This document provides information about headlands and bays, including:
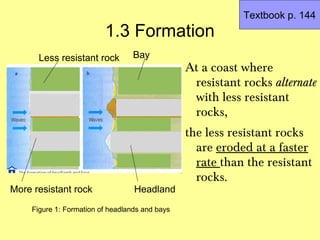
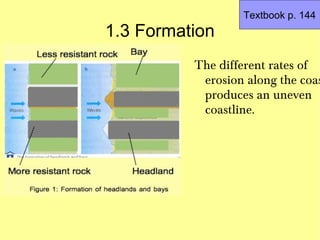
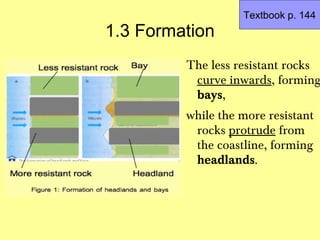
1) Headlands and bays are formed by the uneven erosion of coastlines composed of bands of rock with varying resistance. More resistant rocks like granite and basalt form headlands, while less resistant rocks like chalk, sandstone and shale erode more quickly to form bays.
2) Waves concentrate their energy at headlands, eroding them more, while weakening along wider bays where sediments are deposited.
3) Students are expected to learn about beaches, spits and tombolos from their textbook for homework, with examples of different beach gradients based on sediment coarseness.




![1.3 Formation
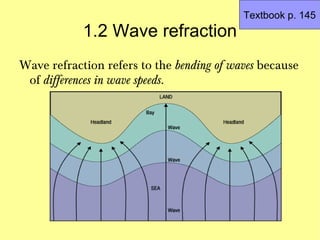
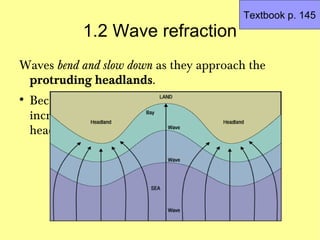
Wave energy is concentrated at the headlands
because the waves bend as they approach the
protruding headlands.
This is due to the waves slowing down as they reach
the shallower waters in front of the headlands while
other waves not affected by the headlands continue
ahead at the same speed. [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4headlandsbays-120626100800-phpapp01/85/Coasts-Headlands-and-Bays-5-320.jpg)