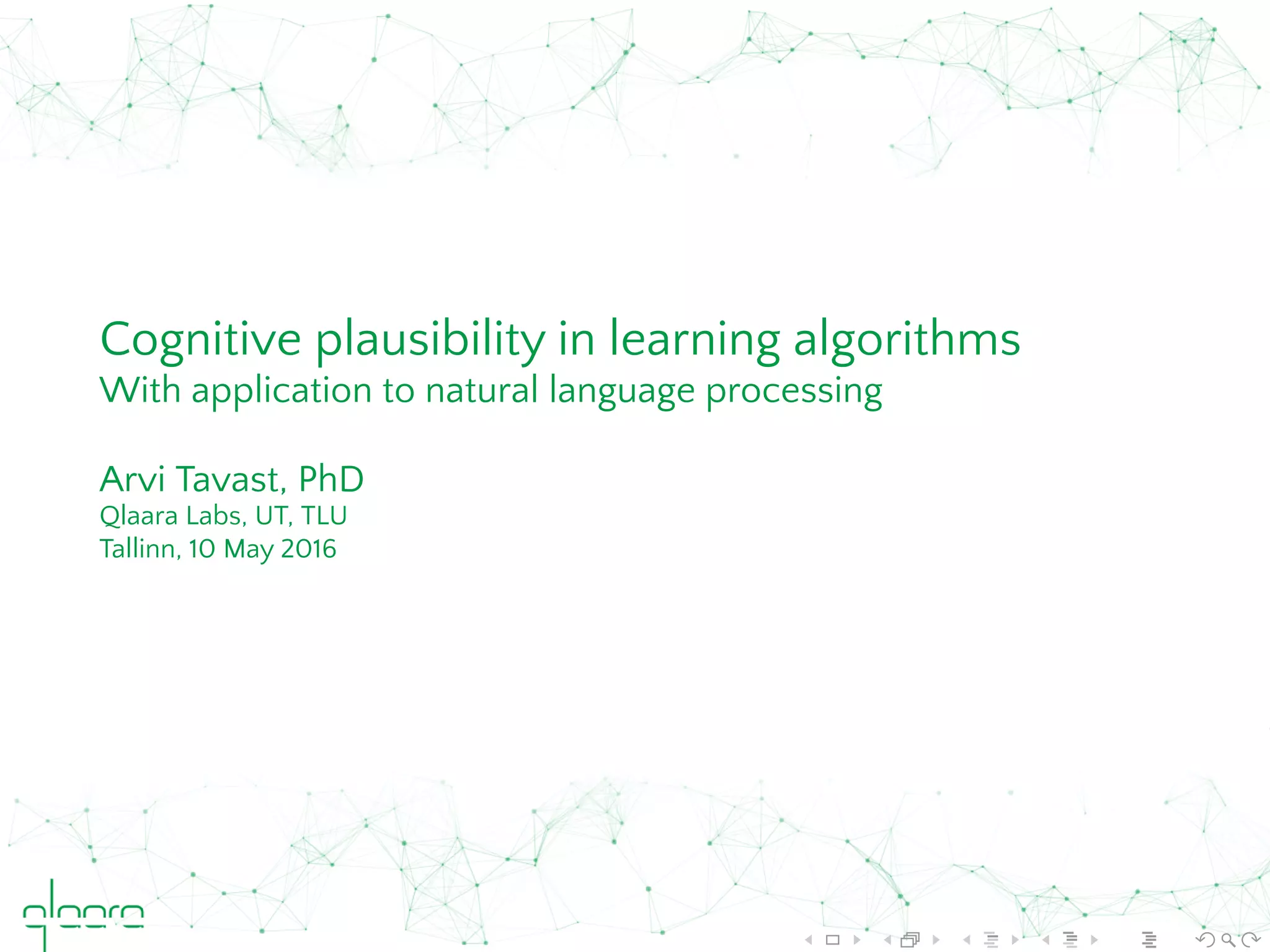
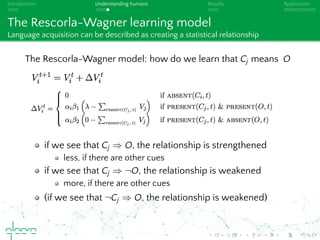
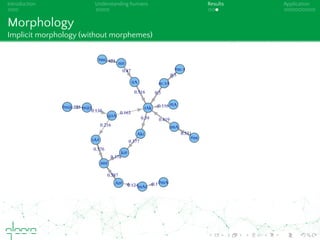
This document discusses cognitive plausibility in learning algorithms, with a focus on natural language processing. It outlines the author's background and motivation, which is to model human learning and communication more accurately. Some key points made include: understanding language acquisition as discriminative learning rather than compositional; explaining features of human language through models like Rescorla-Wagner learning; and how naive discrimination learning can be applied to NLP tasks through an incremental learning algorithm. The document also provides an overview of available NLP tools and limitations in fully achieving language understanding.