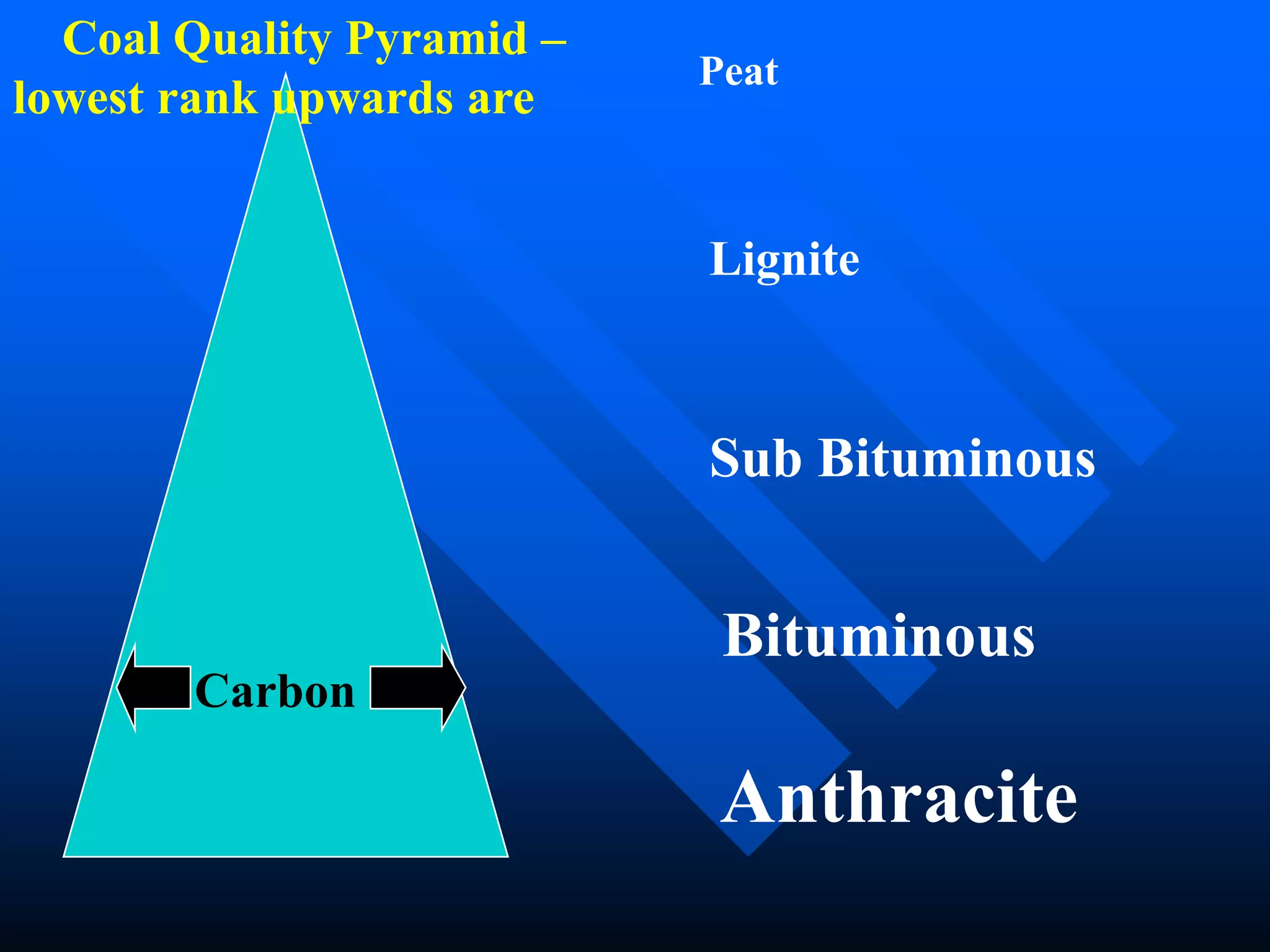
The document provides an overview of coal including its origin, classification, and characteristics. Coal is a sedimentary rock formed from the accumulation of vegetation, categorized into four main types: lignite, bituminous, subbituminous, and anthracite, each defined by varying carbon content and properties. It emphasizes the importance of coal as a vital energy source for various applications, highlighting its role in modern society.