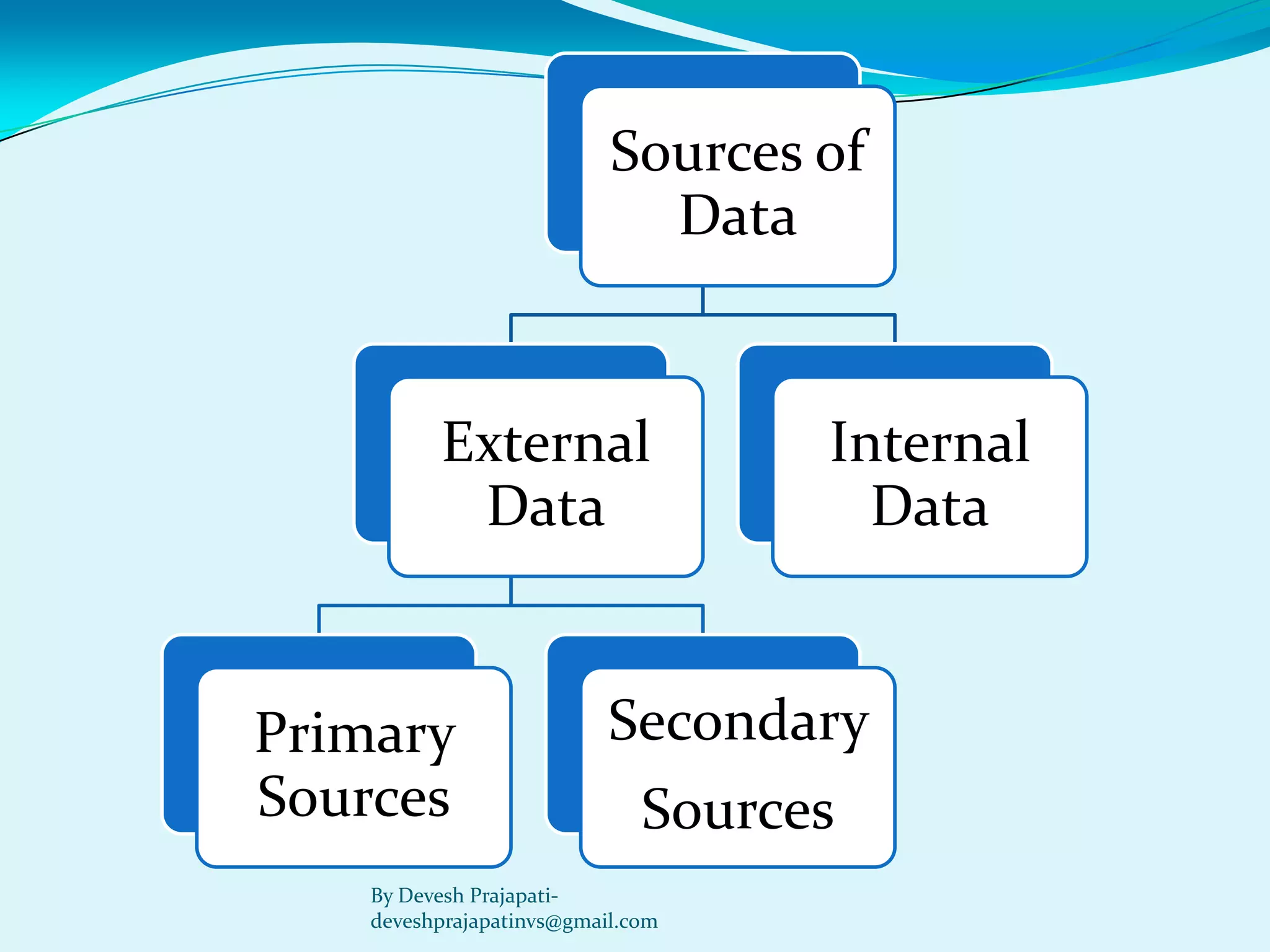
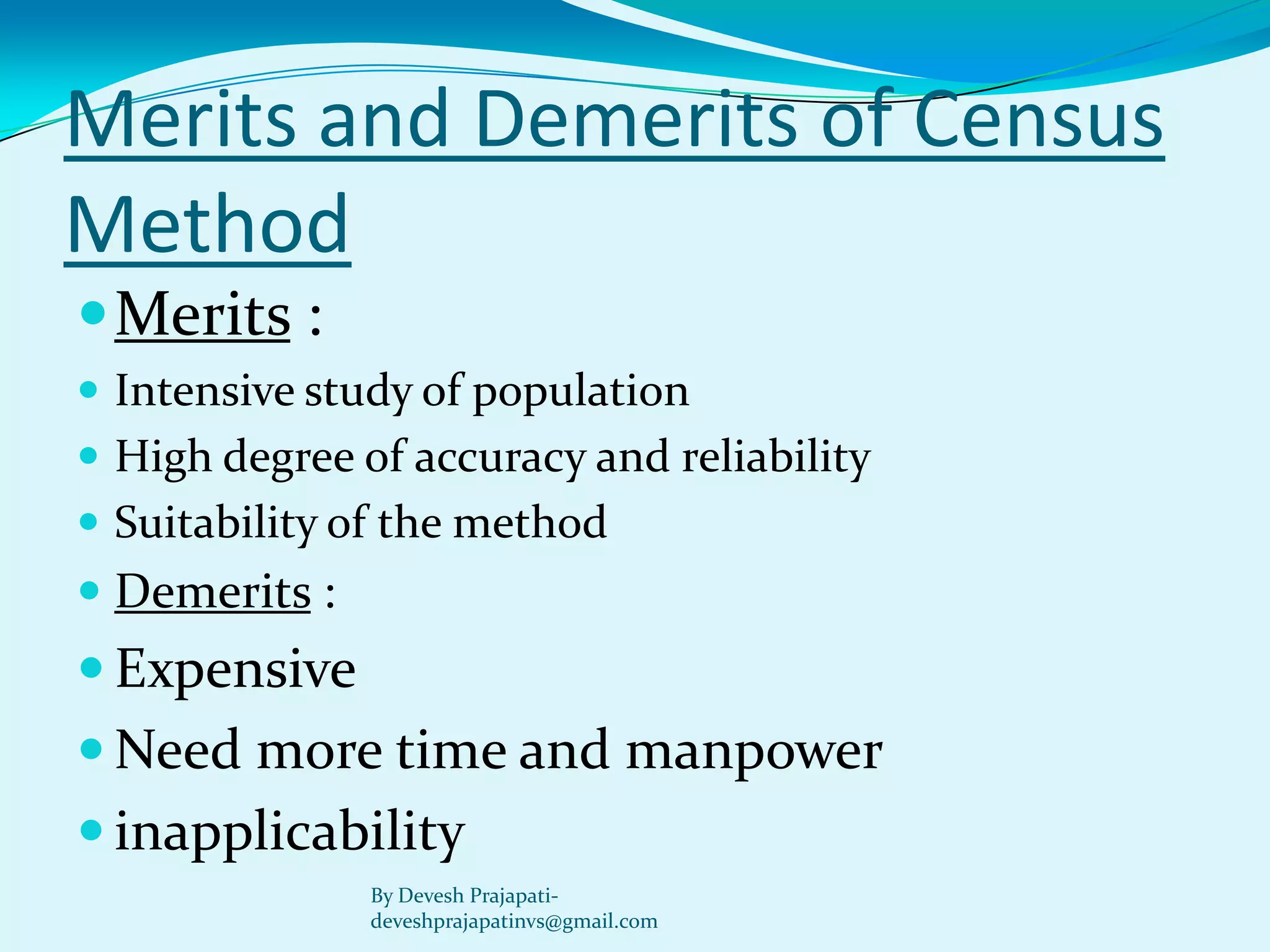
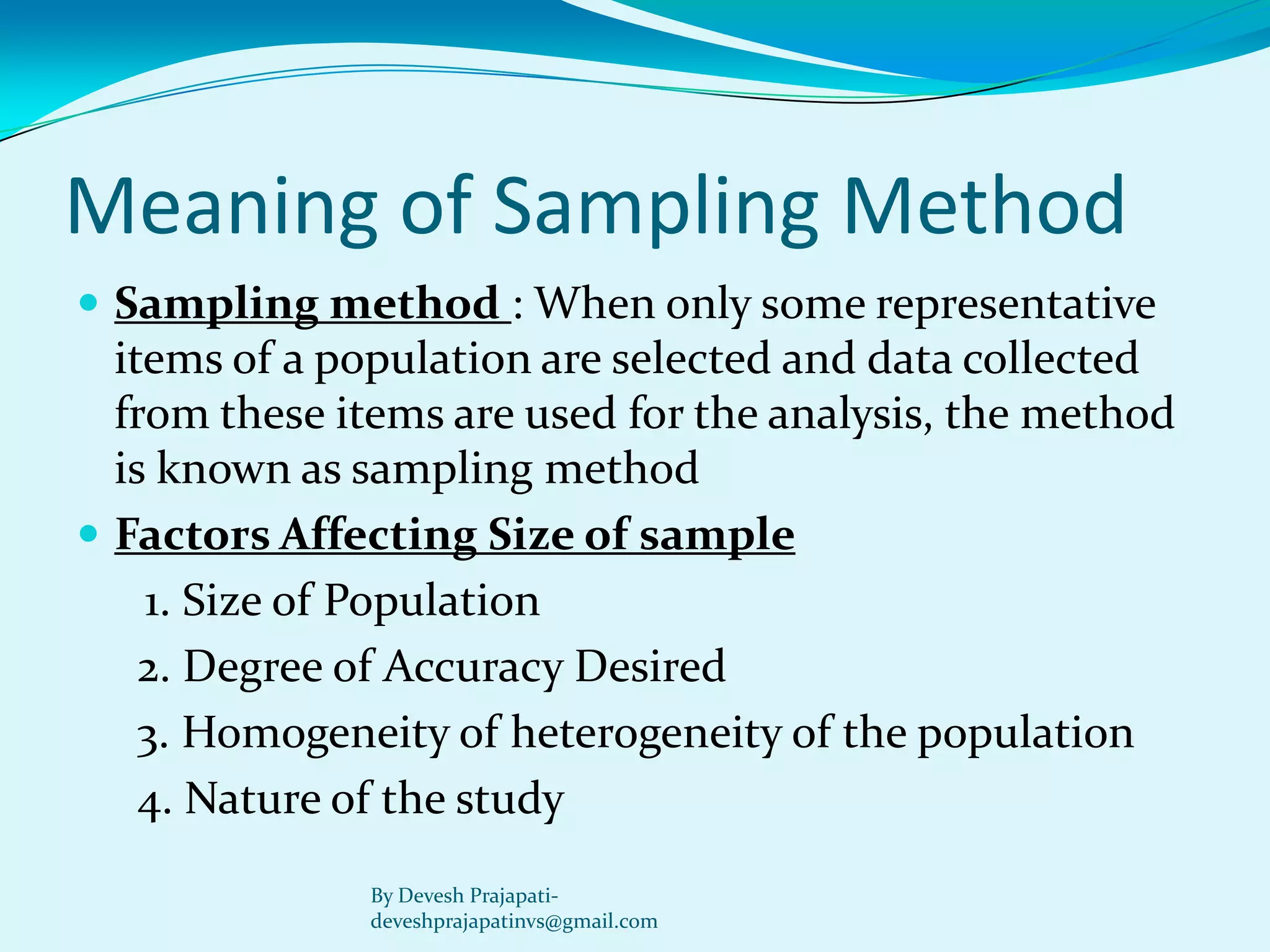
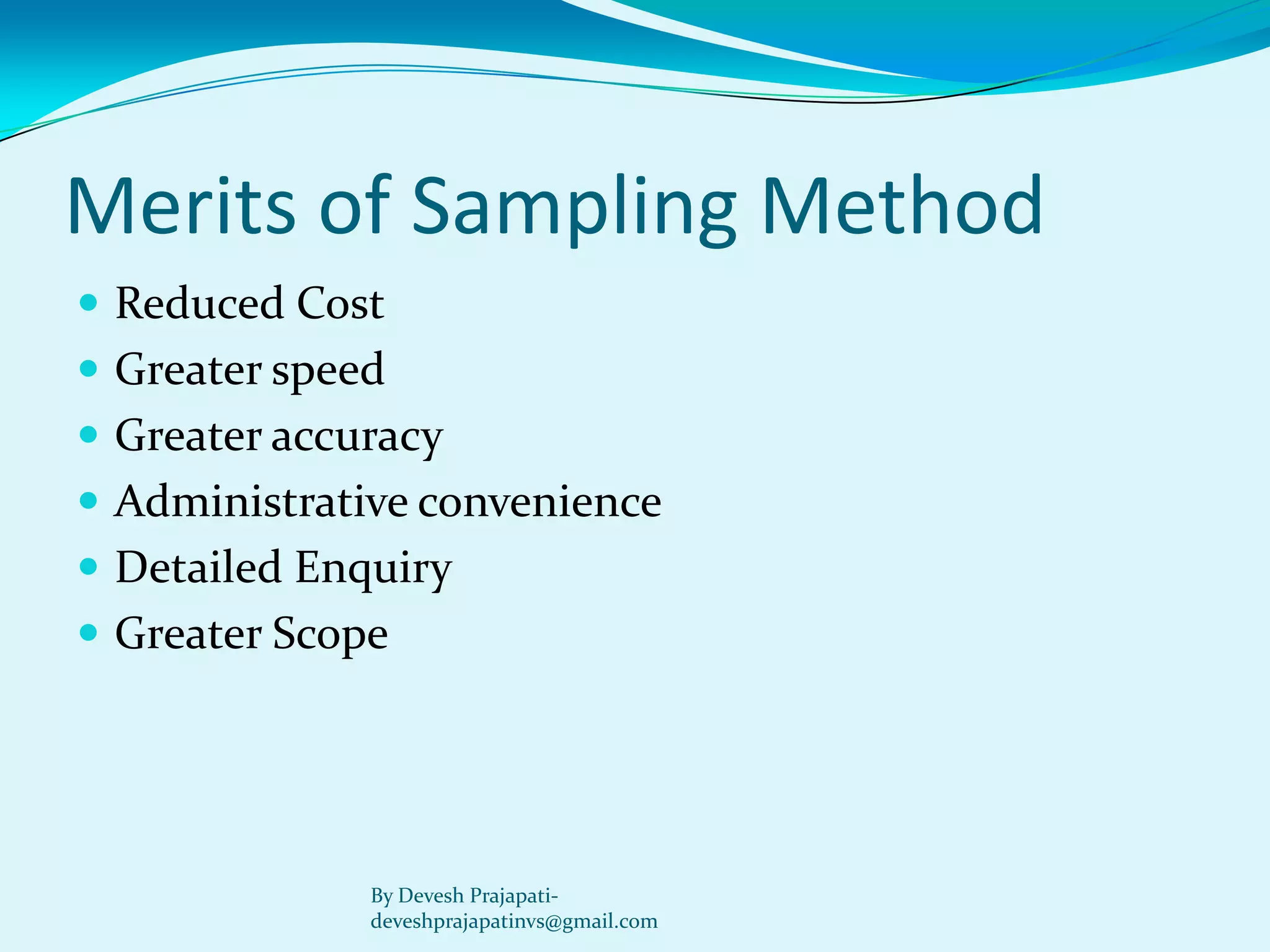
The document discusses statistical enquiry and methods for collecting data. It describes the different sources of data, both internal and external to an organization. External primary data is collected directly by the investigator through methods like surveys, while secondary data comes from existing published and unpublished sources. The document also discusses sampling methods like random sampling and their merits and demerits compared to a full census. The goal of statistical analysis is to reach solutions to economic problems but there may be statistical errors in the estimated values from collected data versus actual values.