus on organizations, departments, processes or employees.
- Talent management is using strategic human resource planning to improve business value and help companies achieve their goals. It includes recruiting, developing, rewarding and evaluating employees.
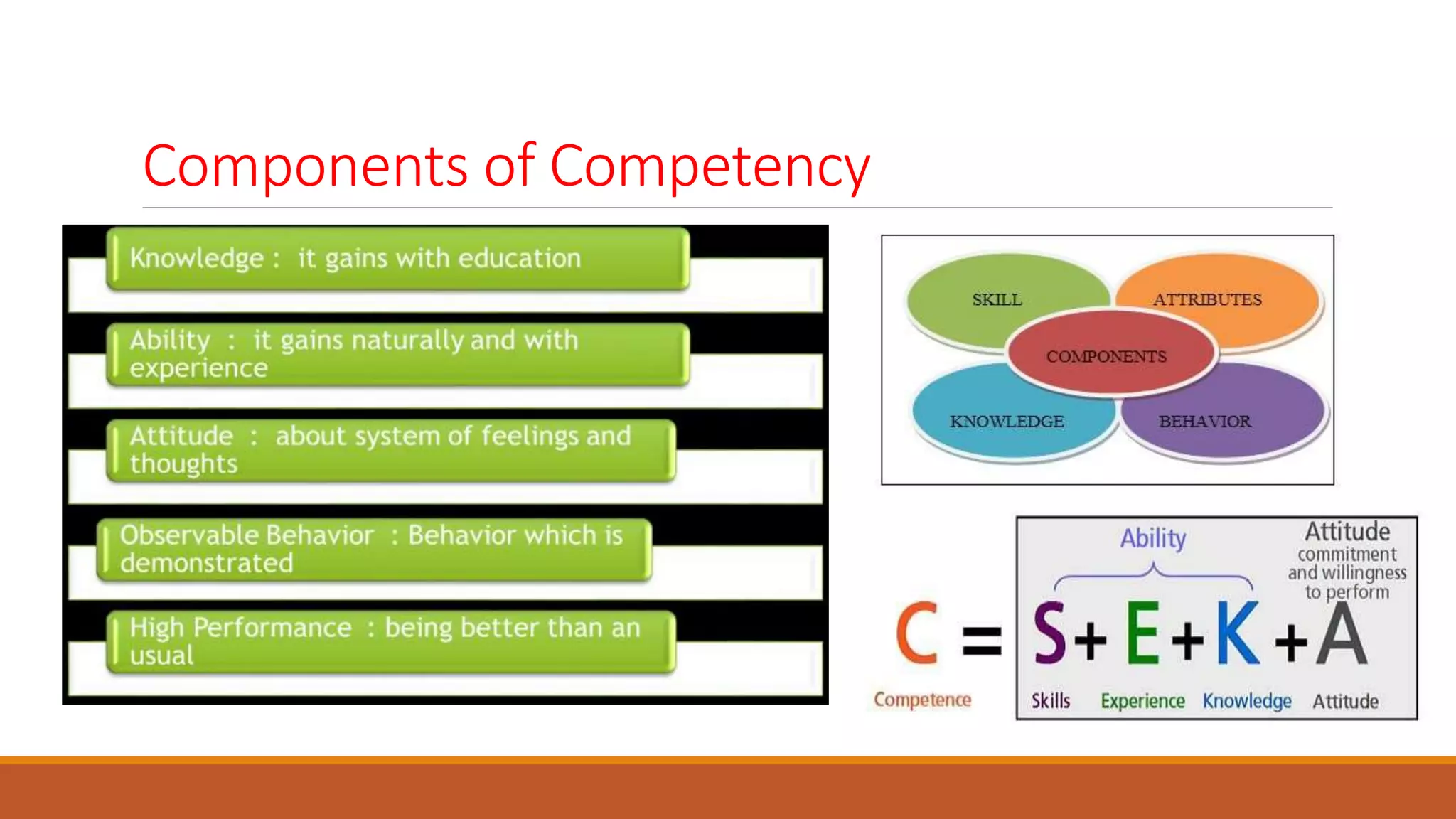
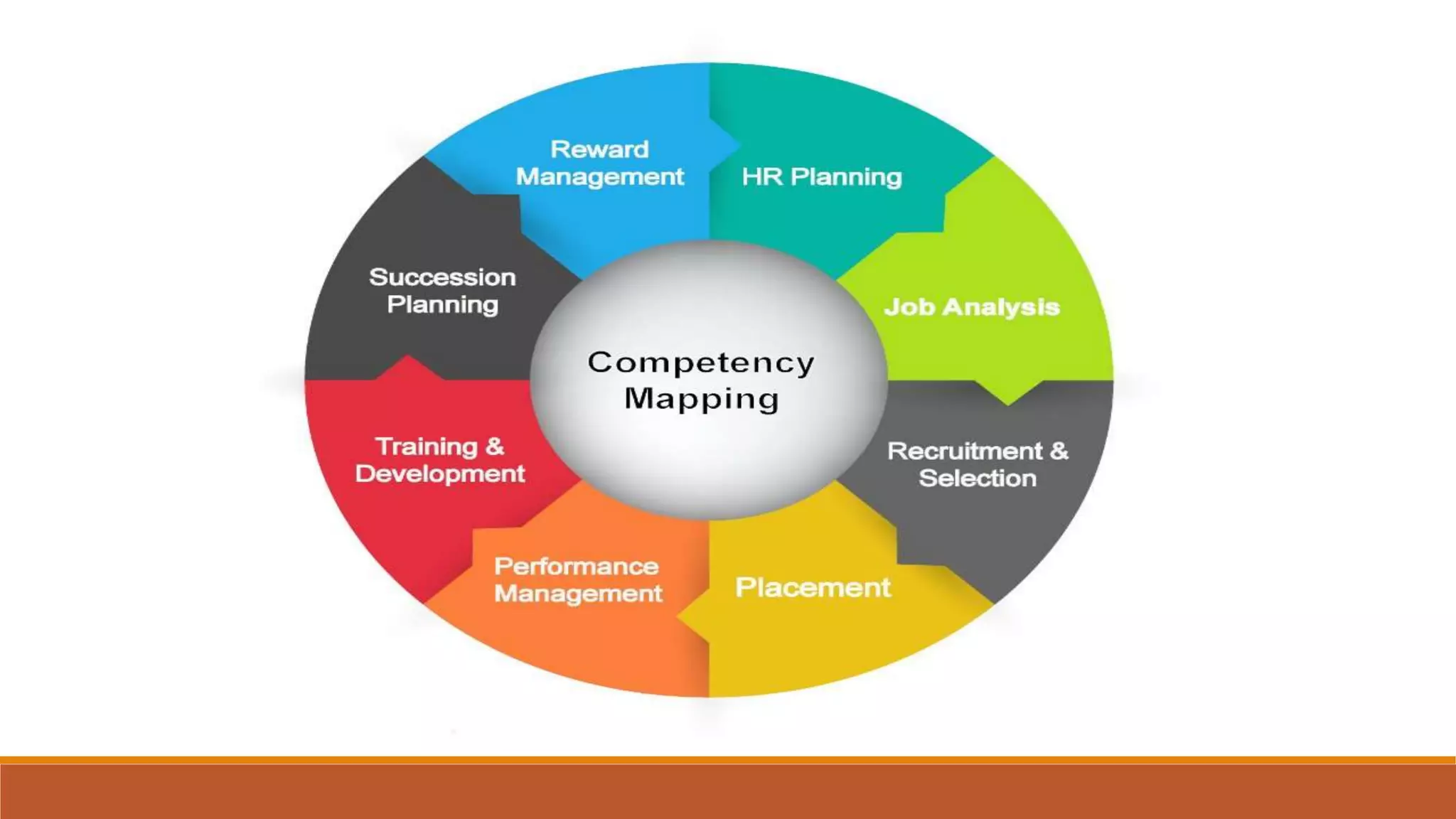
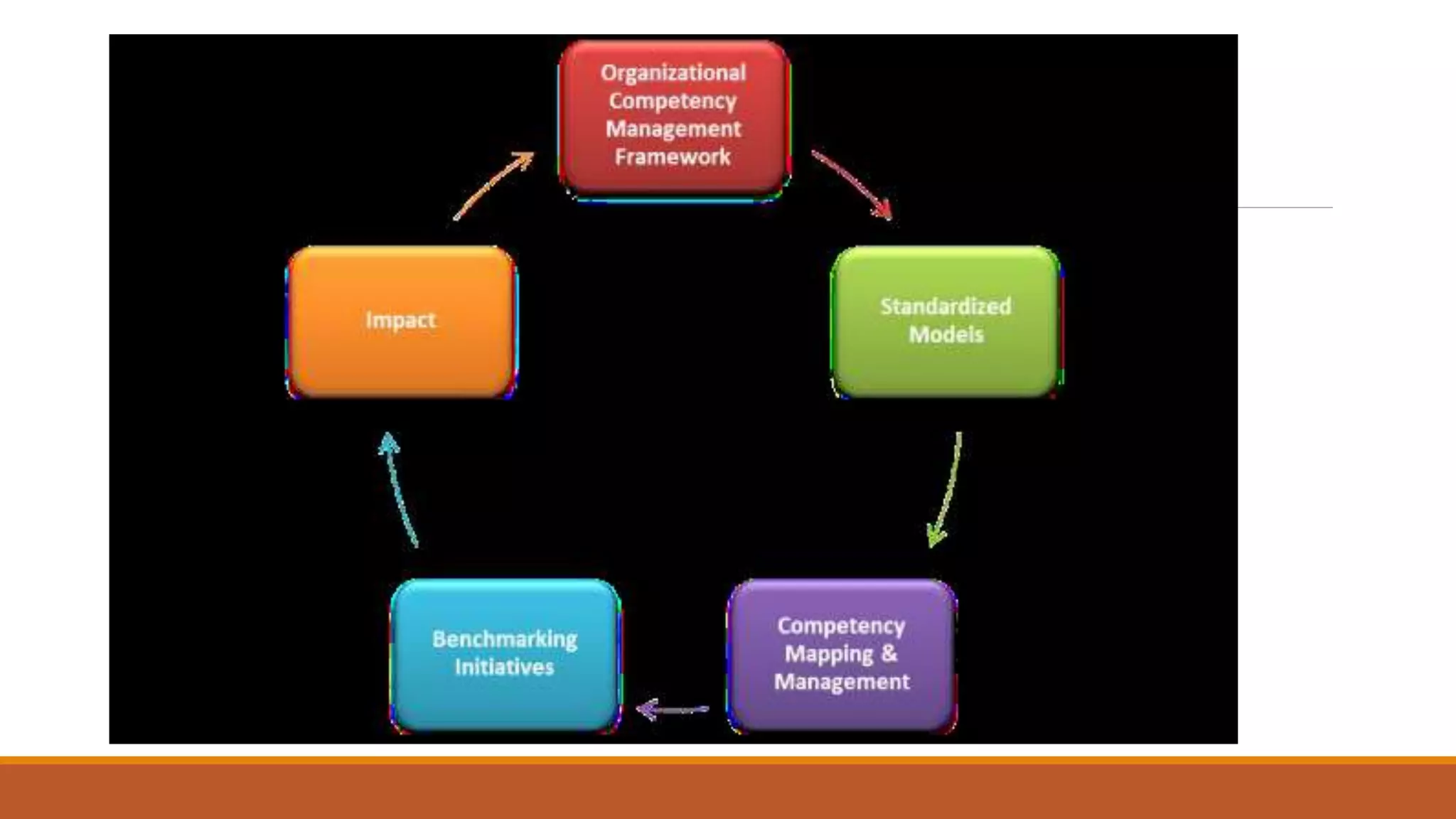
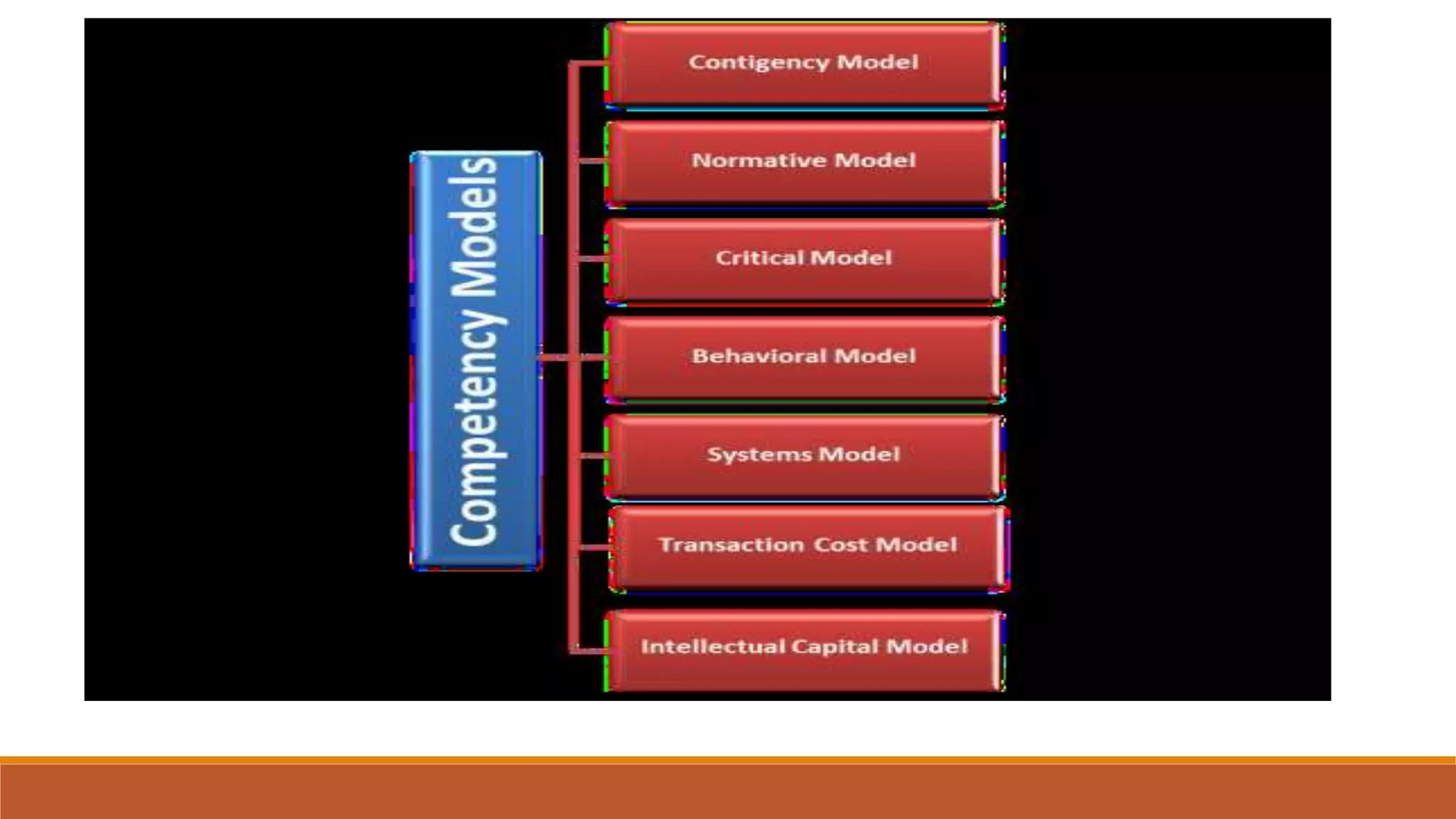
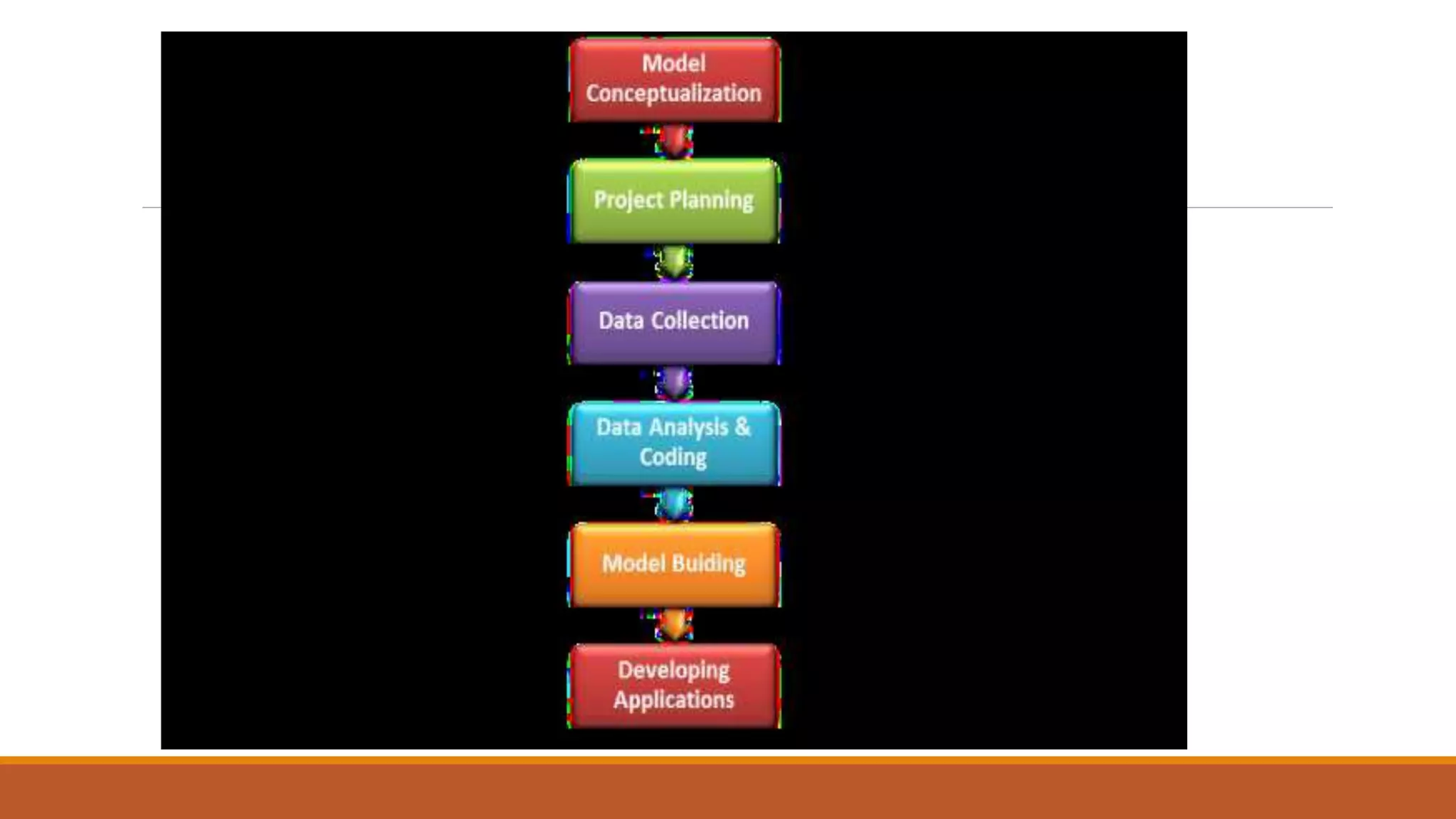
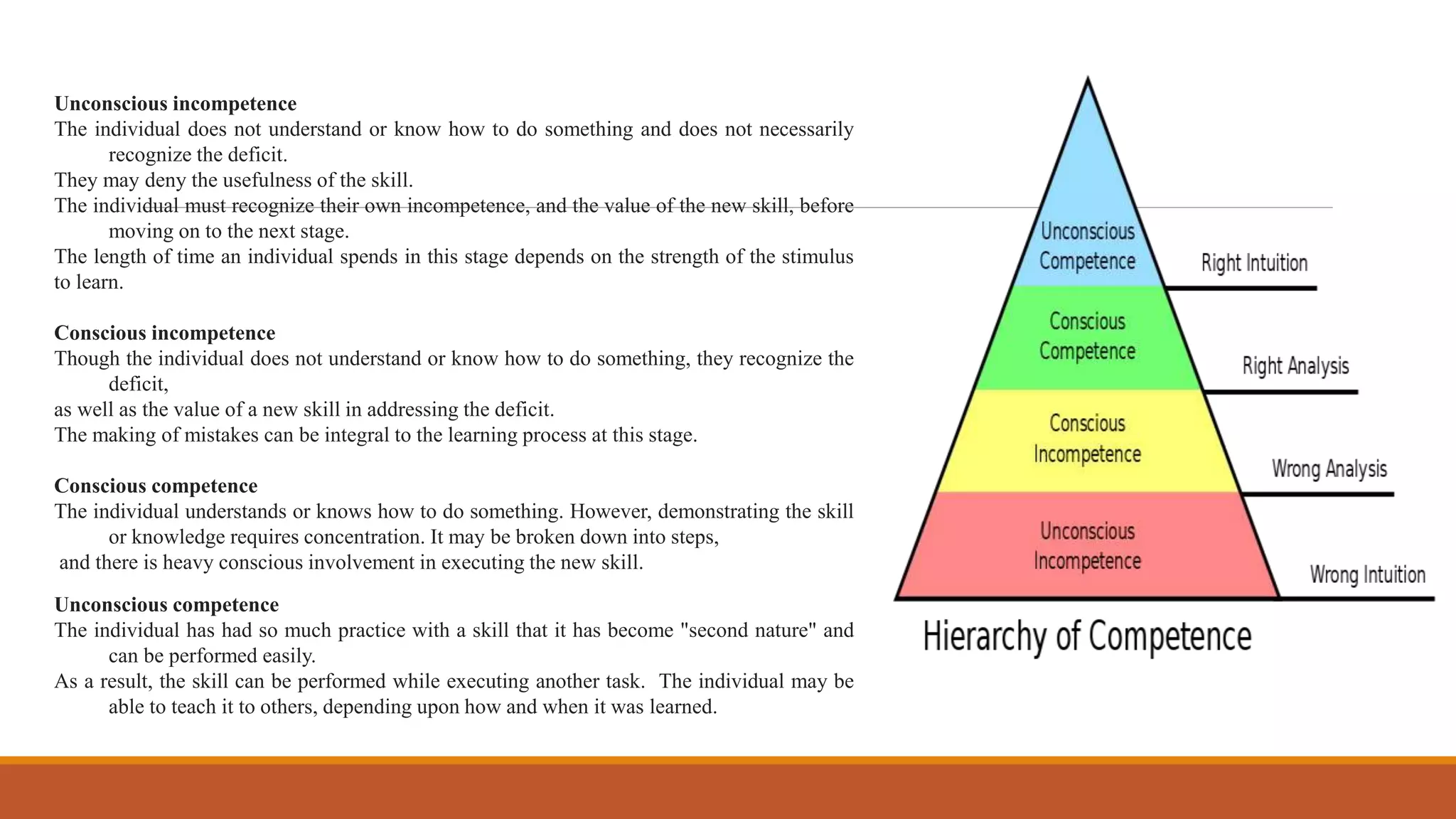
- Competency management identifies the skills, behaviors and abilities needed for roles. It is used to develop, evaluate and improve employees' competencies to enhance performance.