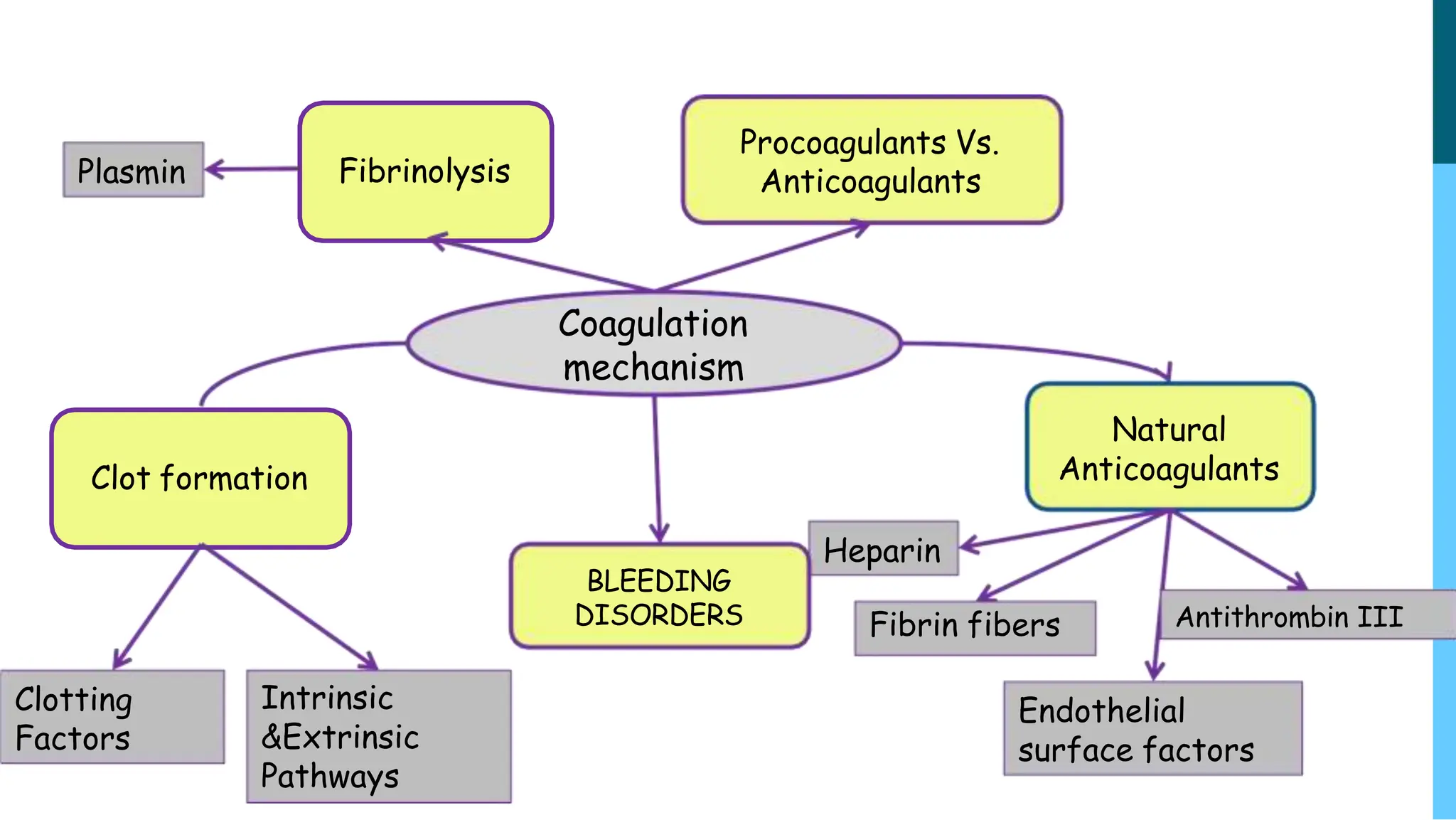
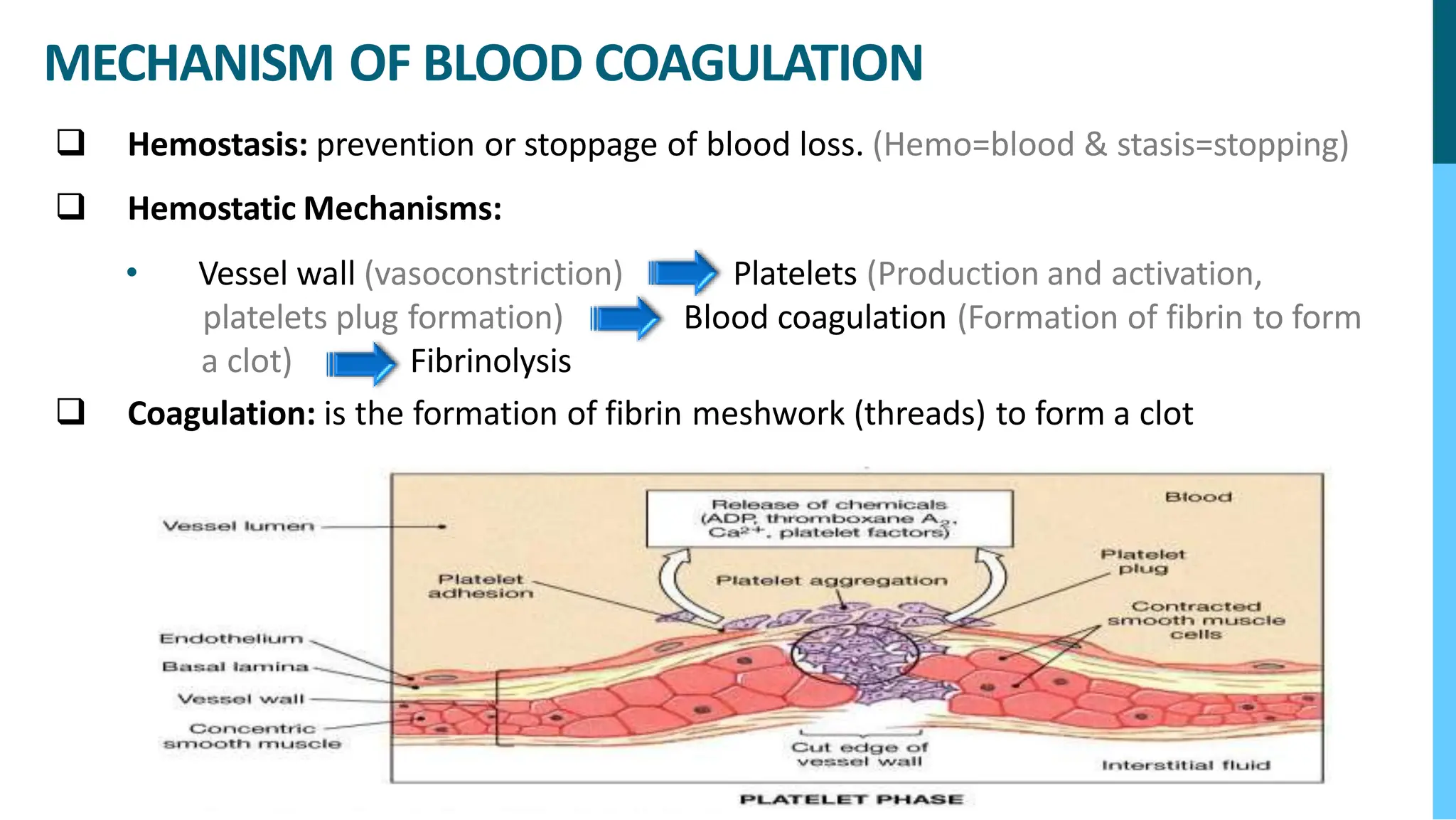
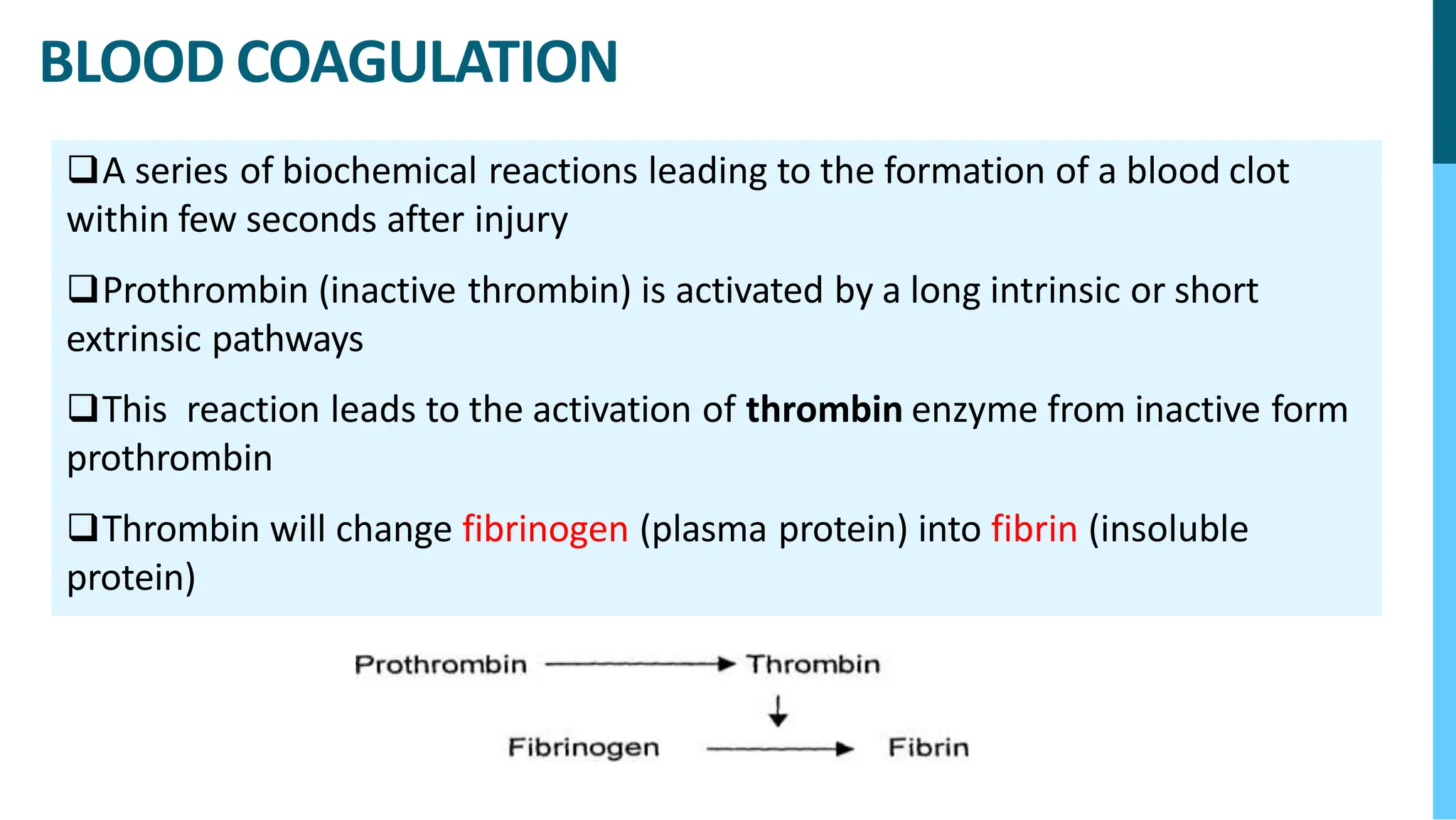
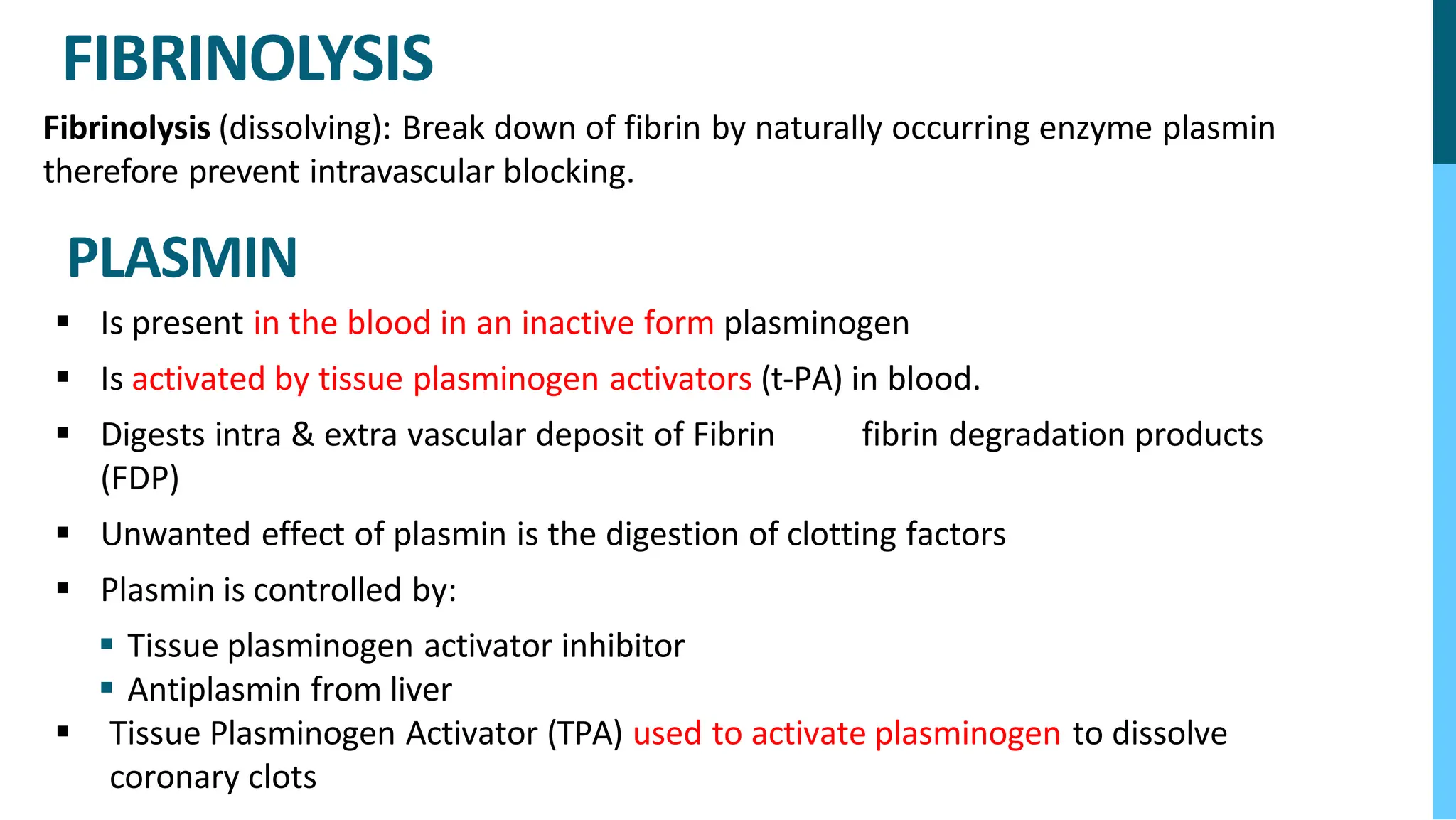
The document discusses various blood disorders that affect red blood cells, including different types of anemia. It describes iron-deficiency anemia, which can be caused by low iron intake or blood loss. Anemia of chronic disease is common in people with kidney disease or other chronic illnesses. Pernicious anemia results from a vitamin B12 deficiency due to problems absorbing the vitamin. Aplastic anemia occurs when the bone marrow does not produce enough red blood cells or other blood cells.