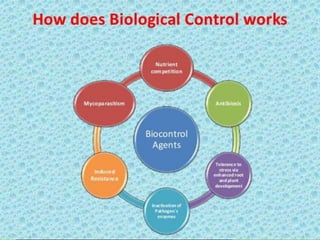
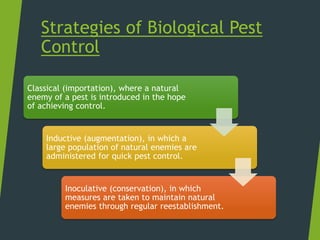
This document discusses biocontrol agents used for biological pest control. It defines biocontrol as using living organisms to control pests like insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases. The document outlines the history of biocontrol and describes common types of biocontrol agents like parasitoids, predators, and entomopathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and nematodes. It discusses strategies for biocontrol and provides advantages like being environmentally friendly and reducing chemical pesticide use, as well as disadvantages like pathogens developing resistance.