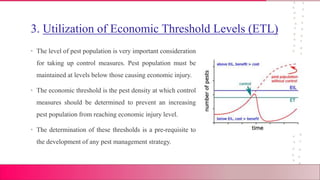
This document summarizes an assignment on the ecological principles of integrated pest management (IPM) submitted by a student. It defines IPM as a process that controls pest populations while minimizing impacts on people and the environment by focusing on long-term prevention. A successful IPM program uses a combination of biological control, habitat manipulation, cultural practices, and resistant varieties. The core principle is to reduce pesticide use and only intervene when monitoring shows it is necessary. The document then outlines four key principles of IPM: 1) considering the ecosystem, 2) pest surveillance, 3) using economic threshold levels, and 4) applying minimum selective hazards.