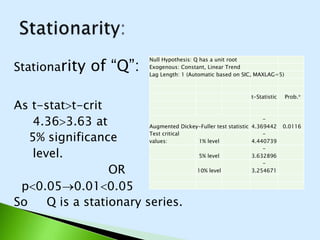
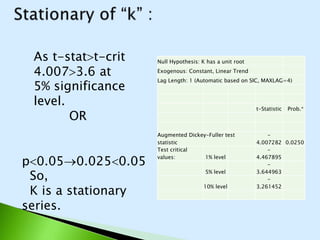
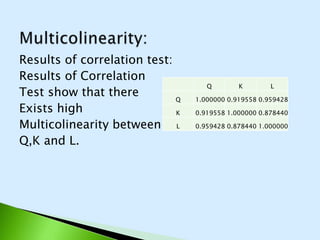
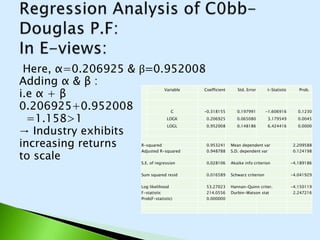
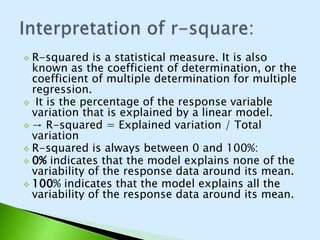
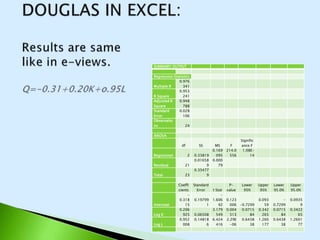
The document describes the Cobb-Douglas production function and the results of estimating its parameters. It finds that labor (L) and capital (K) explain 95% of the variation in output (Q) according to the estimated equation Q=-0.31+0.20K+0.95L. Diagnostic tests show the variables are stationary and there is no multicollinearity. The model is found to be statistically significant and a good fit to the data based on the F-statistic and R-squared value. It is determined that industry exhibits increasing returns to scale since the estimated coefficients of K and L sum to above 1.