Embed presentation
Downloaded 191 times




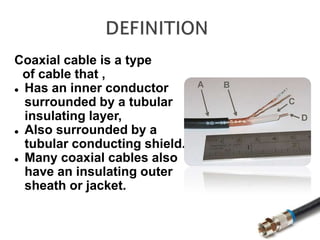







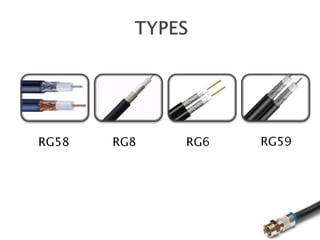






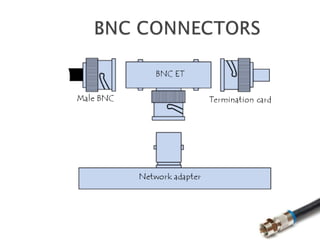
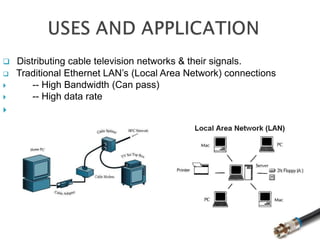




This document discusses coaxial cable and includes a list of team members. It defines coaxial cable, describes its history and construction. It explains that coaxial cable has an inner conductor surrounded by insulating and outer conducting layers. It provides examples of different types of coaxial cables and common connectors. Finally, it outlines some key uses of coaxial cable in transmitting radio frequency signals and video/audio, and lists advantages like low cost and noise immunity and disadvantages like higher attenuation.

























