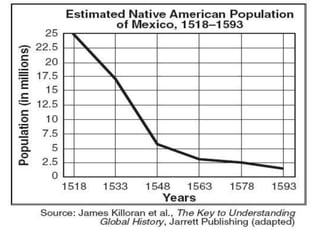
The Columbian Exchange refers to the significant transfer of crops, livestock, ideas, and diseases between the Old World and New World following Columbus's voyage in 1492. This exchange led to major demographic and agricultural changes, with the introduction of crops like potatoes and sugarcane boosting populations and economies in the Old World while devastating Native American populations through introduced diseases. Additionally, it spurred large-scale migrations and the transatlantic slave trade due to labor demands in the Americas.