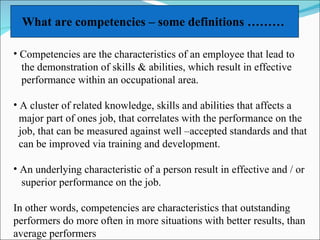
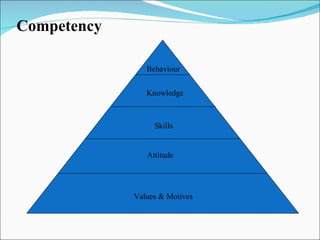
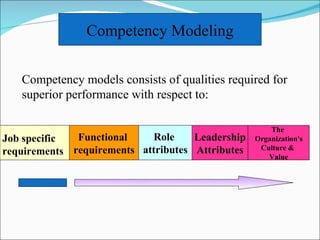
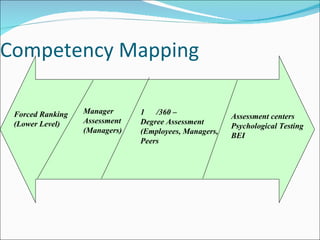
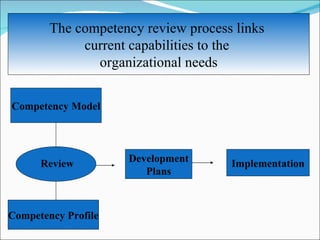
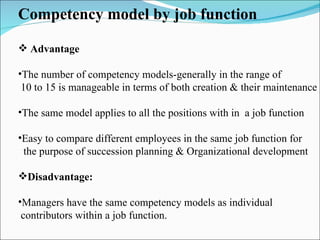
Competencies are characteristics of employees that lead to effective job performance. They include skills, abilities, knowledge, and behaviors. Competencies help employees deliver better to customers by addressing their needs and skills gaps. They also help organizations achieve high performance by setting expectations for career progression and increased productivity. Developing competency models involves determining the qualities needed for superior performance in functions, leadership, jobs, roles, and organizational culture. It requires collecting data through methods like behavioral interviews, expert panels, surveys, and job analysis.