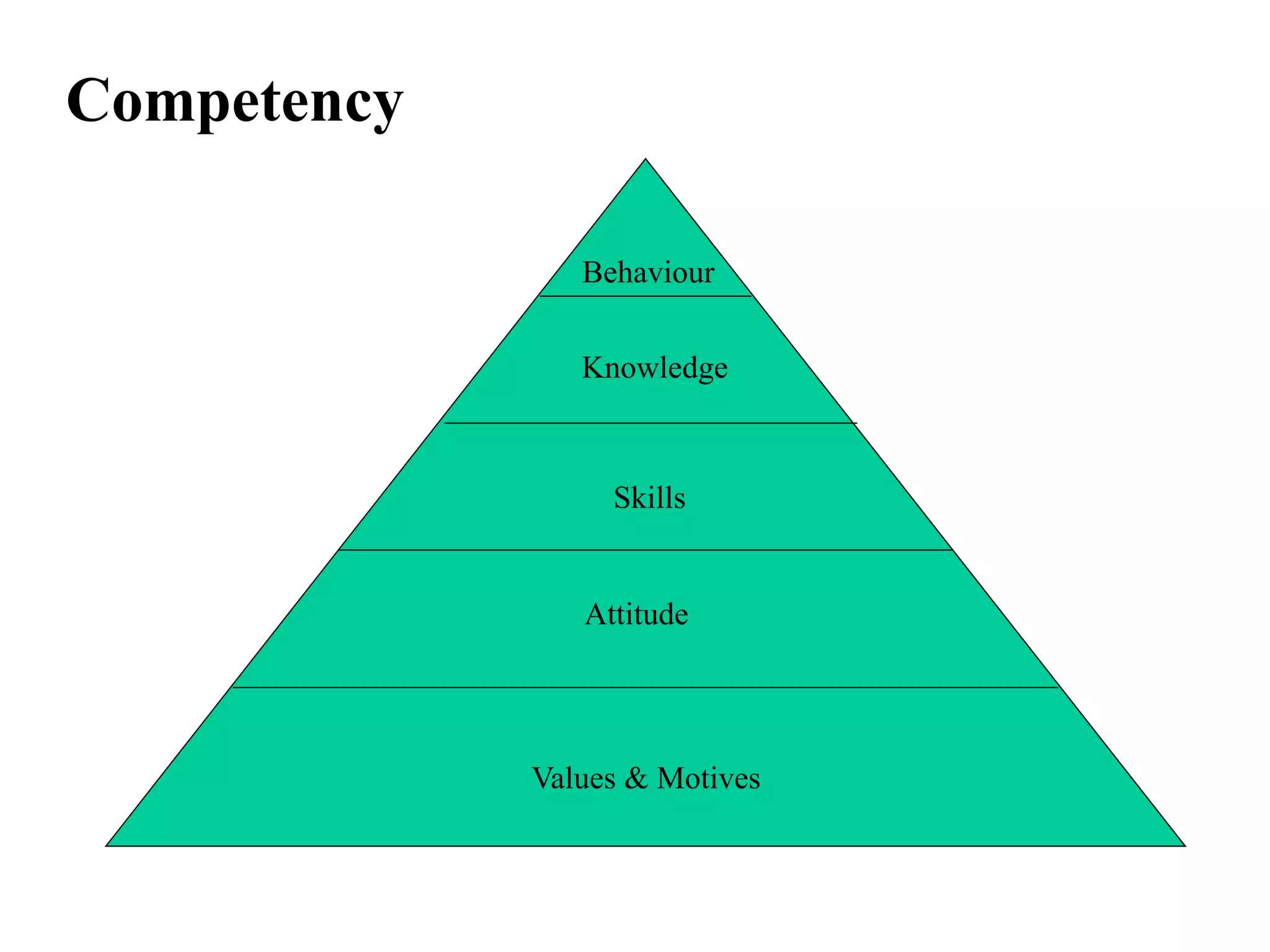
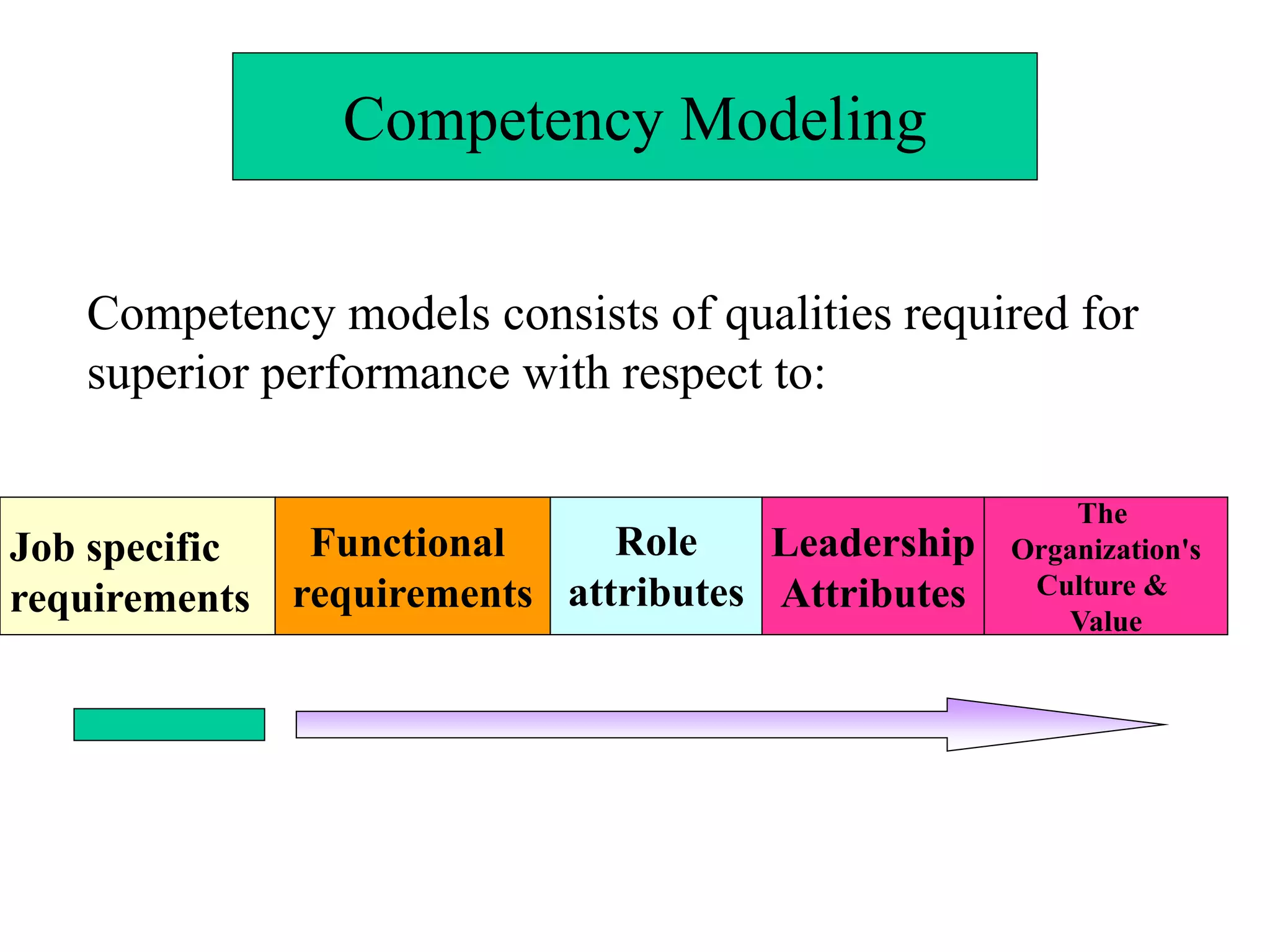
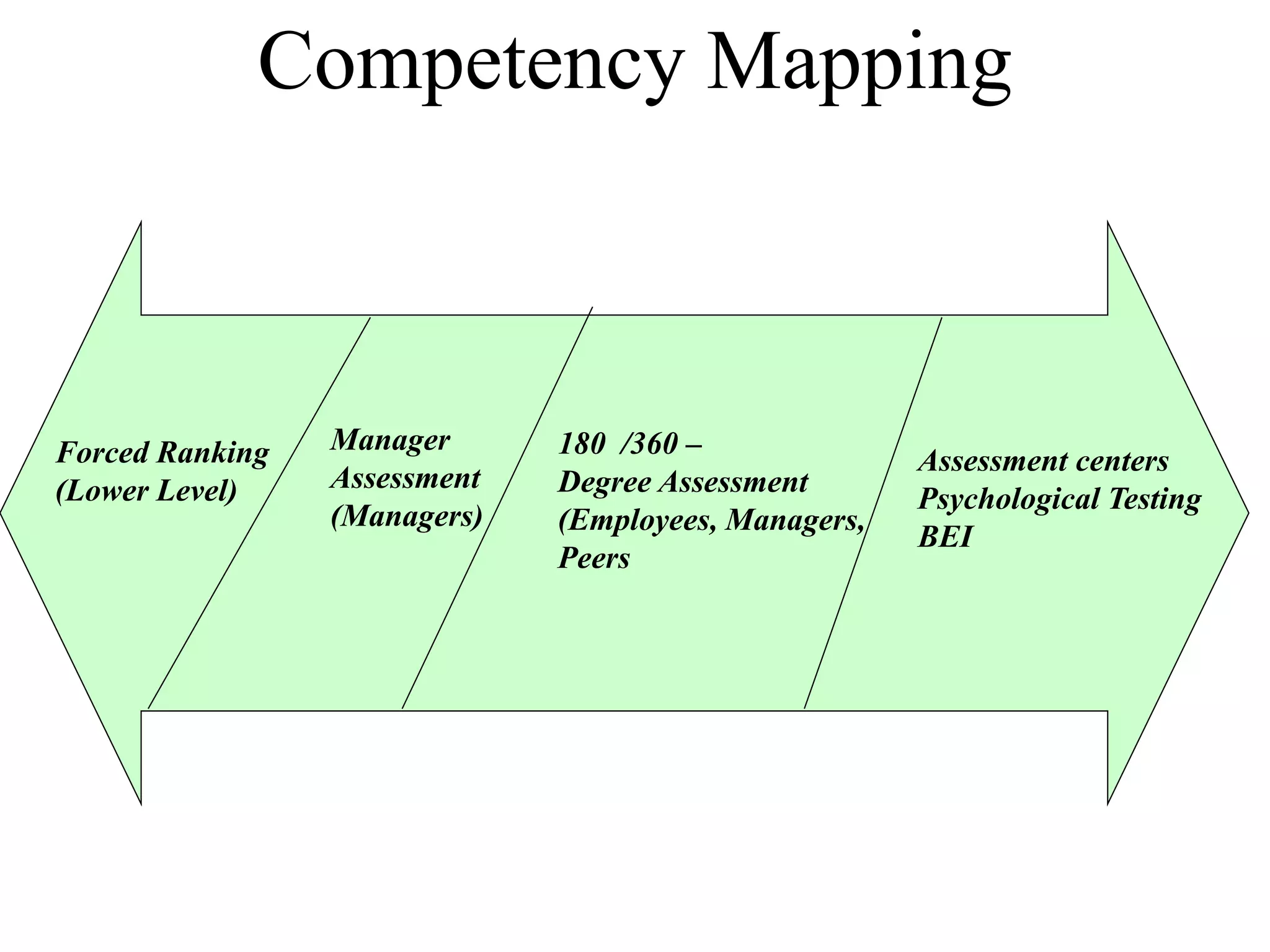
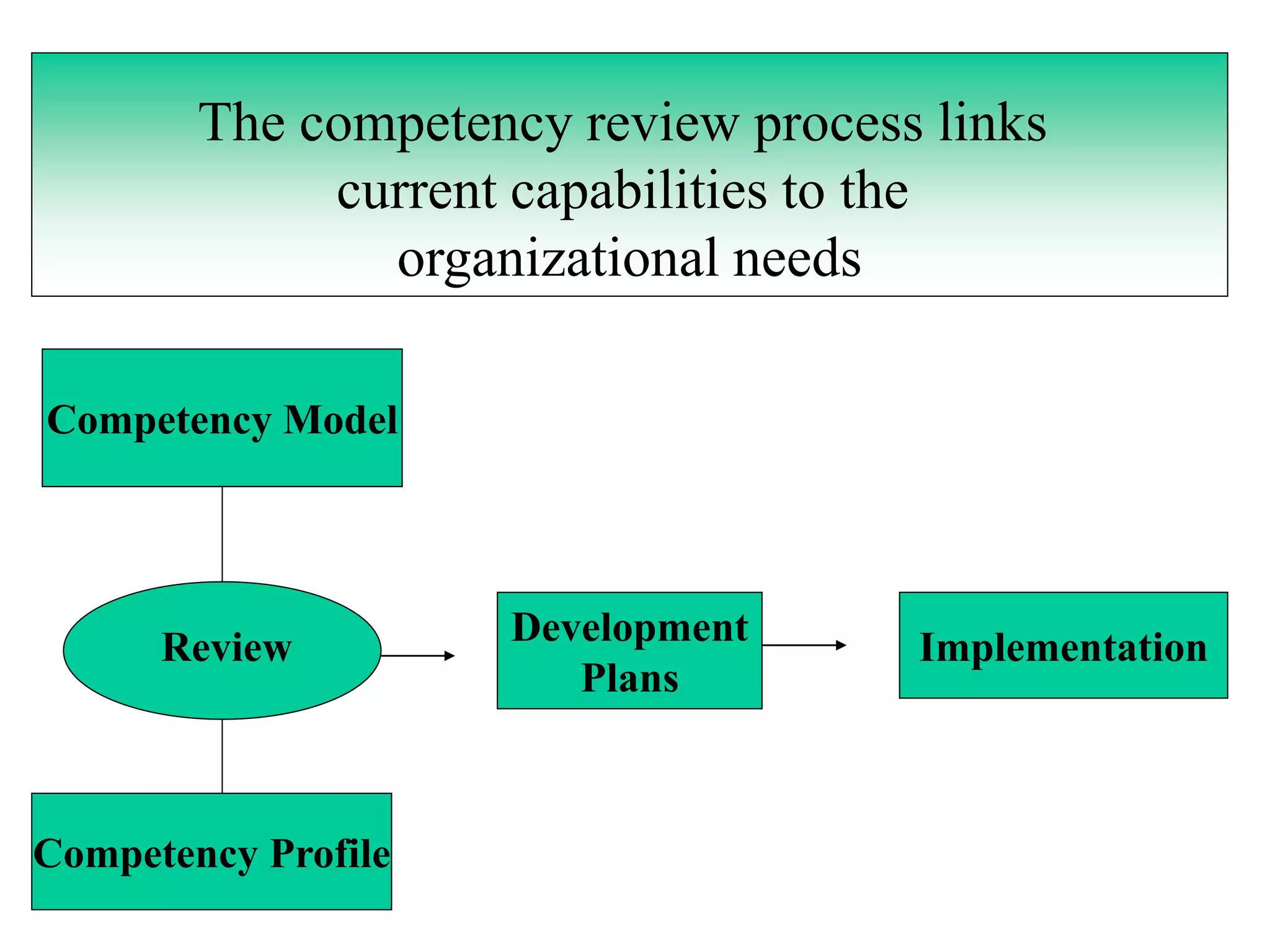
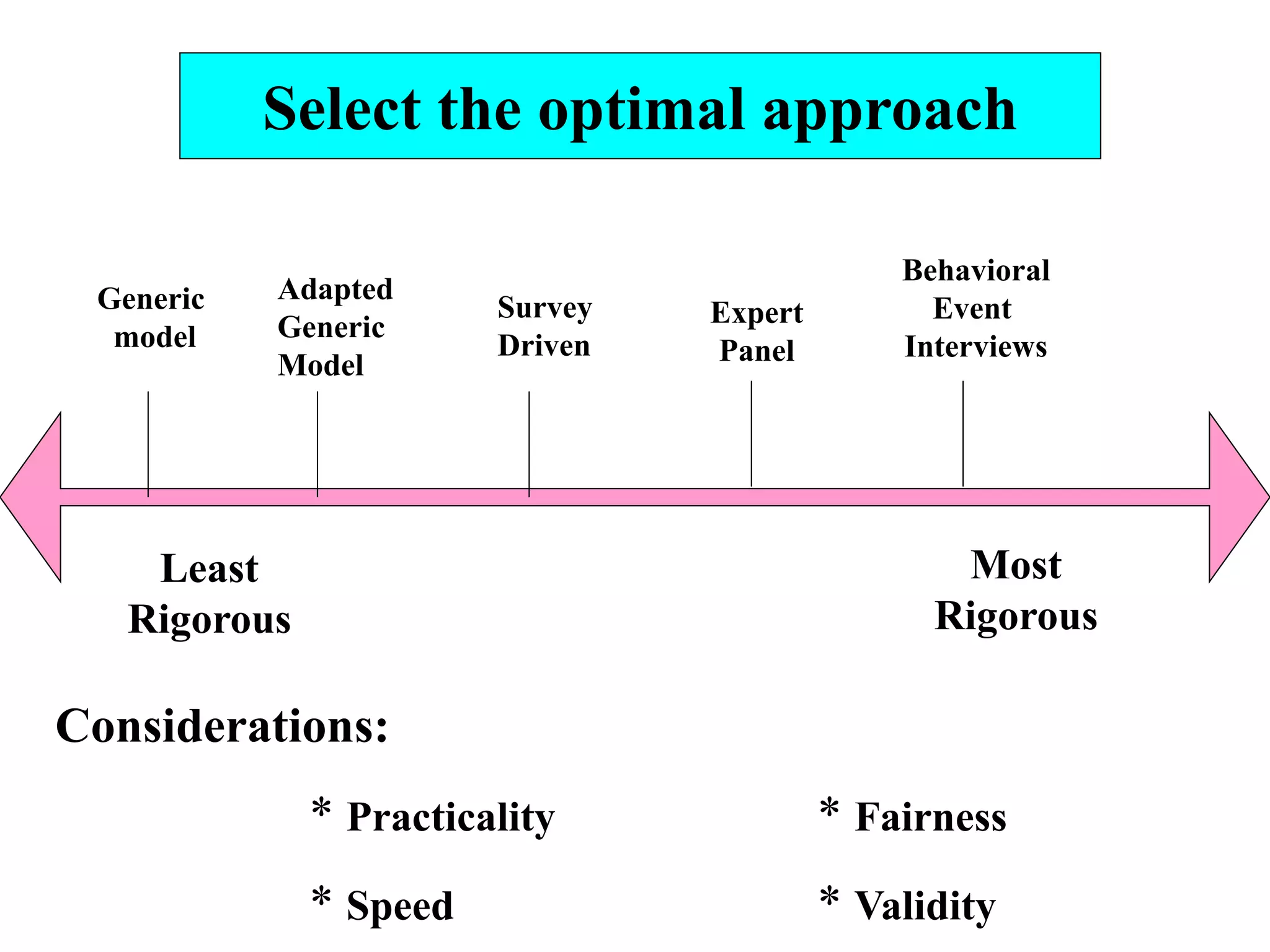
The document defines competencies as characteristics that lead to effective job performance, including skills, knowledge, abilities, and behaviors. Competency models identify the competencies needed for different roles and levels of work. Developing competency models involves collecting data through methods like behavioral interviews, expert panels, surveys, and job analysis. Models can be designed for specific jobs, functions, levels, or the whole organization. The level of proficiency in competencies expected varies by role and seniority.