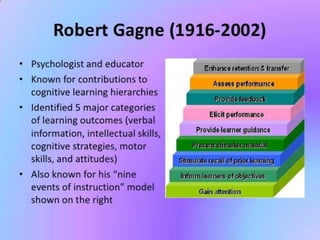
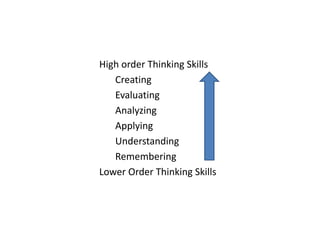
The document discusses the application of cognitive theory in the classroom. It outlines key concepts in cognitive theory such as how people think, understand, and learn. It discusses theorists like Paivio who developed dual coding theory, Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences, and Bloom's taxonomy of learning domains. The document also provides examples of how teachers can apply cognitive theory concepts in the classroom, such as using expository teaching, meaningful learning methods, and dual coding. It also discusses how students can apply cognitive theory by using memory techniques and connecting new information to existing knowledge.