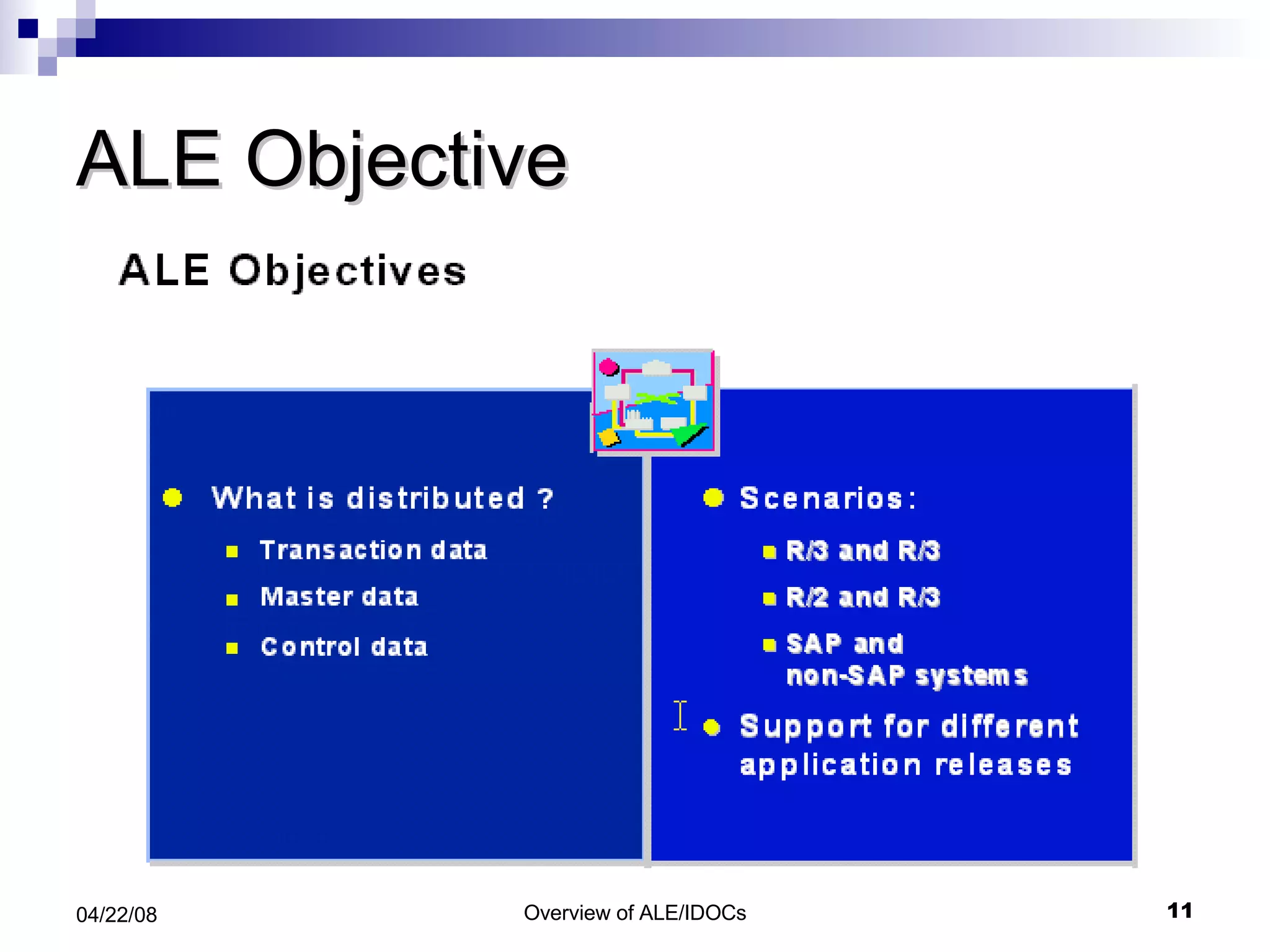
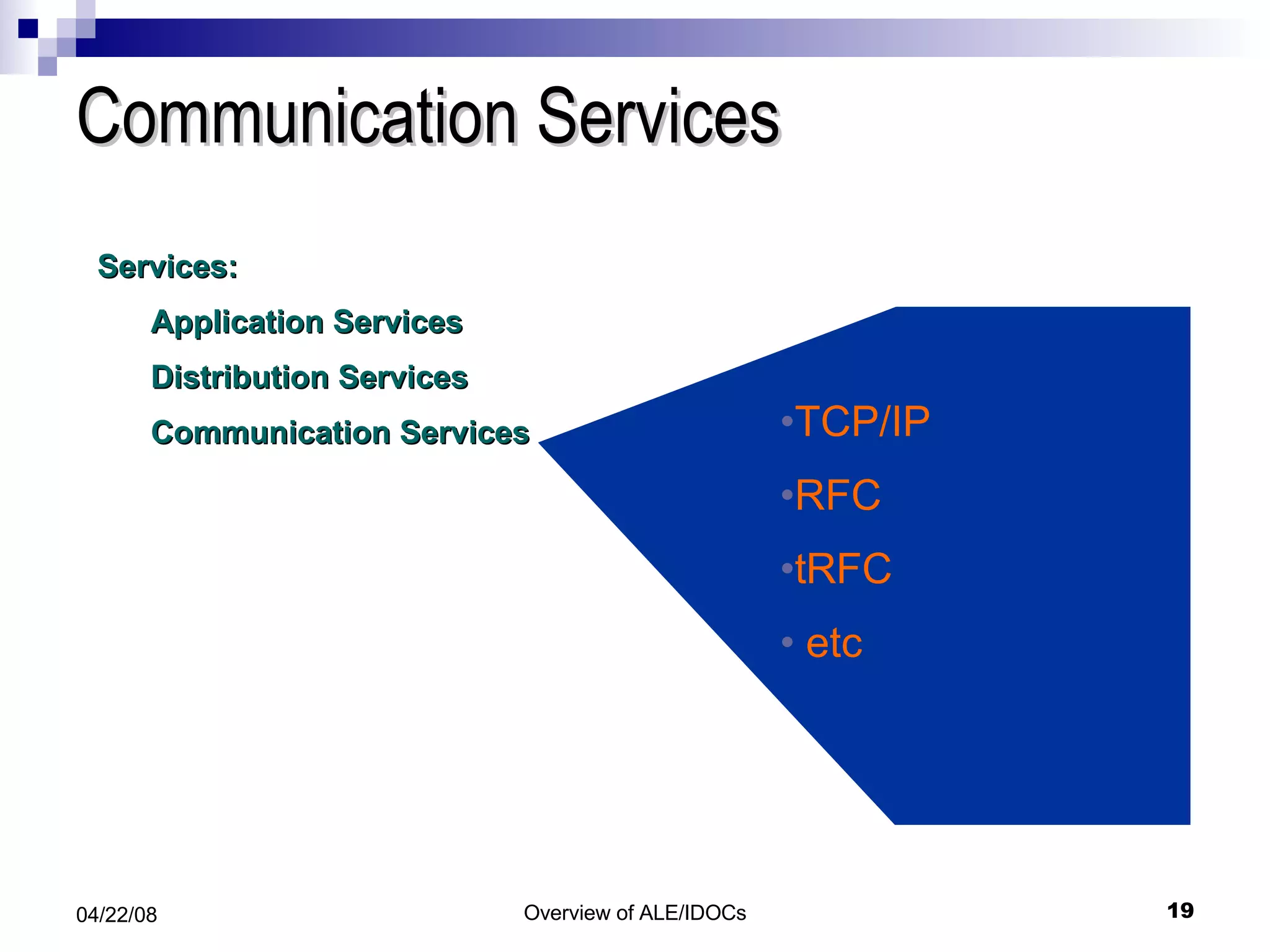
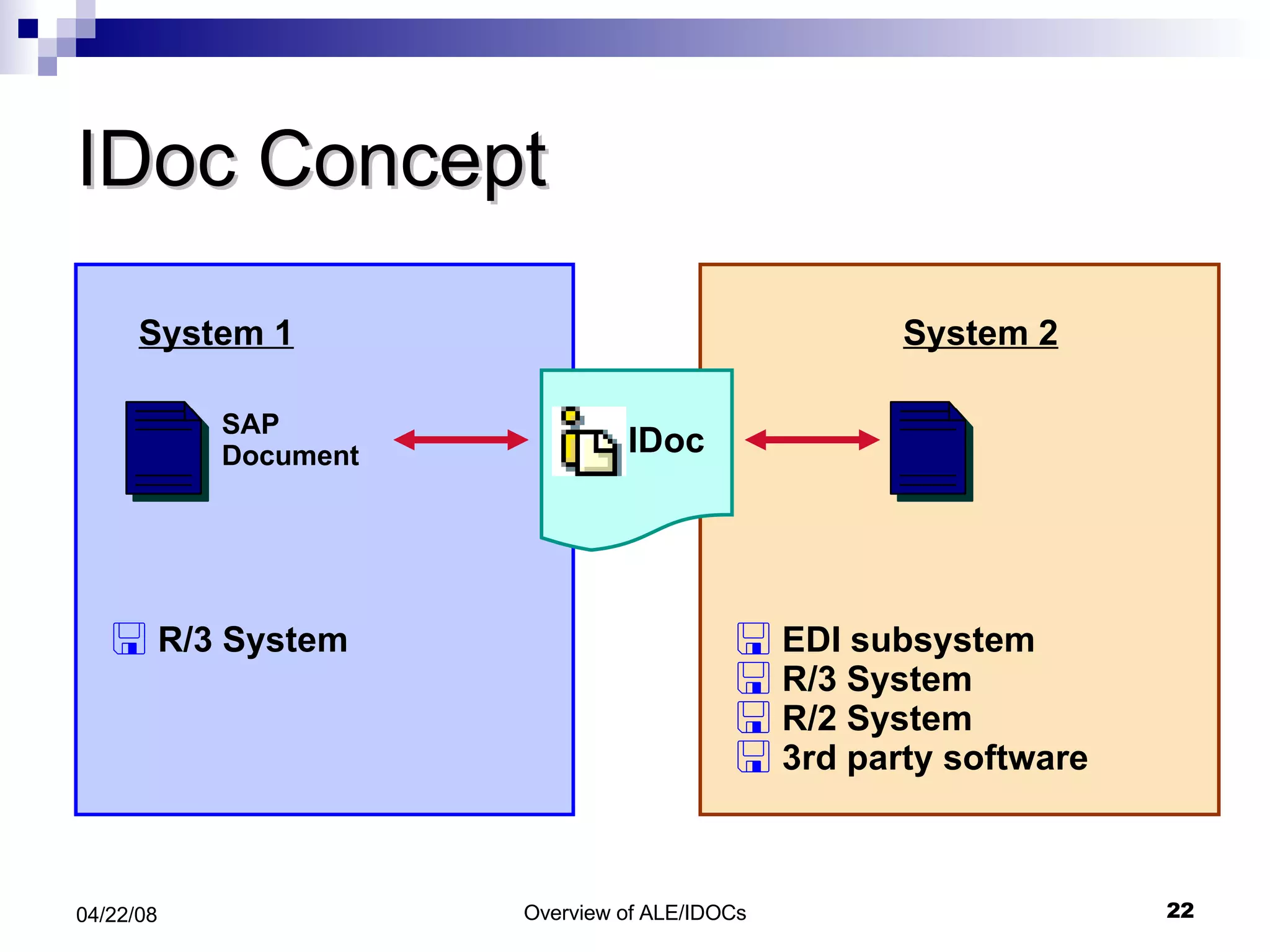
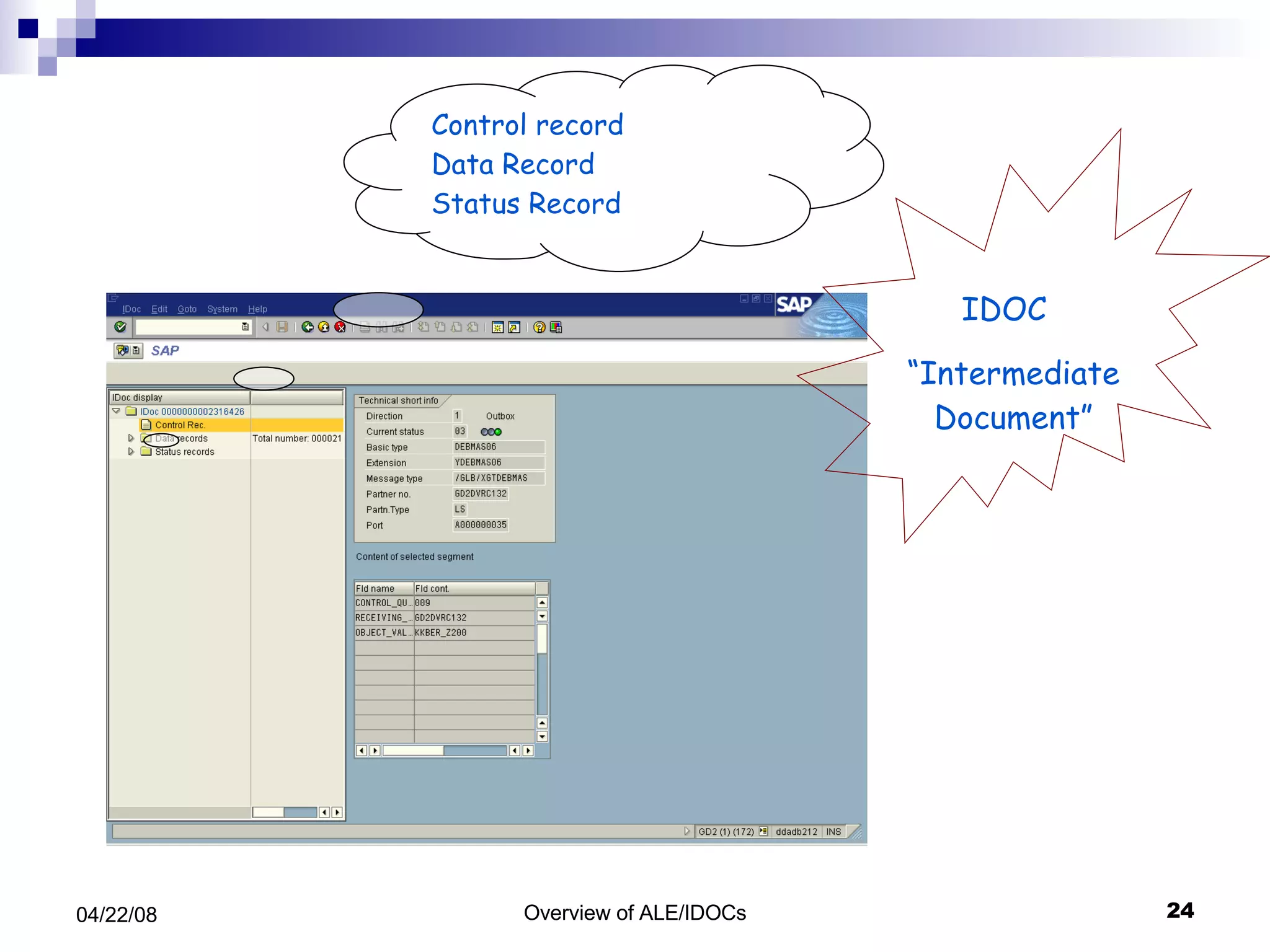
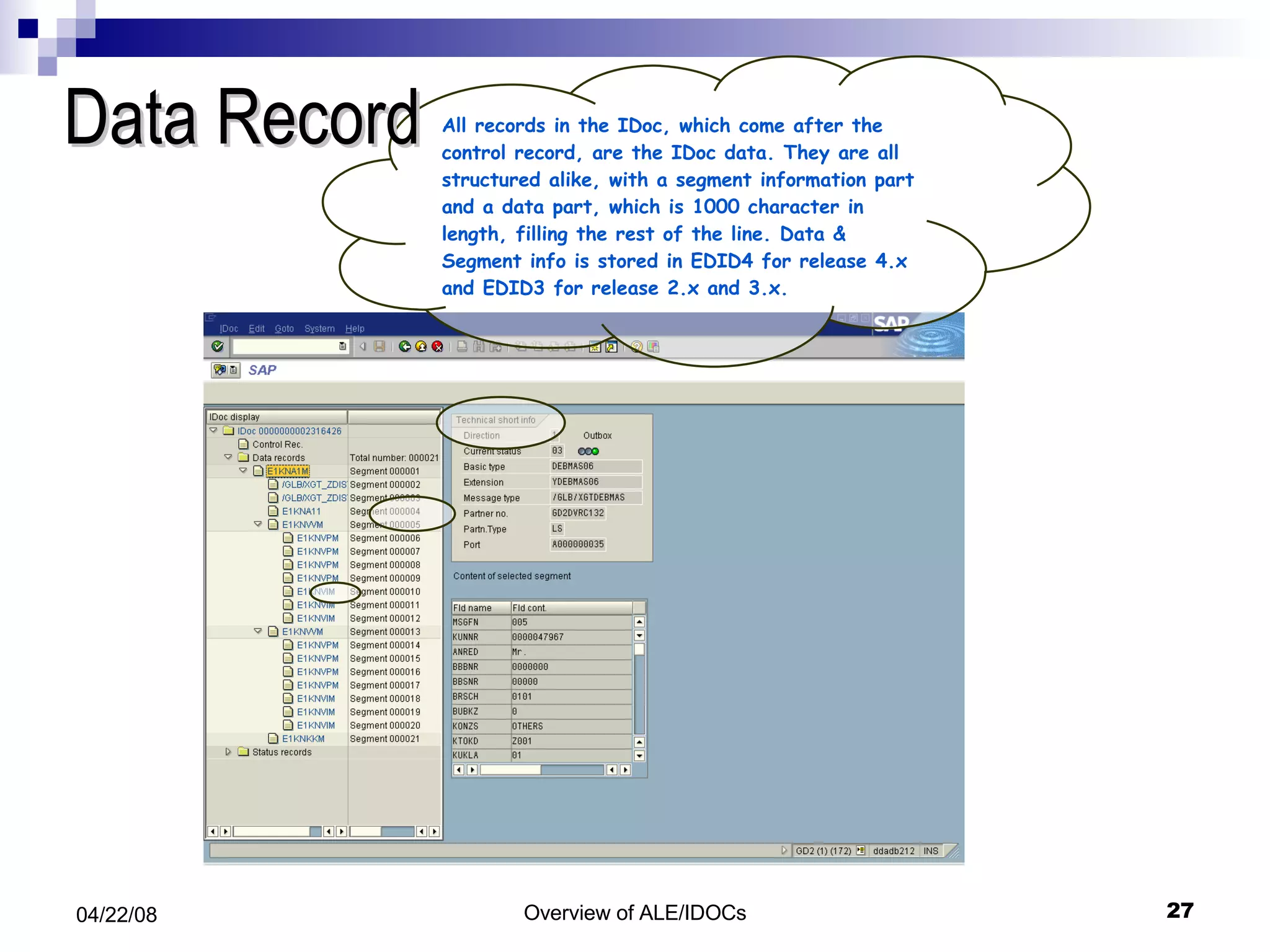
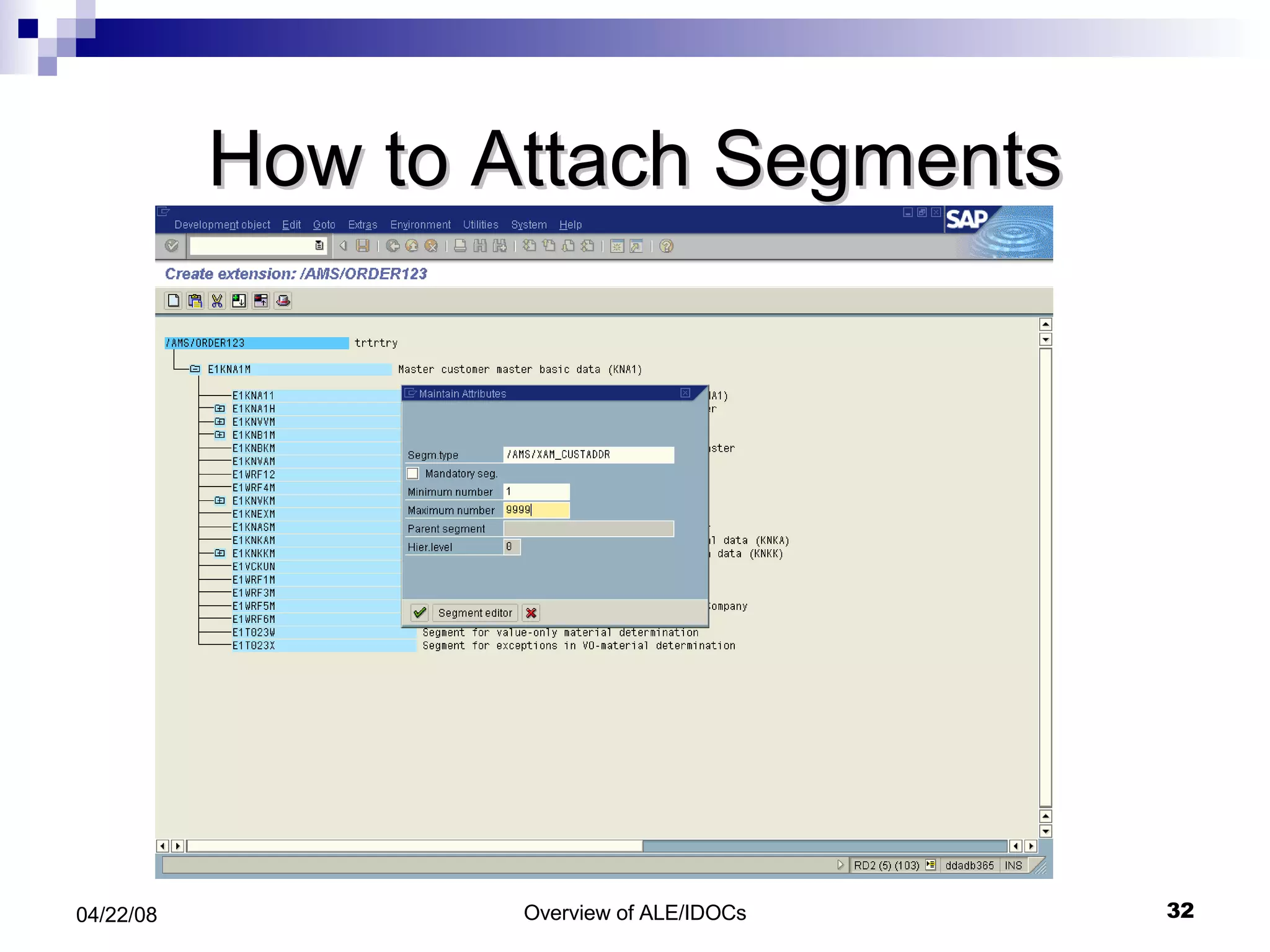
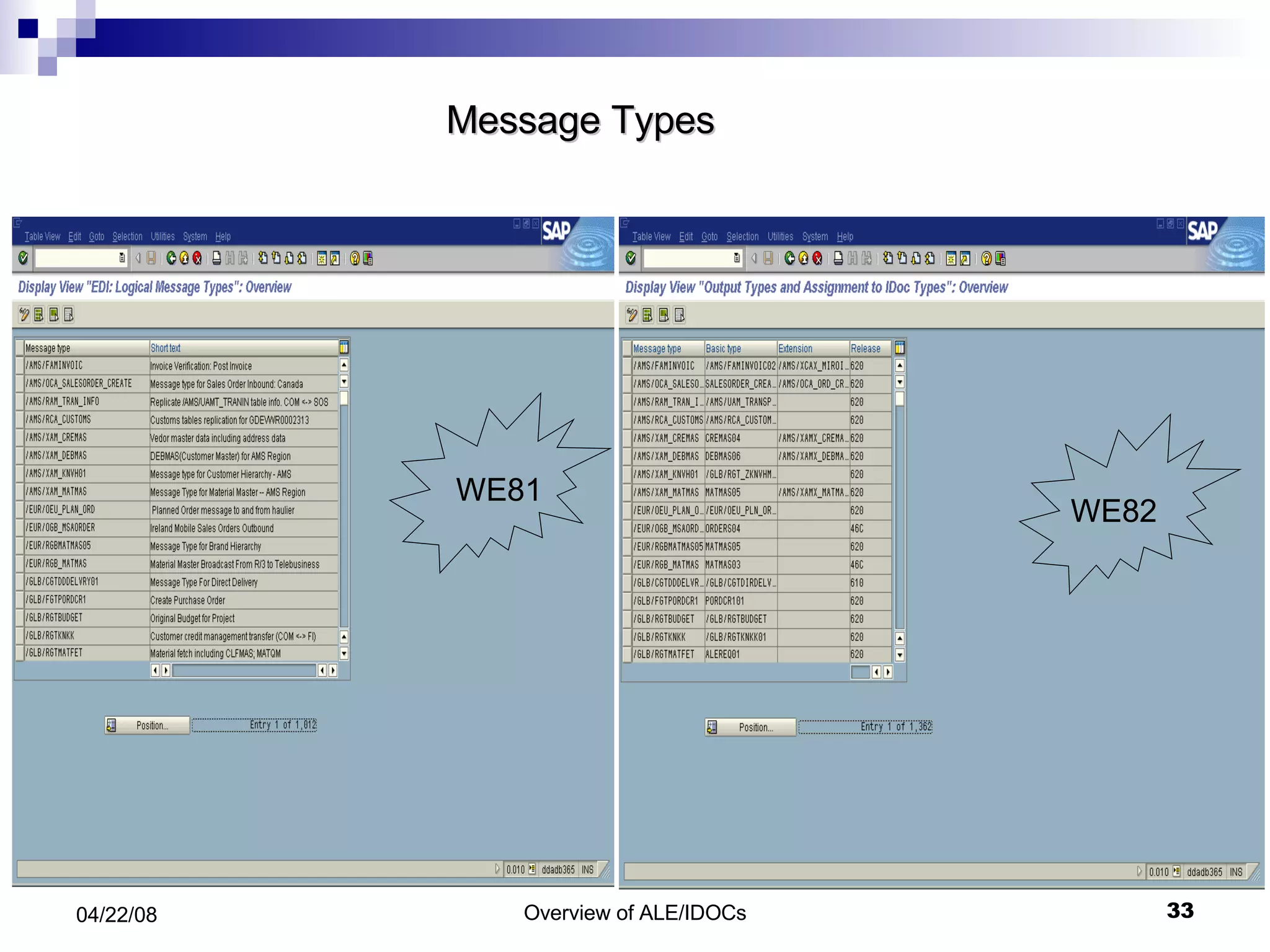
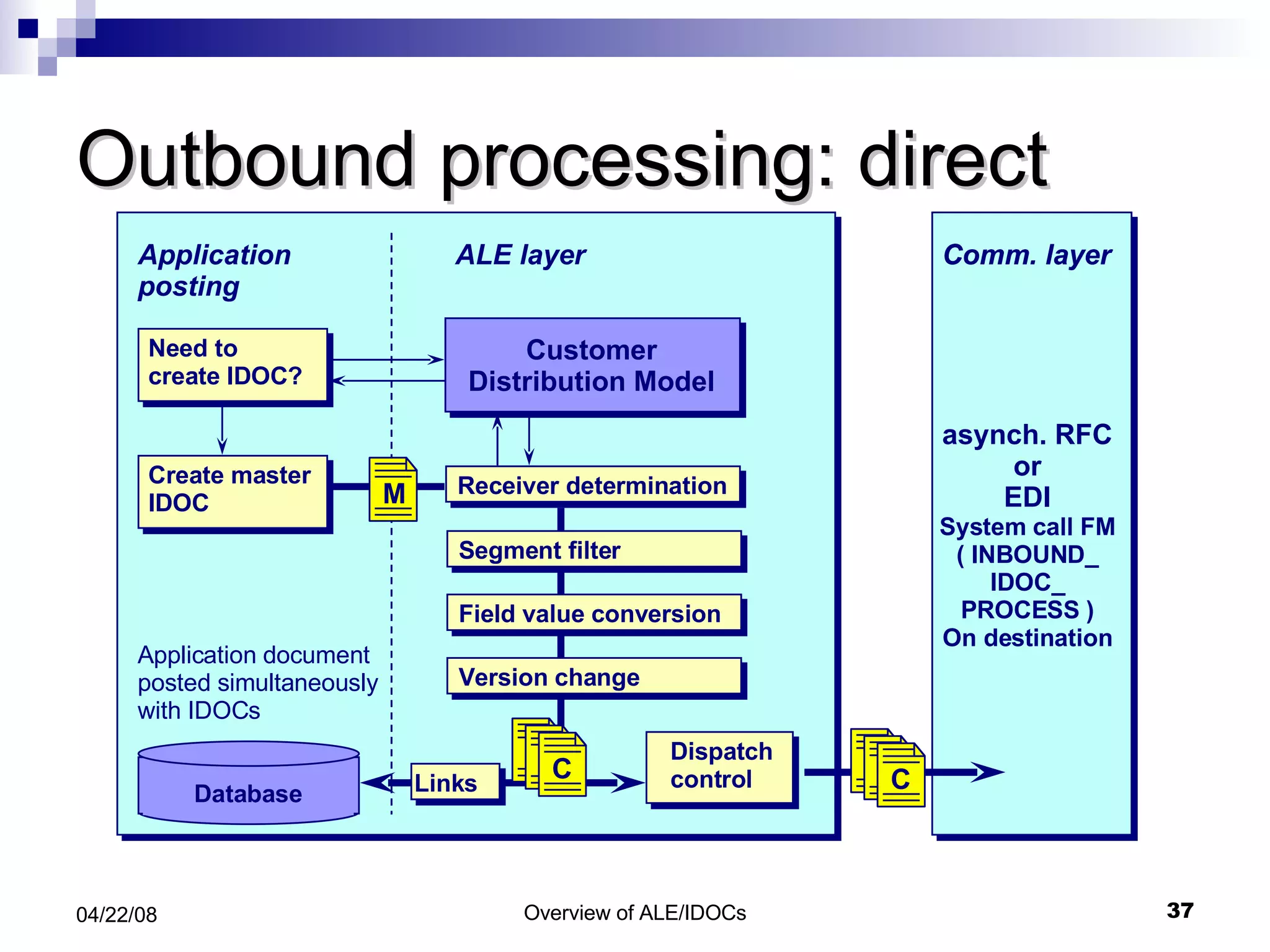
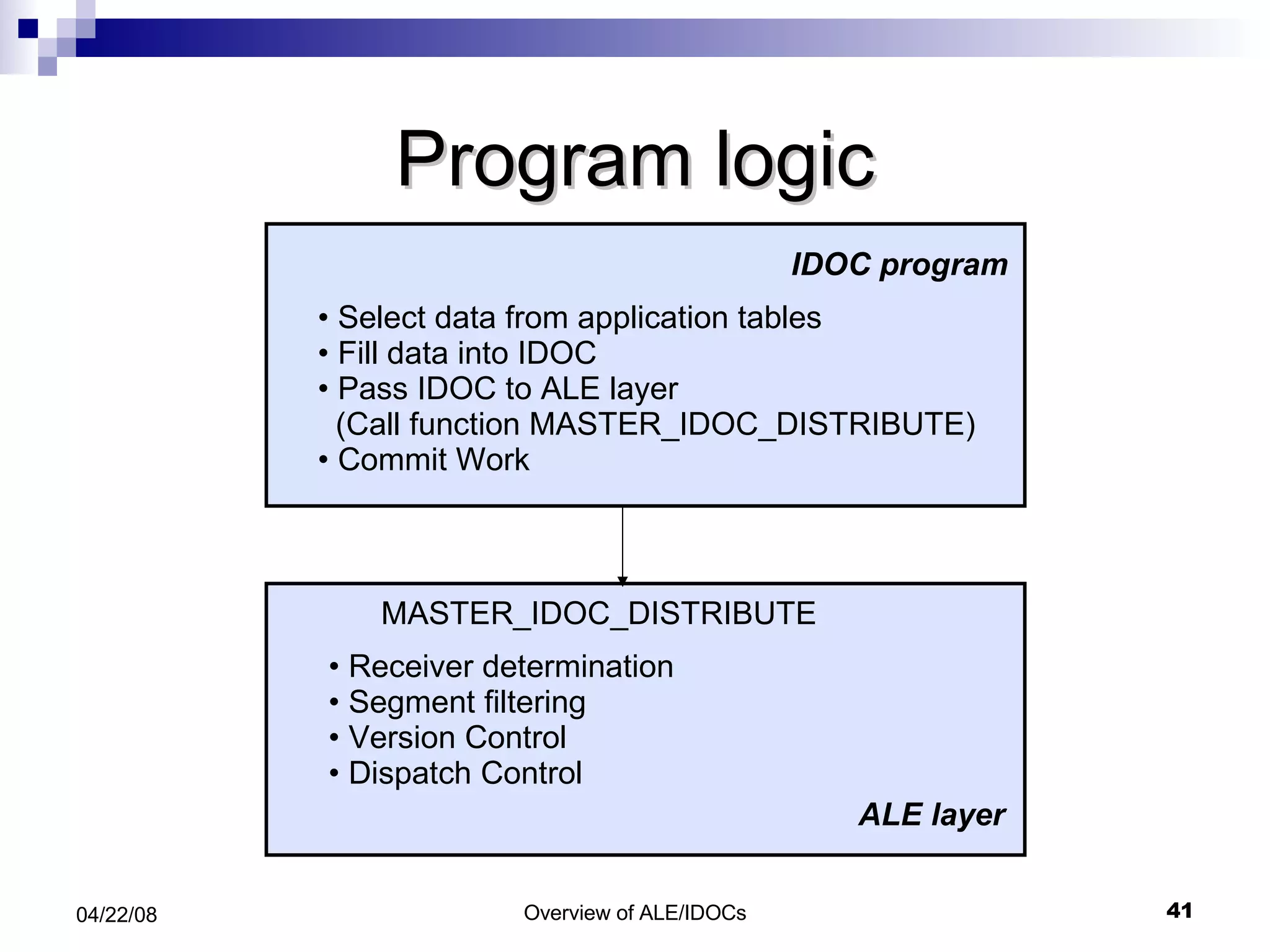
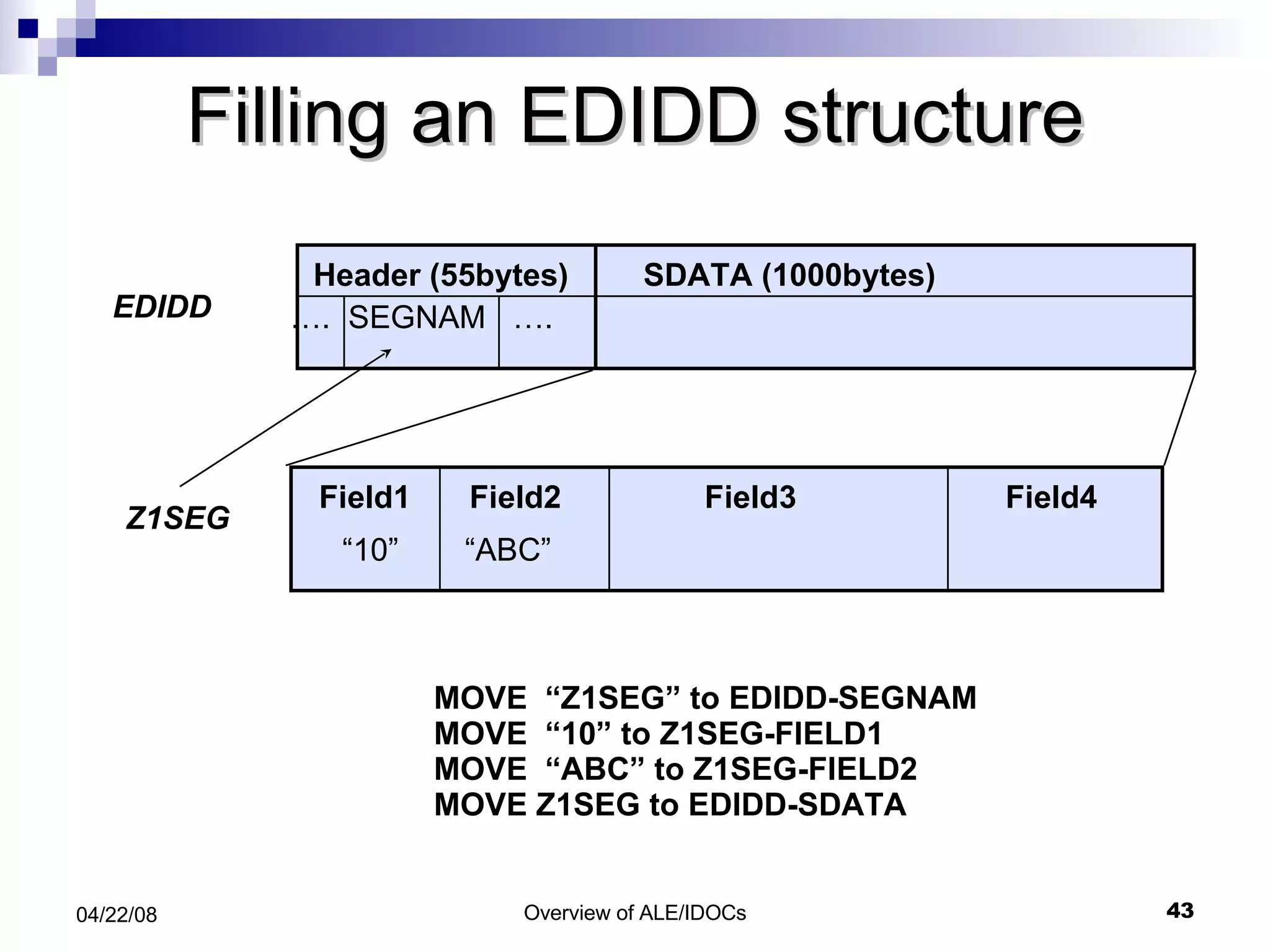
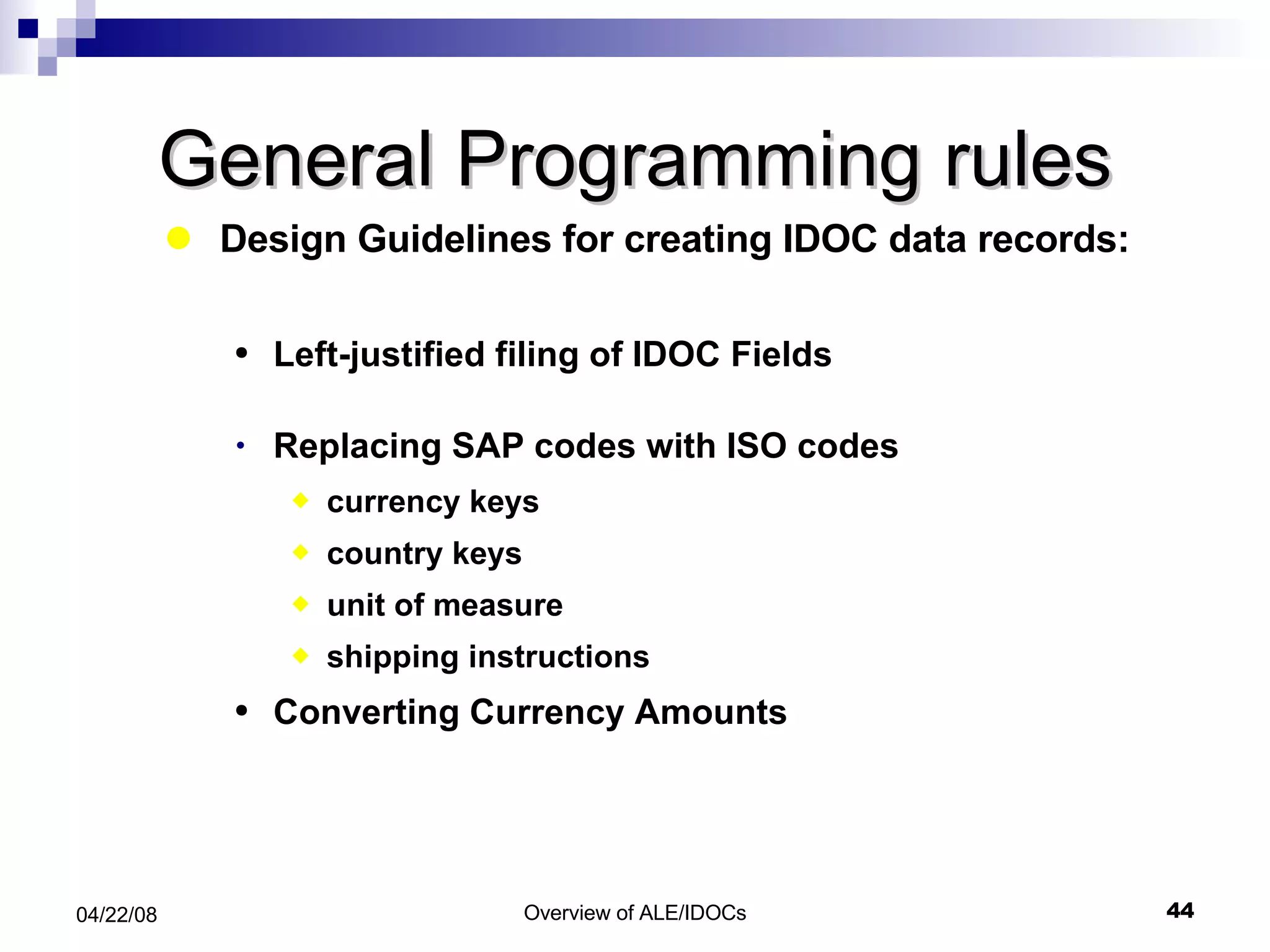
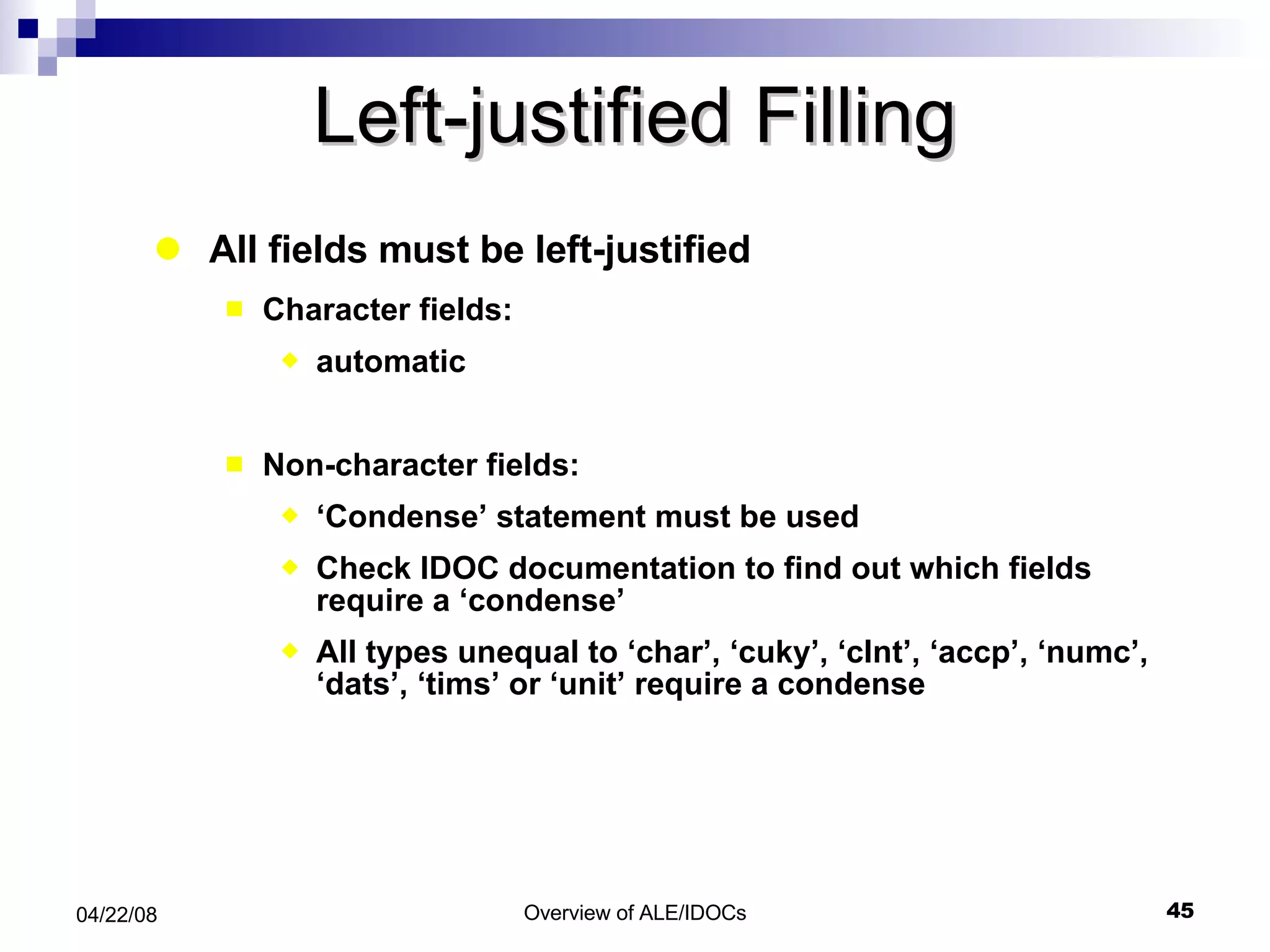
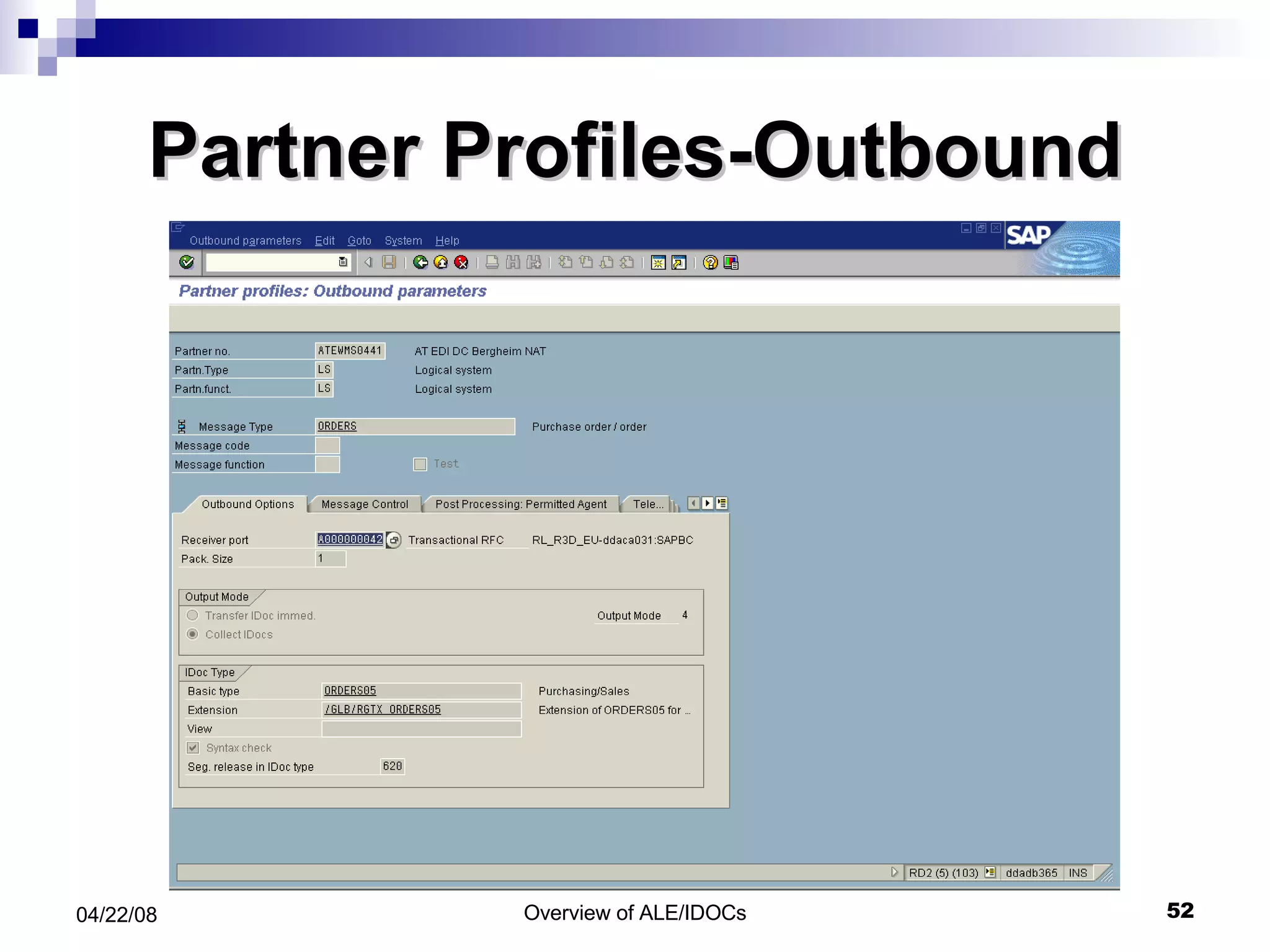
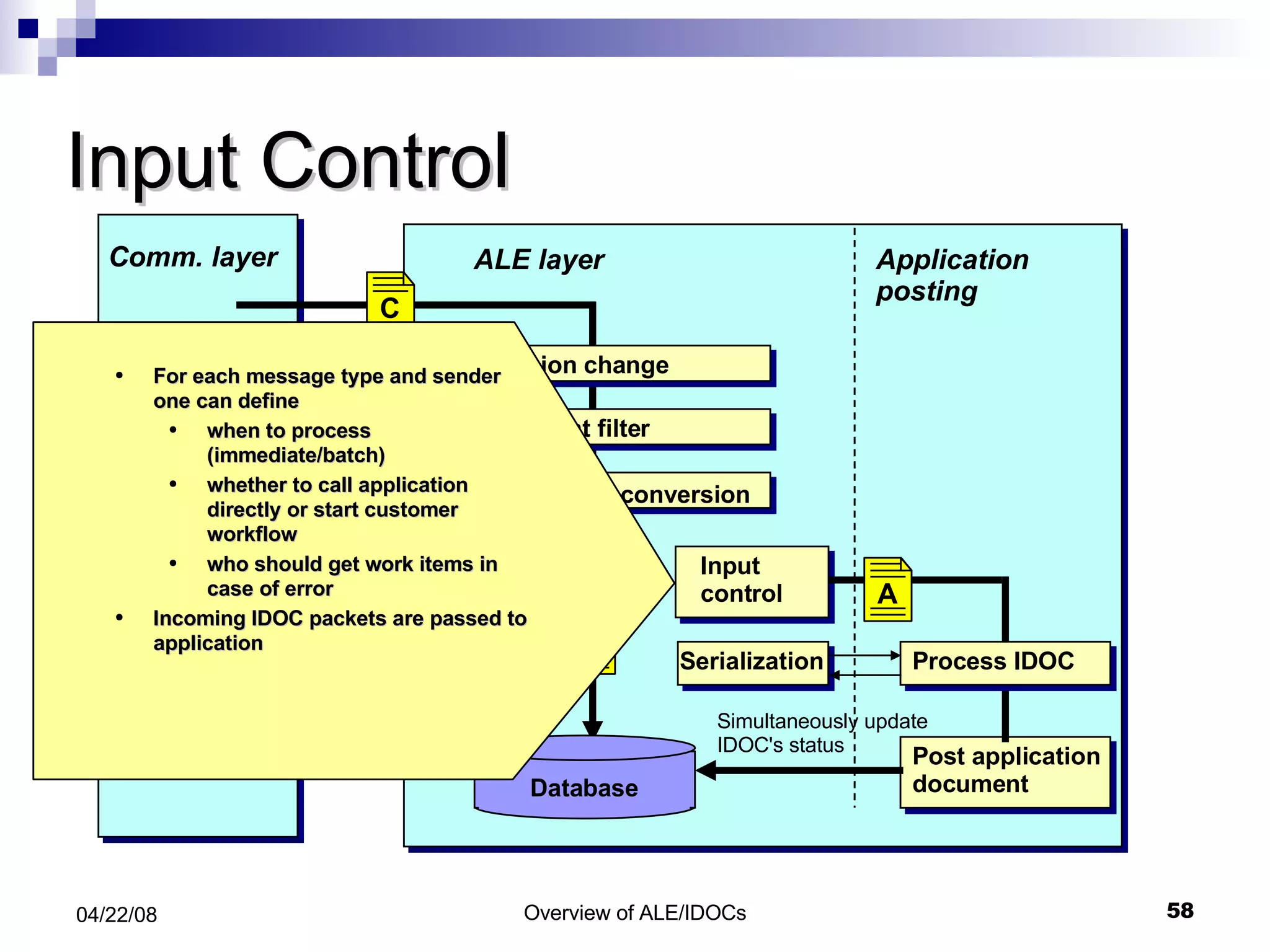
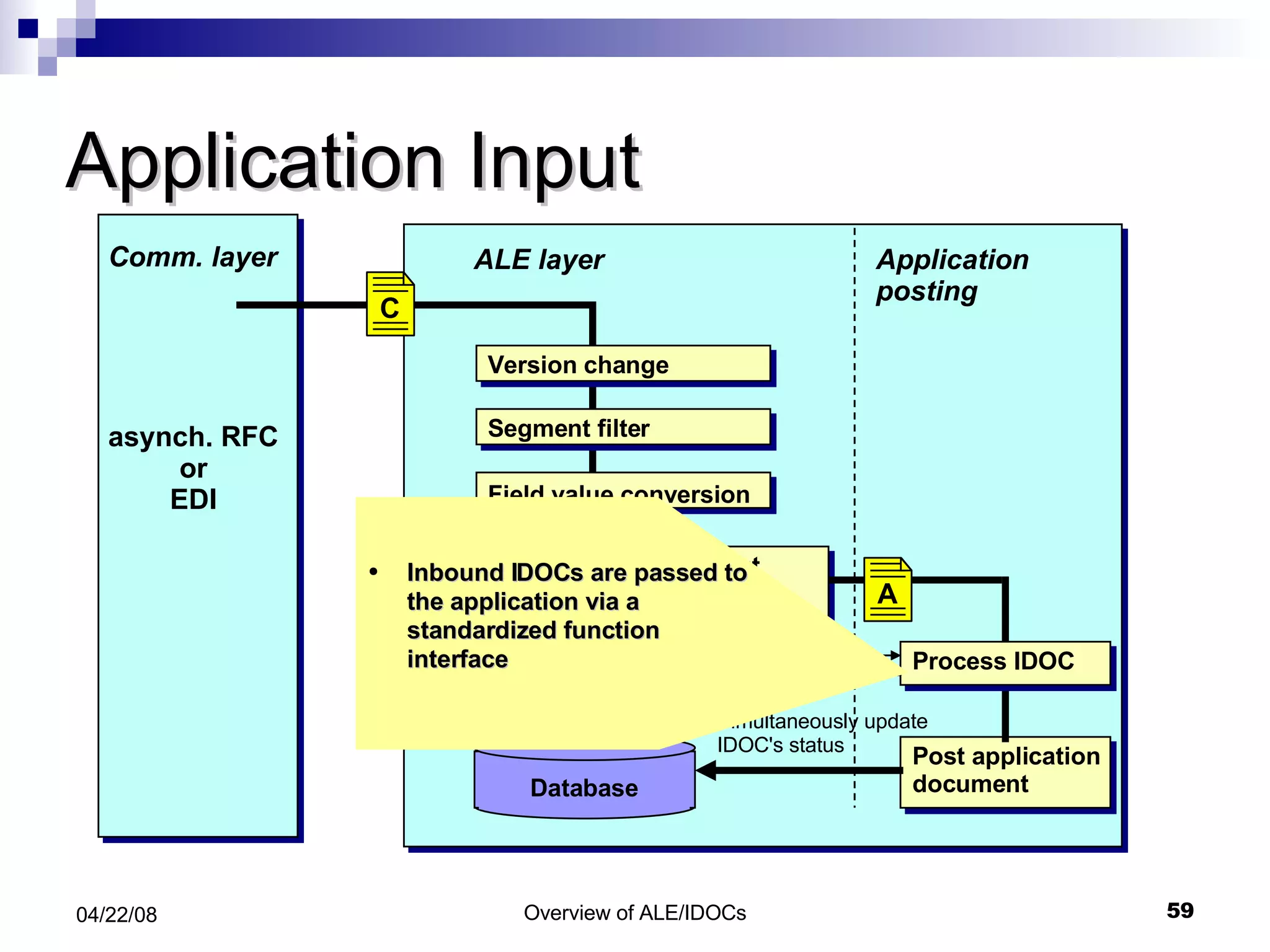
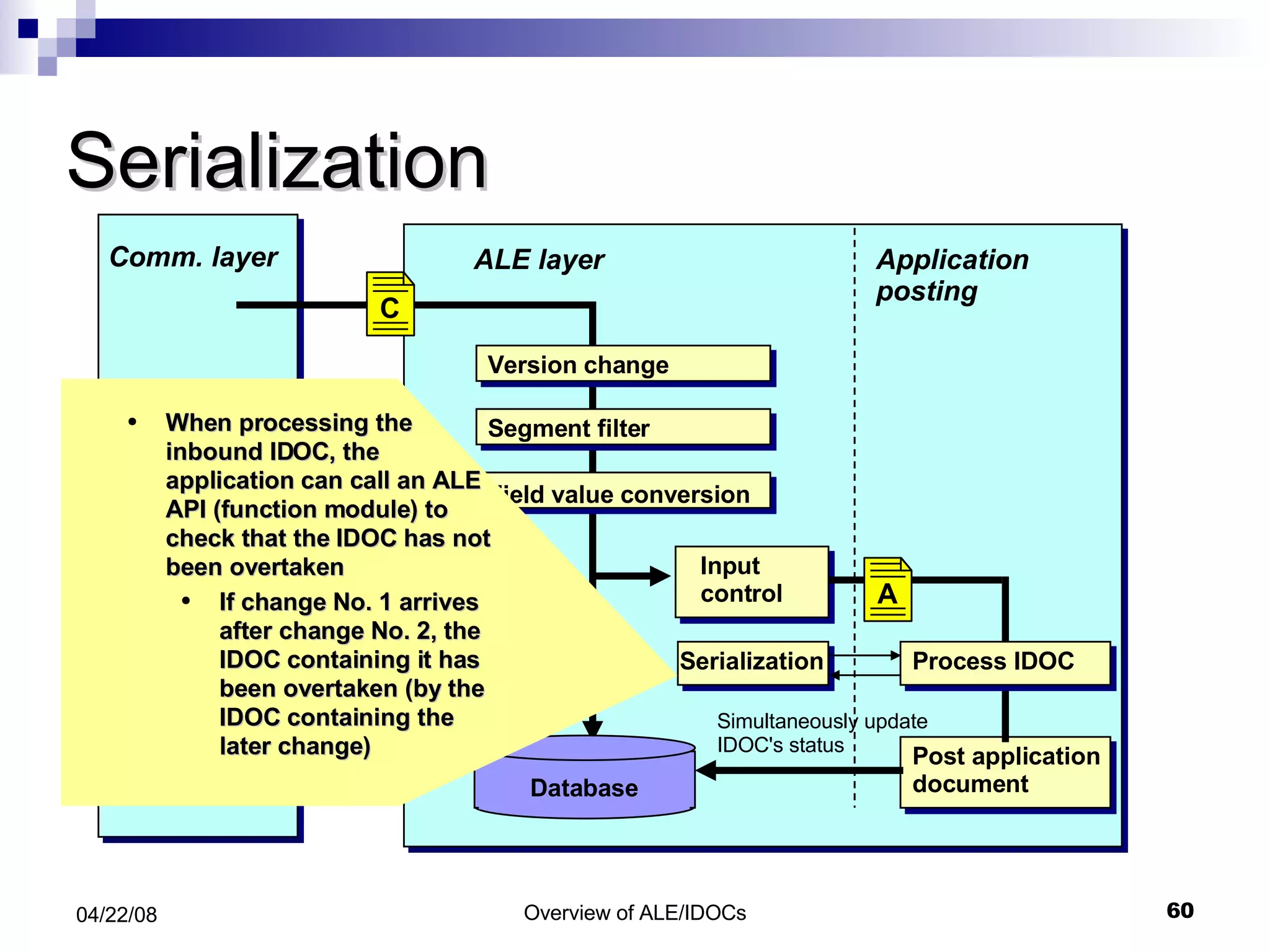
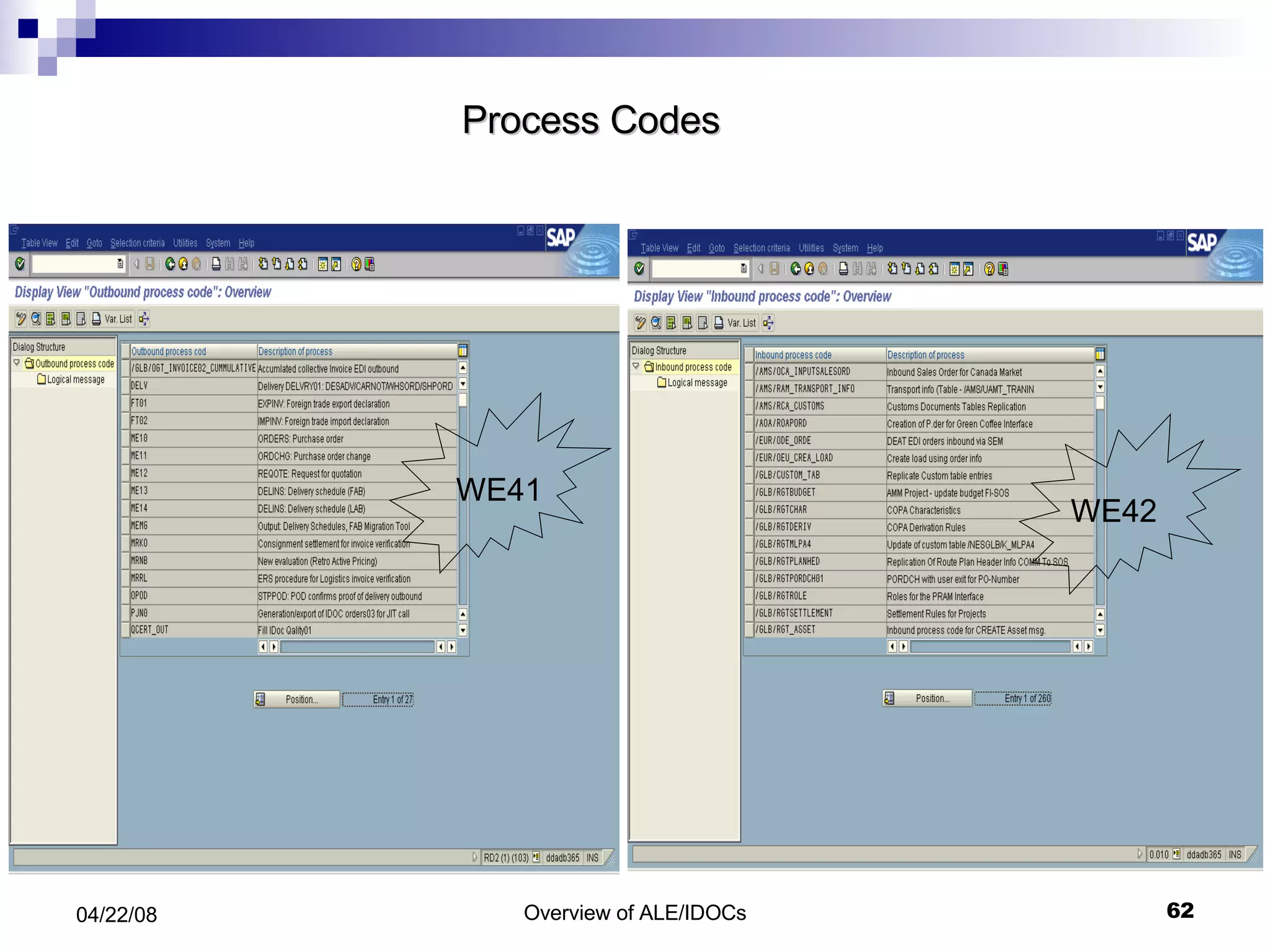
The document provides an overview of Application Link Enabling (ALE) and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in SAP. It describes what ALE and EDI are, the components and basic concepts of ALE like IDocs, and how outbound and inbound processes work in ALE. It also discusses topics like configuration requirements, monitoring IDocs, and questions about ALE.