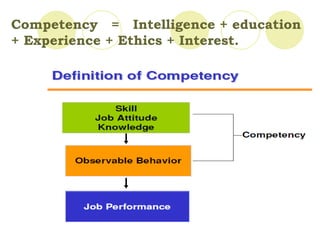
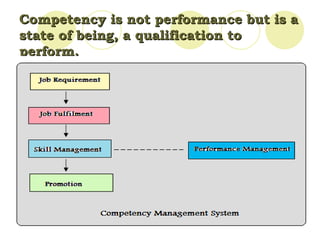
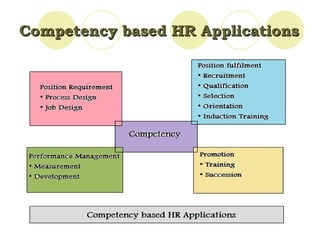
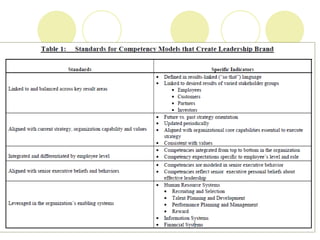
Competency mapping is the process of identifying the key competencies required for jobs in an organization and incorporating those competencies into HR processes like recruitment, training and performance evaluation. It helps align employee skills and behaviors with organizational goals. Competencies can be generic, managerial, technical or behavioral. Competency frameworks organize competencies and behavioral indicators. Competency models are only effective when competencies are linked to business strategy and results, applied consistently across levels, and modeled by senior leadership. Benefits include focused employee development and a leadership brand that sustains competitive advantage.