This module covers effective communication skills for middle managers, including different types of communication, listening skills, asking questions, and using body language appropriately. The key points covered are:
1) Communication methods include written, spoken, symbolic, visual, and multimedia. Effective communication relies on clear understanding between parties.
2) Listening skills are important, including maintaining eye contact, taking notes, being present, and avoiding distractions.
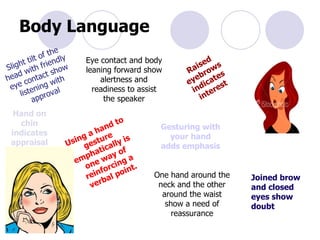
3) Body language conveys much - eye contact, gestures, posture and more can communicate confidence, interest or other meanings. Matching body language helps build rapport.