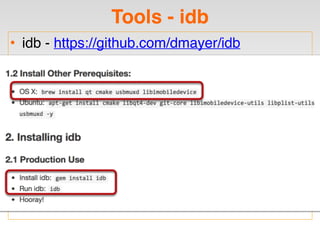
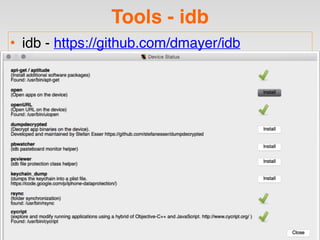
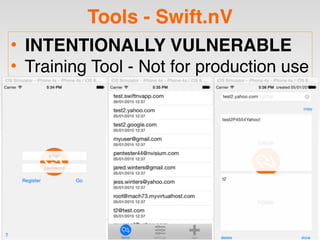
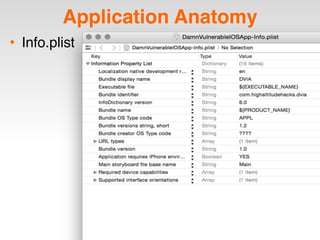
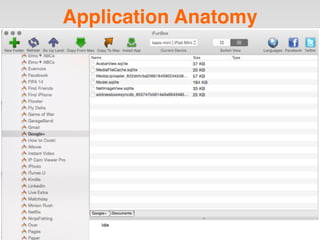
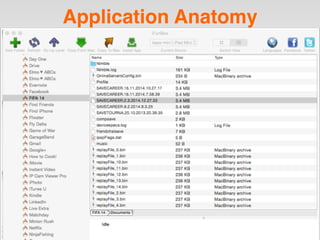
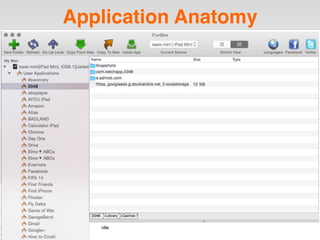
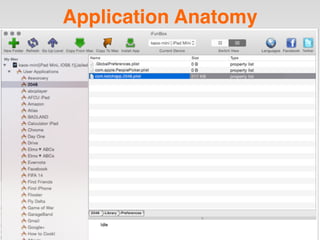
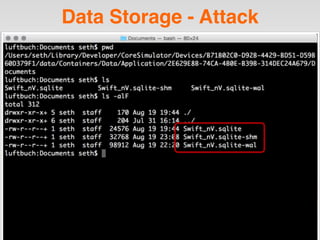
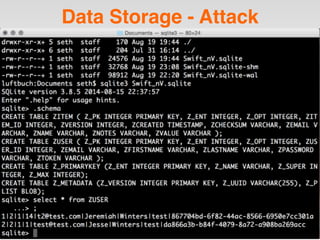
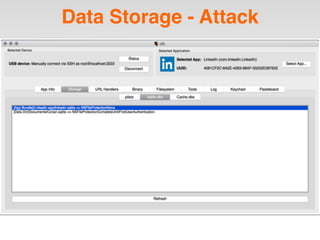
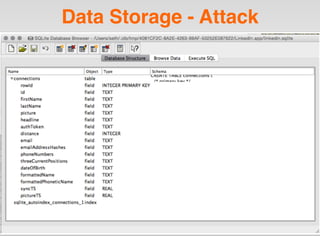
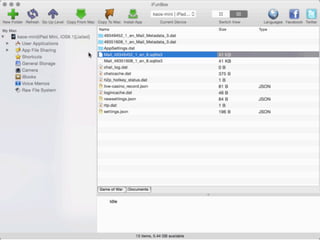
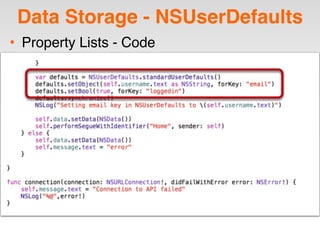
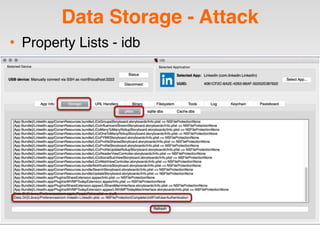
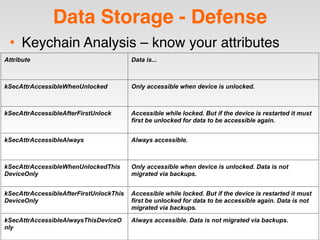
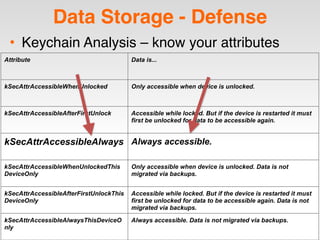
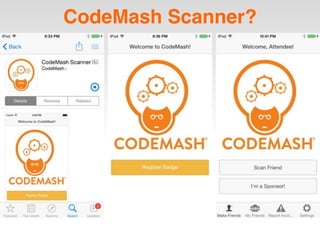
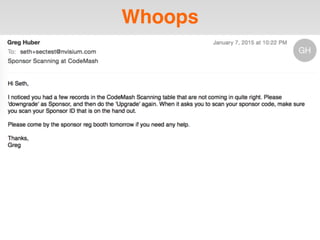
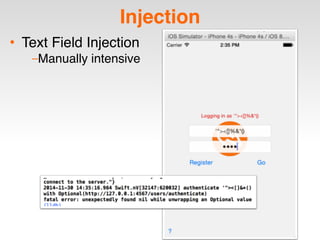
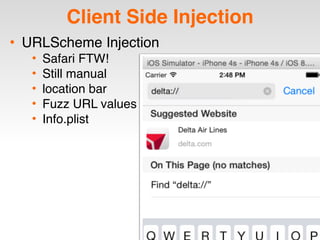
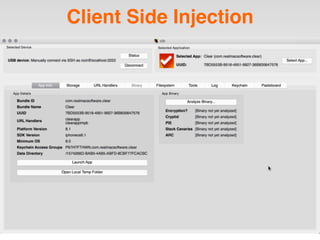
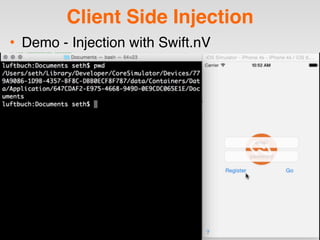
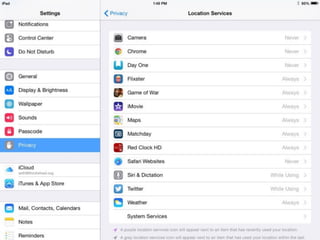
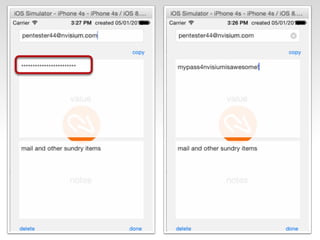
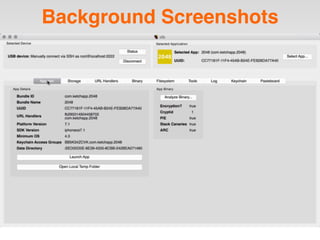
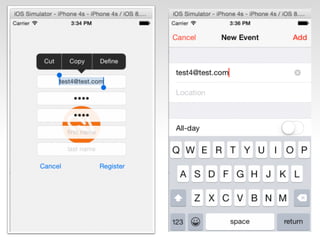
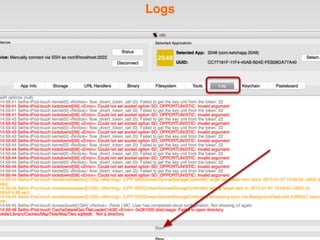
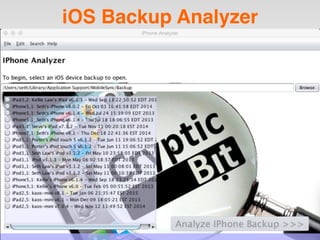
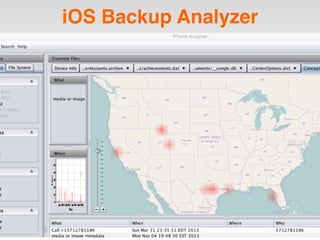
The document is a presentation by Seth Law on practical attack and defense strategies for iOS applications, highlighting tools, application anatomy, data storage, network communications, client-side injection, and privacy concerns. It emphasizes the risks associated with mobile app security, such as insufficient transport layer protection and the importance of encryption and secure data handling. The presentation further discusses defenses against various attacks and concludes with a message stressing the challenges of security in application development.