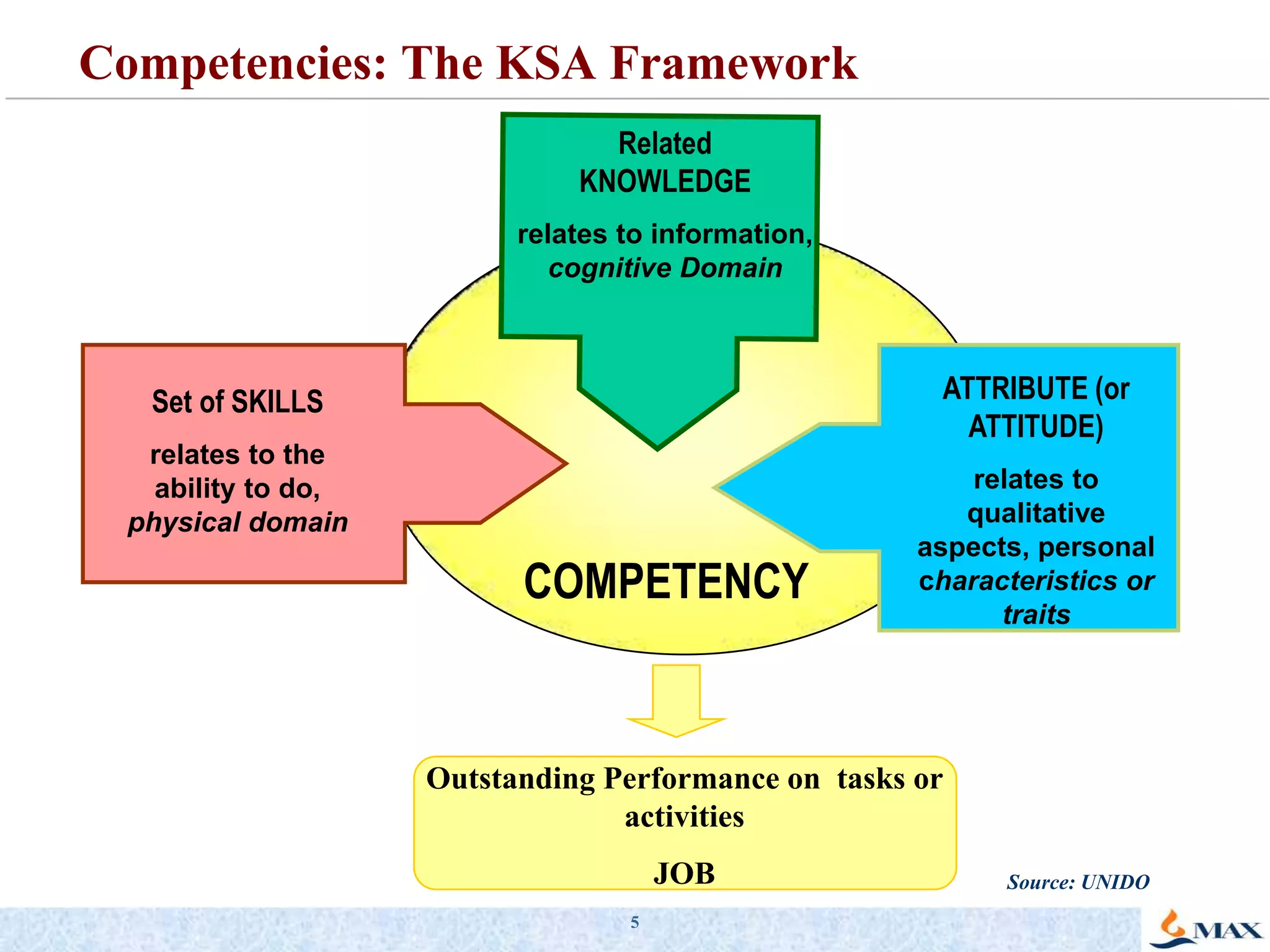
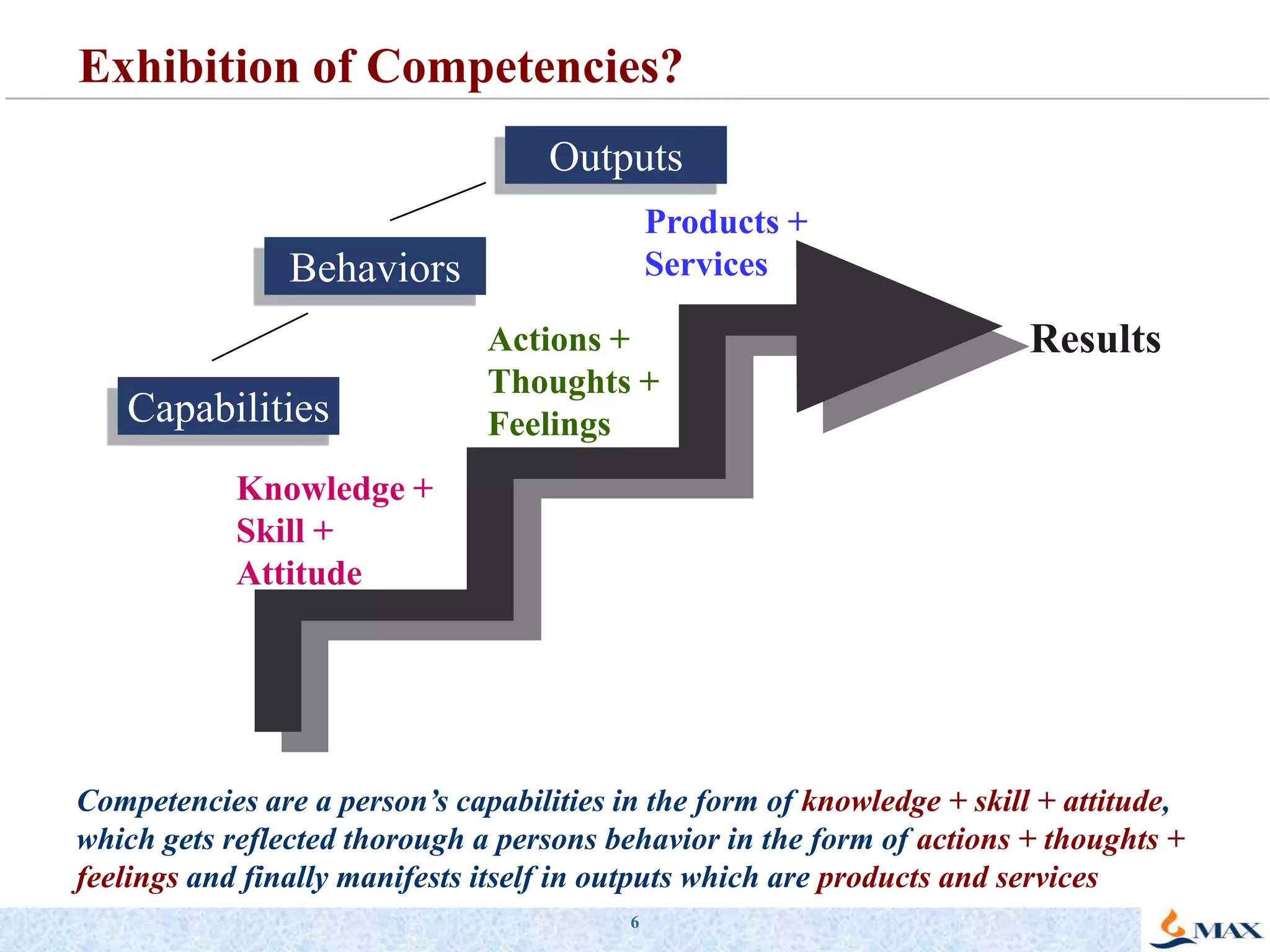
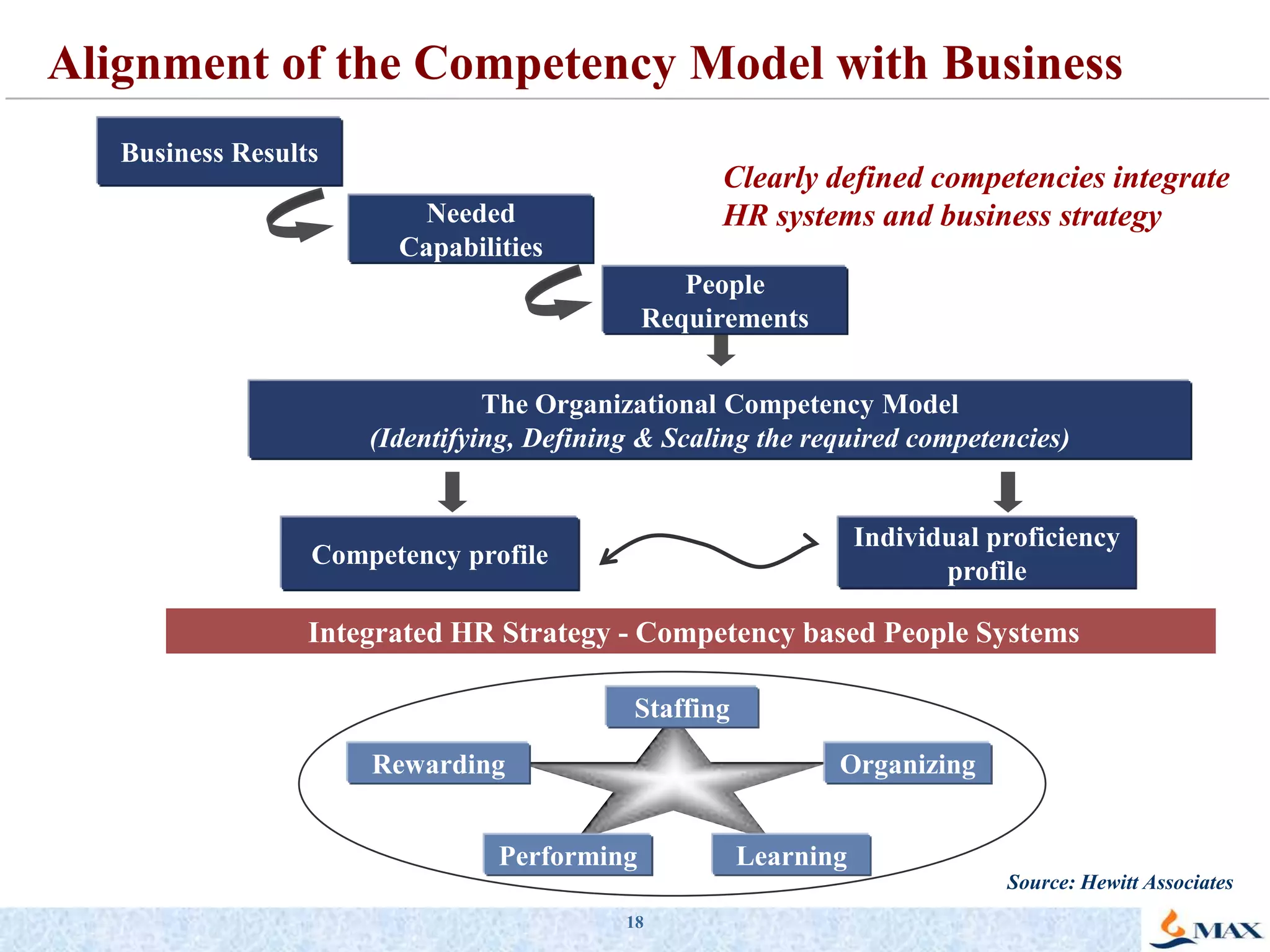
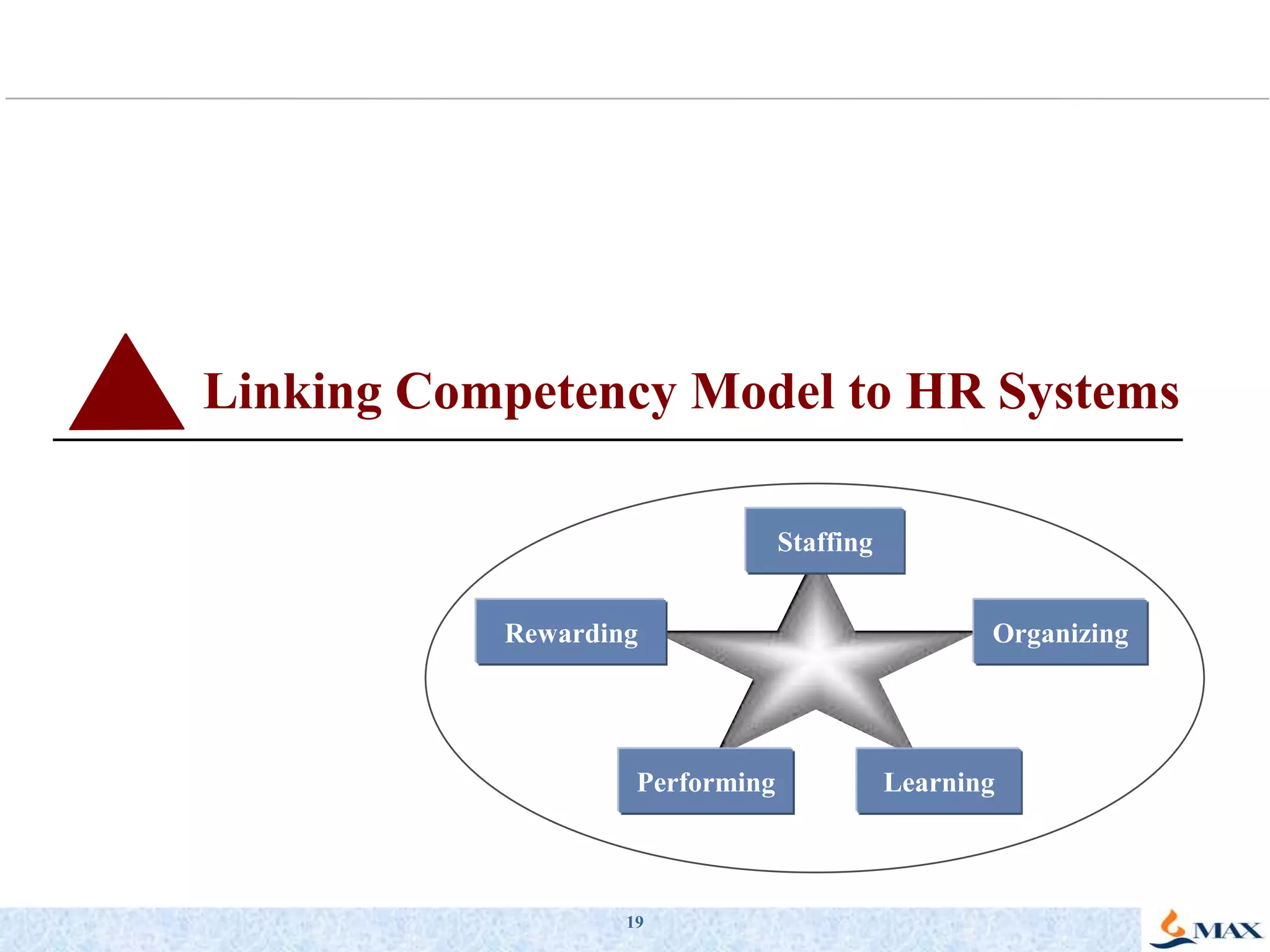
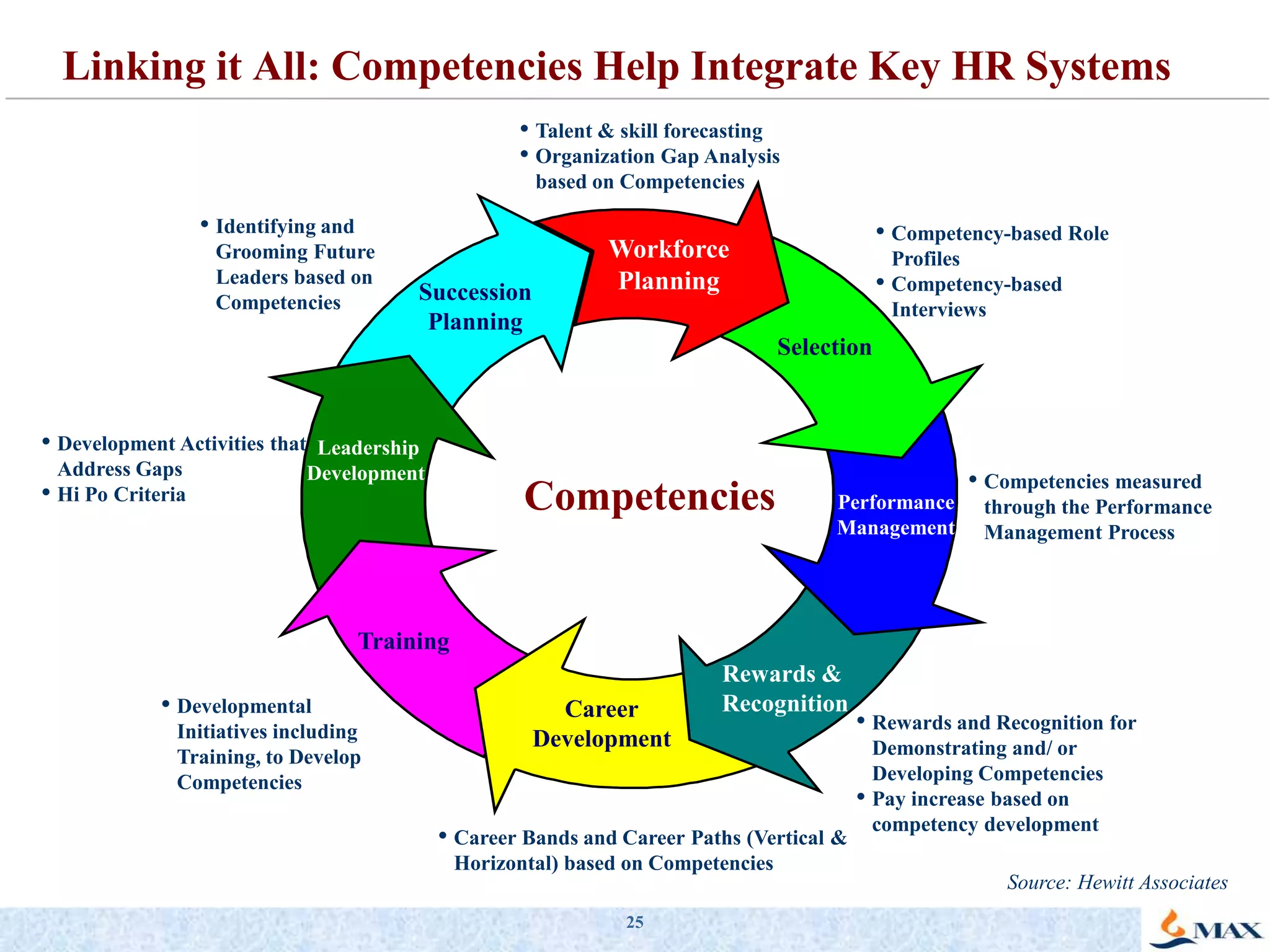
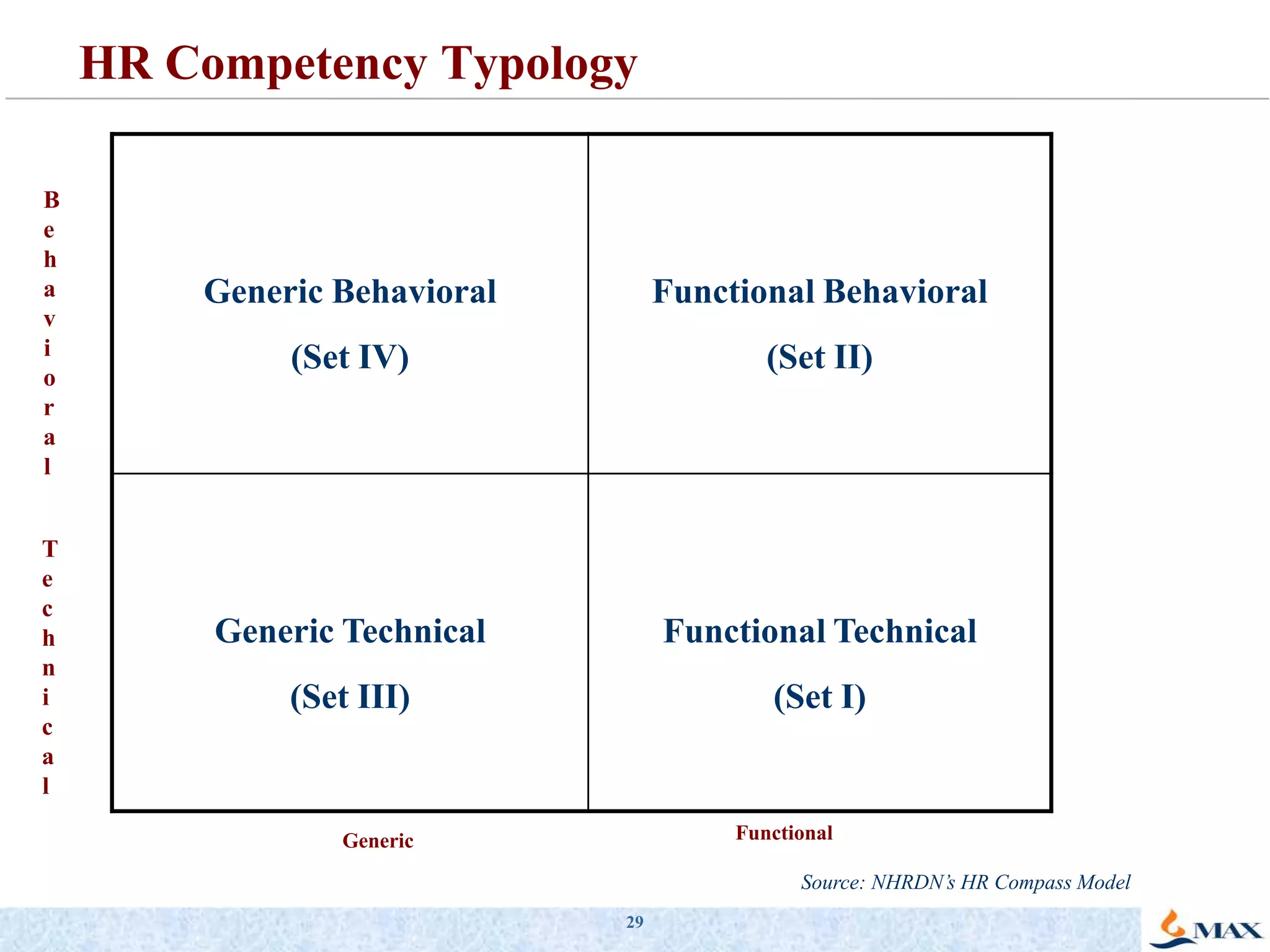
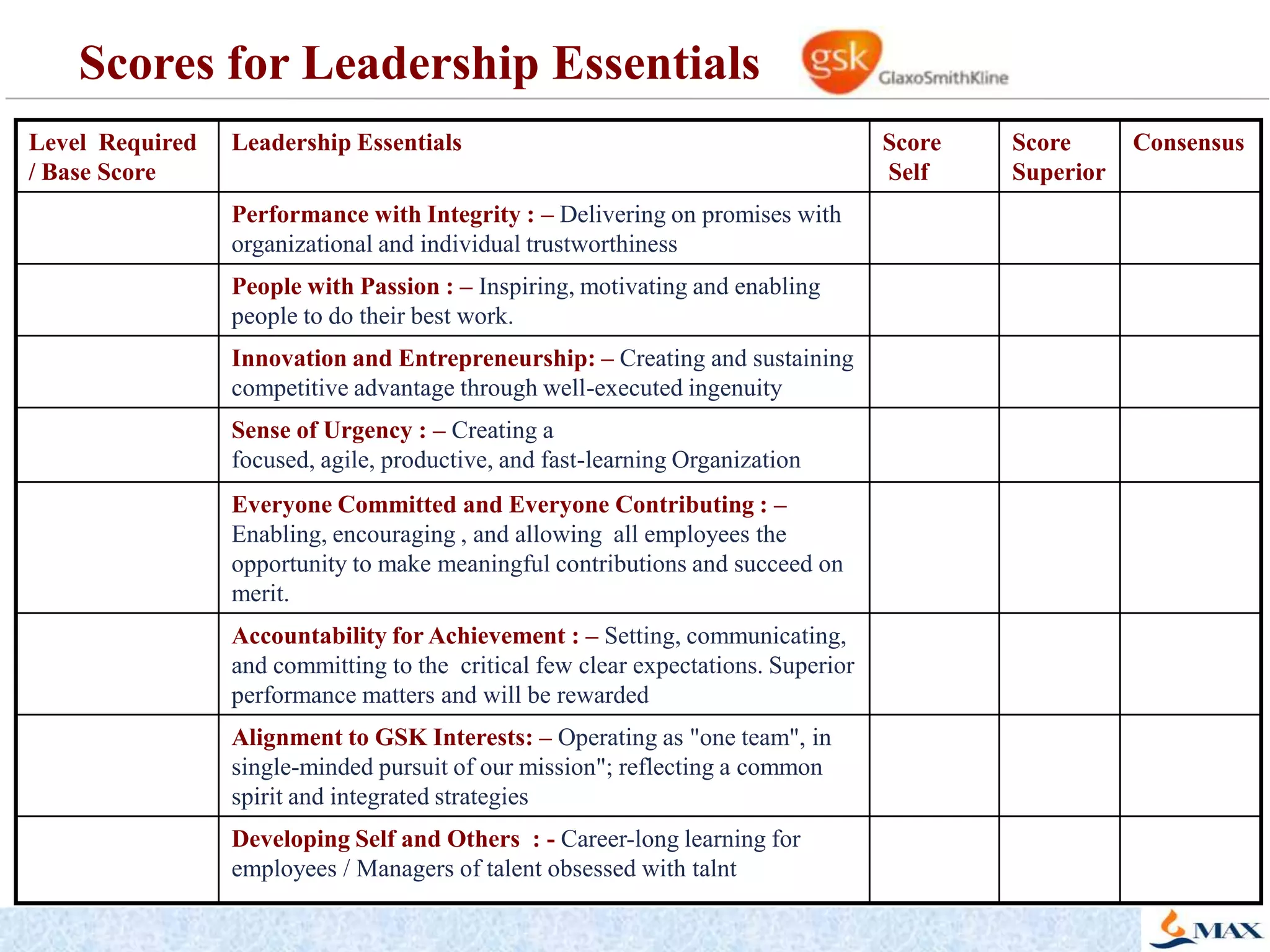
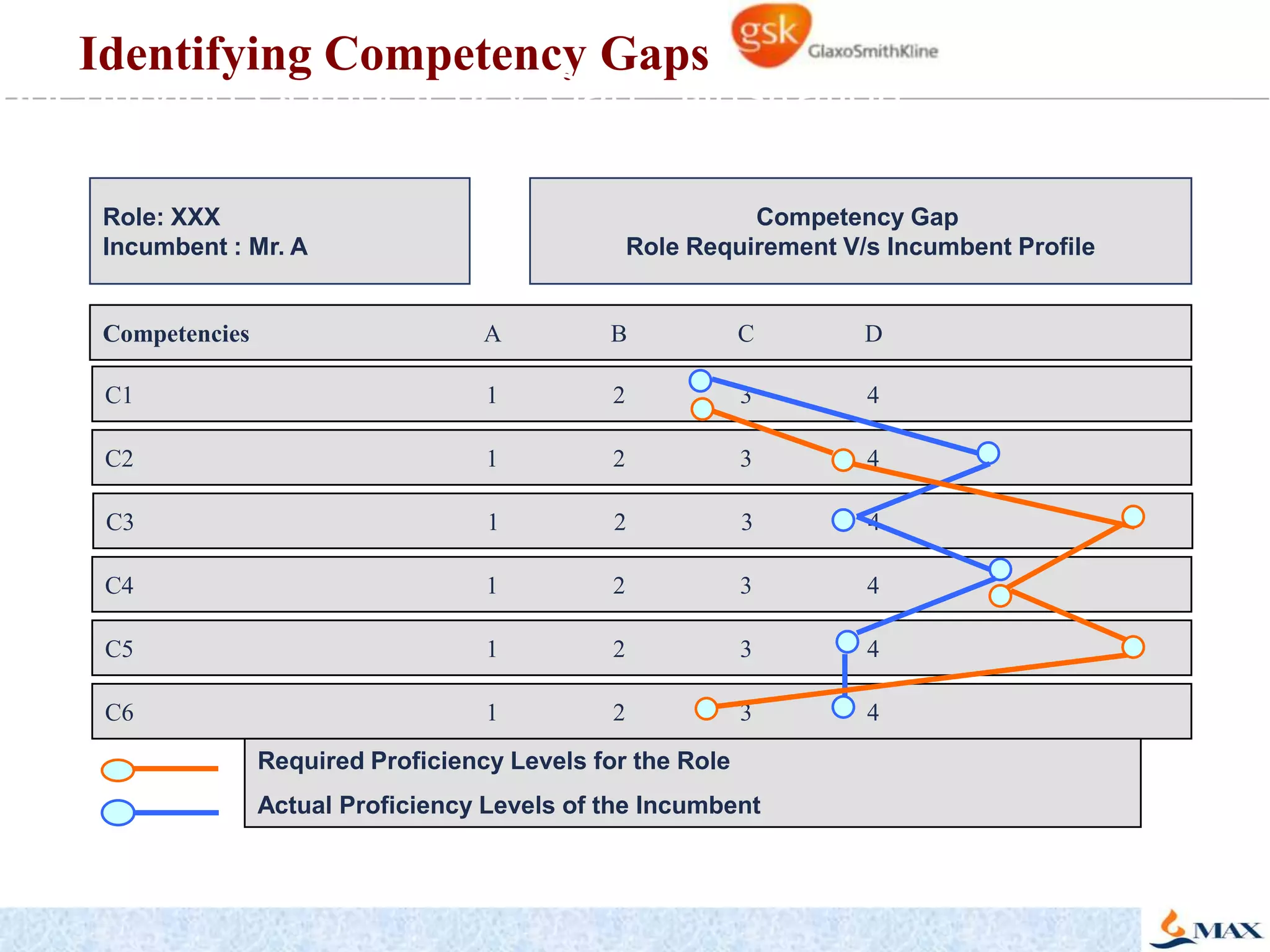
This document discusses competency models and their importance and use in human resource systems. It defines competencies as underlying characteristics like knowledge, skills, attitudes, and behaviors that result in effective job performance. Competency models identify the competencies required for successful performance in roles. When competency models are developed correctly and integrated into key HR systems like staffing, learning, performance management and rewards, they can help align an organization's people strategies with its business goals and strategies. This allows the organization to have the right people with the right skills to achieve business objectives. The document provides examples of competency models and their use in different HR systems from various organizations.