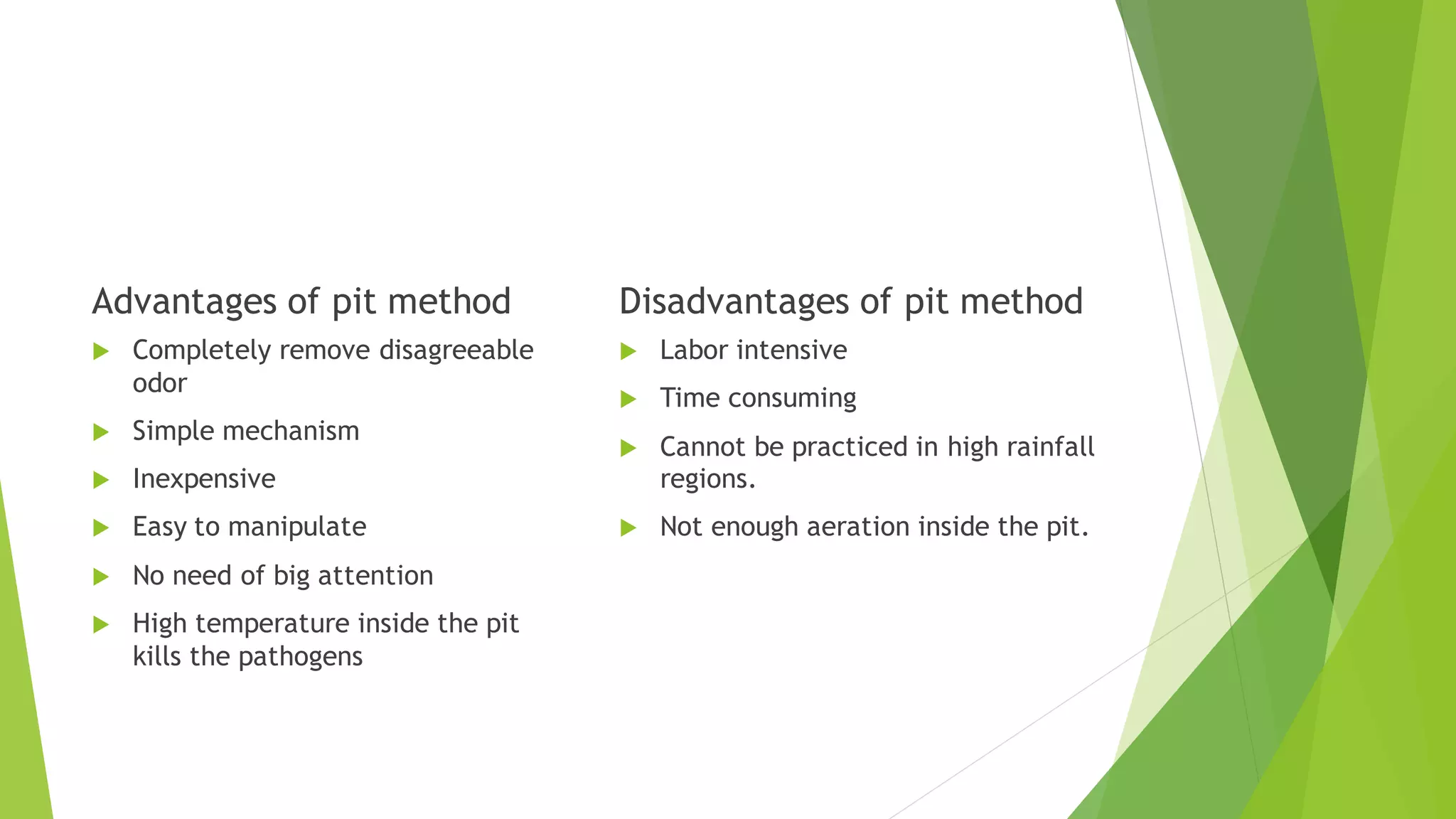
The document discusses different types and methods of composting. It describes compost as organic matter that is decomposed through composting and is rich in nutrients. There are two main types of composting - aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic composting uses air and generates high temperatures, breaking down organic waste quickly without smells. Various composting methods are described, including the pit, heap and NADEP methods which involve layering organic materials in pits or piles and turning the materials to aid decomposition. Microorganisms and their roles in the composting process are also outlined.