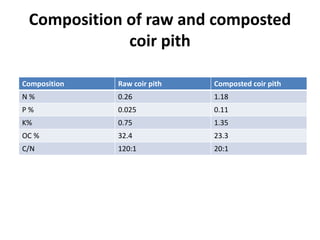
Coir pith compost is made from coir dust, a byproduct of the coir industry, mixed with organic and inorganic materials. The process involves mixing coir dust with leaves, weeds, cattle dung, fungi culture, rock phosphate, and micronutrients. The mixture is piled in layers and turned regularly over 4 months to mature. Composted coir pith has higher nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and organic carbon than raw coir dust. It improves soil properties when applied as fertilizer and is used in nurseries and around trees. While beneficial, it may not be economical to purchase and immature compost could negatively impact crops.