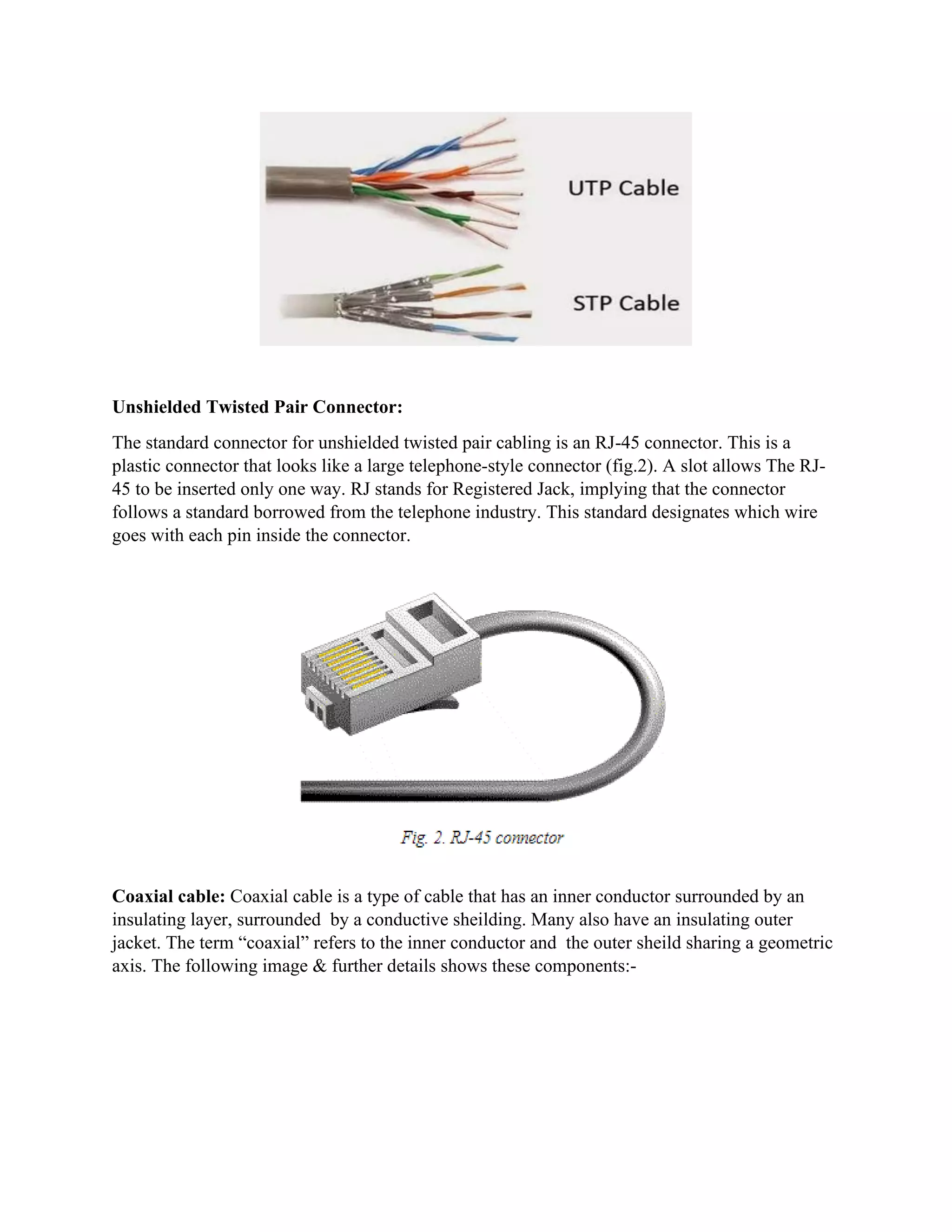
This document provides an overview of various types of computer networking cables and connectors including twisted pair, coaxial, fiber optic, straight-through, and crossover cables. It details their characteristics, uses, and the importance of choosing the right type based on network requirements. The document also highlights the evolution toward better cable performance and the potential shift to wireless networking.